Version 1
advertisement
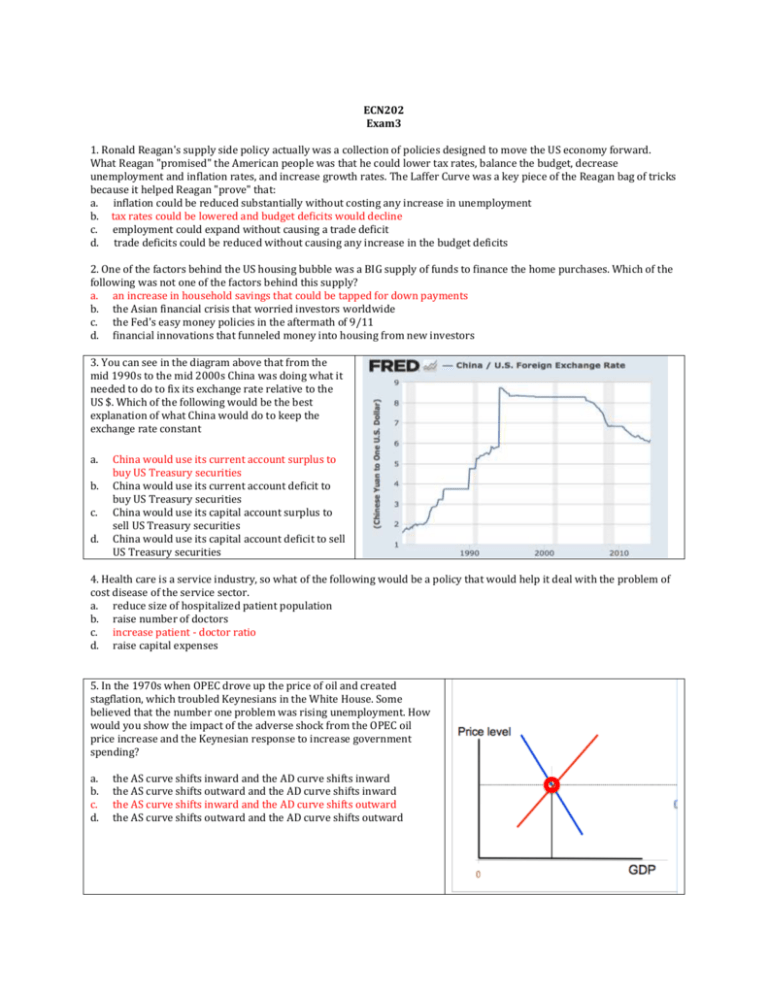
ECN202 Exam3 1. Ronald Reagan's supply side policy actually was a collection of policies designed to move the US economy forward. What Reagan "promised" the American people was that he could lower tax rates, balance the budget, decrease unemployment and inflation rates, and increase growth rates. The Laffer Curve was a key piece of the Reagan bag of tricks because it helped Reagan "prove" that: a. inflation could be reduced substantially without costing any increase in unemployment b. tax rates could be lowered and budget deficits would decline c. employment could expand without causing a trade deficit d. trade deficits could be reduced without causing any increase in the budget deficits 2. One of the factors behind the US housing bubble was a BIG supply of funds to finance the home purchases. Which of the following was not one of the factors behind this supply? a. an increase in household savings that could be tapped for down payments b. the Asian financial crisis that worried investors worldwide c. the Fed's easy money policies in the aftermath of 9/11 d. financial innovations that funneled money into housing from new investors 3. You can see in the diagram above that from the mid 1990s to the mid 2000s China was doing what it needed to do to fix its exchange rate relative to the US $. Which of the following would be the best explanation of what China would do to keep the exchange rate constant a. b. c. d. China would use its current account surplus to buy US Treasury securities China would use its current account deficit to buy US Treasury securities China would use its capital account surplus to sell US Treasury securities China would use its capital account deficit to sell US Treasury securities 4. Health care is a service industry, so what of the following would be a policy that would help it deal with the problem of cost disease of the service sector. a. reduce size of hospitalized patient population b. raise number of doctors c. increase patient - doctor ratio d. raise capital expenses 5. In the 1970s when OPEC drove up the price of oil and created stagflation, which troubled Keynesians in the White House. Some believed that the number one problem was rising unemployment. How would you show the impact of the adverse shock from the OPEC oil price increase and the Keynesian response to increase government spending? a. b. c. d. the AS curve shifts inward and the AD curve shifts inward the AS curve shifts outward and the AD curve shifts inward the AS curve shifts inward and the AD curve shifts outward the AS curve shifts outward and the AD curve shifts outward 6. The solid line in the graph is of the US government’s ____. a. b. c. d. Debt held by foreigners/GDP Outlays/GDP Tax revenues/GDP Debt/GDP 7. Alan Greenspan gave Bill Clinton some advice that prompted him to change his macroeconomic plans for stimulating the economy. Greenspan warned Clinton that if he cut taxes and increased the deficit, then this would reduce GDP because it would drive up interest rates. This is an old idea – an example of ____. a. Crowding out b. The Multiplier c. The Liquidity Trap d. The Quantity Theory 8. If I wanted the best measure of how much Greece owes foreign investors that has investors worried, it would be ____. a. Budget deficit b. Trade deficit/GDP c. Debt/GDP d. Budget deficit/GDP 9. You probably noticed that once again tuition costs rose this year and the expectation is they will rise again next year. This is not good news, but at least you know how to explain the rapid increase. The theory that would best explain the rising tuition costs would be______. a. crowding out b. cost-disease of the service sector c. Hume's law d. quantity theory of money 10. What is the best explanation of the movement of the exchange rate after the onset of the Great Recession in 2008? [ be careful] a. an outward shift in the D curve for US $ b. an outward shift in the S curve for US $ c. an outward shift in the S curve for US $ and an inward shift in the D curve for US $s d. an outward shift in the D and bigger outward shift in the S curves for US $ 11. What was the "trigger" behind the economic crisis in the Celtic Tiger (Ireland)? a. unsustainable trade deficits b. unsustainable budget deficits c. an unsustainable rise in its currency d. an unsustainable housing boom 12. Which of the following is not one of the “stories” we can tell about economic growth. a. Economic growth is a relatively new phenomenon in the span of world history b. The growth superstar in the post WW II era has been Asia c. Economic growth has been higher in China than in India since 1980 d. Economic inequality has increased with the higher rates of economic growth e. The first growth star in Asia after WW II was China 13. Ronald Reagan's supply side policy actually was a collection of policies designed to move the US economy forward and on many fronts the policies will be remembered as a success. Which of the following is something we can say about the Reagan years as President? a. the trade deficit declined substantially b. inflation-adjusted earnings of American workers decreased c. the budget deficits declined sharply d. inequality declined sharply 14. It has been observed that monetary policy is more effective than people originally thought at increasing income and decreasing unemployment. Which of the statements below would explain the increased effectiveness of monetary policy? a. consumption spending was found to be less sensitive to income - the MPC was smaller b. investment spending was found to be more responsive to interest rate changes c. government spending was lower d. the economy was operating near capacity so the AS curve was very steep 15. Given what we know about the monetary policy, which of the following explains what we see in 2008 based on this graph? a. b. c. d. The Fed is raising the discount rate The Fed is raising the required reserve rate The Fed is conducting OMO purchases of securities The Fed was lowering tax rates 16. In the 1970s when OPEC drove up the price of oil and created inflation, this drove up interest rates that troubled the Keynesians in the White House. To get the economy moving they believed we needed to drive down interest rates. Their proposed solution was to a. the Fed to increase the money supply by raising the discount rate b. the Fed to decrease the money supply by buying government securities c. the Fed to increase the money supply by buying government securities d. the Fed to decrease the money supply by lowering the required reserve rate 17. The Great Housing bust didn’t affect everyone the same. Which of the following is true about the impact of the housing bust on net worth? a. It affected the old more than the young b. It affected Whites more than Hispanics c. It affected the more educated more than the less educated d. It affected the poor more than the rich 18. Which of the following statements regarding Greece's economic crisis is NOT true? a. its budget deficit increased sharply as it tried to cut government borrowing b. the value of its currency dropped sharply c. the unemployment rate increased sharply d. Greece's debt rose above 100% of GDP Current account Exports of goods and services and income receipts (credits) Exports of goods and services Goods Services Primary income receipts Secondary income (current transfer) receipts /2/ Imports of goods and services and income payments (debits) Imports of goods and services Goods Services Primary income payments Secondary income (current transfer) payments /2/ 2014 Million $s 3,291,353 2,344,528 1,635,133 709,395 819,705 127,120 3,701,981 2,849,239 2,370,920 478,319 601,801 250,940 19. Above is an abridged version of the Balance of Payments data for the US. Based on the table, what is the approximate value current account deficit in 2014? a. -$730 billion b. -$504 billion c. -$410 billion d. -$230 billion 20. Which of the following can one say based on this table of interest rates when we look at the differences between pre-crisis 2006 and post-crisis 2012? a. b. c. d. The maturity effect decreased The risk premium on corporate bonds decreased The decline was biggest in short-term lending Real interest rates declined 21. In the late 1970s there was a BIG ideological shift that took place at the Fed when Fed Chair Paul Volcker announced a policy shift that moved the Fed policy toward monetarism. Which of the following best reflects the shift in attitudes at the Fed? The Fed _______ a. should refocus its efforts on maintaining the level of unemployment at its full employment rate b. should refocus its attention and stop trying to stabilize interest rates c. should focus its attention on the budget deficit d. should stop focusing its attention on stabilizing the money supply 22. The 1980s represented an important ideological shift in US economic thinking and policy. Which of the following was not one of the goals of the Reagan revolution when Reagan assumed control of the presidency? a. move emphasis from short-term to long-term b. reduce size of US government c. worry less about stabilization and more about growth d. focus more on AD that AS 23. Based on the analysis of interest rates, which of the following statements is true? a. b. c. d. If the upper graph represents the rate on German bonds, the lower graph represents the rate on Greek bonds If the upper graph represents the rate on US Treasury bonds, the lower graph represents the rate on Aaa bonds If the upper graph represents the rate on Baa corporate bonds, the lower graph represents the rate on Aaa bonds If the upper graph represents the rate on short-term Treasury bonds, the lower graph represents the rate on long-term Treasury bonds Profit 5,000 5,000 Profit tax 2500 2500 Cost of machine 1000 1000 I tax credit No tax credit Profit tax + tax credit 2500 Tax saving 0 Net Cost of Machine 1000 24. In the table above you see some data similar to what we saw in class. You are to use this table to determine how much the company will save on the cost of the machine if a 10% Investment (I) tax is enacted? a. $500 b. $200 c. $100 d. $50 25. Which graph best captures the market for US $s when US investment in China slows down as result of recession? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 26. If a Keynesian respond to the lower GDP and higher prices caused by an adverse supply-side shock by reducing government spending, what will happen to prices and GDP? a. GDP and CPI rise b. GDP and CPI fall c. GDP rises and CPI falls d. GDP falls and CPI rises 27. When you look at the world you see a remarkable range in economic growth rates - some real success stories and some real economic disasters. At the end of the 20th century you would say that economic growth rates were low and population growth rates were high in ___, while in ____ the reverse was true. a. Europe Africa b. Africa East Asia c. East Asia Africa d. America Europe e. Africa Latin America 28. The graph is of the US ____. a. b. c. d. Debt Debt / GDP Deficit Deficit / GDP 29. As the deadline for a Greek Bailout approaches, Greeks are taking their money out of Greek banks and purchasing US Treasuries? If we were looking at the market for US$s, the ___ . a. S curve will shift out b. D curve will shift out c. S curve will shift in d. D curve will shift in 30. Which of the following statements is NOT true? a. when the US government runs a deficit its debt increases b. the last time the US debt declined was during the Bush II years c. one of the differences between the government's finances and your is that the government can print money to pay off its debt d. the government owes much of its debt to itself 31. This graph is an indicator of ____ a. b. c. d. monetarism the hockey stick effect[ quantitative easing the Quantity Theory 32. Bill Clinton came to office promising to get the economy moving out of a recession and he proposed a standard fiscal policy – an increase in government spending and a cut in taxes. Fed Chair Alan Greenspan took the President aside and convinced him his policy would not work, which prompted Clinton to state, "You mean to tell me that the success of the program and my reelection hinges on the Federal Reserve and a bunch of fucking bond traders?” The essence of Greenspan’s advice was that Clinton should rethink his plan and ___ a. increase in government spending to spur increased investment spending and raise tax revenues b. increase in taxes to drive down interest rates and spur increased investment spending c. decrease in government spending to push interest rates up and spur increased investment spending and raise tax revenues d. decrease in taxes to spur increased investment spending and raise tax revenues 33. The story Greenspan told Clinton about an alternative to the proposal he made as a candidate went something like which of the following? a. the tax cut will decrease the deficit which will raise interest rates and stimulate investment spending which shifts the AD curve out and also will shift in the AS curve b. a decrease in government spending will increase the deficit which will raise interest rates and reduce investment spending which shifts the AD curve back in and also will shift in the AS curve c. a tax increase will decrease the deficit which will lower interest rates and stimulate investment spending which shifts the AD curve out and also will shift out the AS curve d. the increase in government spending increase will decrease the deficit which will raise interest rates and stimulate investment spending which shifts the AD curve out and also will shift in the AS curve 34. When Greece joined the euro, the trilemma meant that Greece would ___ a. Need to impose capital controls on its citizens and limit their ability to take money out of the country b. Lose control over their domestic money supply c. Suffer a budget deficit d. See its trade deficit rise substantially e. See greater volatility in the value of its currency 35. In the diagram to the right you can see the impact of the Great Recession on foreclosure rates plus how it’s impact varied across different groups. Which of the following would be the group with the highest jump in foreclosure rates? a. Prime fixed-rate mortgages b. Prime adjustable rate mortgages c. Subprime adjustable rate mortgages d. Subprime fixed-rate mortgages 36. Many of you asked at the outset of the class to discuss the financial relationship between China and the US that has been referred to as MAD II. Where do I see MAD II in the Balance of Payments Account of the US? a. a deficit in the US Balance of Trade and a surplus in the US Capital Account b. a deficit in the US Balance of Trade and a deficit in the US Capital Account c. a surplus in the US Balance of Trade and a surplus in the US Capital Account d. a surplus in the US Balance of Trade and a deficit in the US Capital Account 37. What was it that explains “How Party of Budget Restraint Shifted to ‘No New Taxes,’ Ever.” a. When McCain lost the presidential election in 2008 b. When Reagan was elected president in 1980 c. When President Bush lost the election to Clinton in 1992 d. When Bush was elected in 2000






