Factors Affecting Gene Frequency - Mr. Lesiuk
advertisement

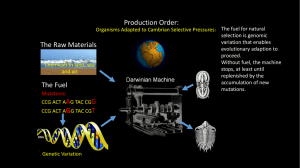
Factors Affecting Gene Frequency 1. Selective Sexual Selection - Only certain phenotypes get chosen by mates. The alleles of the chosen ones increase in frequency. Those alleles not chosen will decrease in frequency. Favoured Frequency INCREASE Unfavoured DECREASE Example: Peacock fancy feathers in males – chosen to reproduce. Non-fancy tails – frequency of alleles will go down. 2. Differential Migration -If a certain phenotype moves out of an area. The frequency of those alleles decreases. Emigrate – Move Out Immigrate – Move In Ones that moved away: Frequency DECREASE Ones that stay: Frequency INCREASE Example: Long necked giraffes on a plain. 3. **** Natural Selection****: -Certain phenotypes survive and those alleles increase in frequency. The alleles of unsuccessful ones decrease. “Survival Of The Fittest” Favoured Frequency INCREASE Unfavoured DECREASE 4. Isolation:”Founder Effect” -If a small group of individuals is separated from the main group, they may have a different frequency of alleles in their gene pool. -As the population grows, this frequency may be much different from the main group. Frequency CHANGED 5. Random Genetic Drift: -Occurs in small populations -Chance mating, or luck can dramatically change the frequency of alleles in this small gene pool. Example: Imagine a bucket of 250 red marbles and 750 white marbles. A handful of 30 or so marbles would probably not conform to the 3:1 ratio in the bucket. In fact, the smaller the sample, the less accurate might be the final ratio. -Mutation plus Random Genetic Drift can change small populations very quickly. -If the changed group is reunited with the main population, the two groups may now be too different for interbreeding. -We now have 2 species. Frequency CHANGED 6. Mutations: - A change to a gene that is inheritable. - Mutations produce new variations. -Most mutations are slight, otherwise they are usually fatal. -Very few surviving mutants are successful because populations are already quite well adapted to their environments. -Mutations affect the genetic code of DNA and therefore the proteins being produced, occasionally the new mutated gene may give rise to a characteristic/trait that increases survival of that individual, allowing them to out-compete the rest of the population. -Only mutations that affect the sex cells can cause a population to evolve. -These mutations will affect the frequency of alleles.