Physics
advertisement

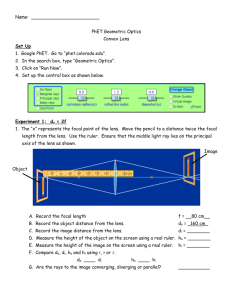
Physics Mr. Harwood Name___________________ Period______ Curved Lens Lab Object: To observe the position and characteristics of images produced by curved lens. Materials: One meter sticks Converging lens Diverging lens Candle Screen Meter stick lens clamp Meter stick screen clamp Procedures: A. Focal length of Converging lens: 1. Arrange your lens, meter stick and screen as in figure 1. Point the lens at a distant object (minimum of 10m) and move the screen along the meter stick until you obtain a sharp image of the distant object on the screen. The distance between the lens and the screen is the approximate focal length of the lens. List this value in the data table. B. Real Images 1. You now know the focal length of the lens. The center of curvature C is twice the focal length. Arrange the two meter sticks, lens, candle and screen as in fin figure 2. 2. Place the candle at a distance greater than C (beyond). Move the screen back and forth along the meter stick until you obtain a sharp image of the candle. Determine the position of the image in relation to the lens. Record your observation in the data table. 3. Place the candle at a distance equal to twice the focal length of the lens ( C ). Locate the image by moving the screen. Record the image distance in the data table. 4. Place the candle at a position that is between F and C. Move the screen back and forth to locate the image. Measure the distance of the image from the lens and record this value in the data table. C. Virtual Images: 1. Move the candle until it is between F and A. See if you can locate an image on the screen. Observe the image in the lens. Record your results in the data table. D. Diverging Lens 1. Place the Diverging lens in the holder. Place the candle some distance from it. Try to obtain an image on the screen. Move the lens or screen, or both. Study the image in the lens. List your results in the data table. Focal Length ( f ) ____________________________ Beyond C Position of object (di = ) At C Between C & F Between F & A Position of image Type of image (real / virtual) Image size (larger / smaller) Direction (inverted or erect) E. Focal length: 1. Measure several object locations and their corresponding image location for your concave lens. Use the measurements and the lens equation 1 1 1 to calculate the f do di focal length of the lens. Compare the calculated focal length with the measured focal length on Part A of the lab. Questions: 1. Summarize the characteristics of images formed by converging lenses in each of the following situations. a. The object is located beyond the center of curvature. b. The object is located at the center of curvature. c. The object is located between the center of curvature and the focal point. d. The object is located between the focal point and the lens. 2. Summarize the characteristics of images formed by diverging lenses. 3. On a separate piece of paper, draw the ray diagrams for each of the trial you recorded. Be sure to identify the location of the image, if it is real or virtual, upright or inverted and larger or smaller.