S2. Manufacture of replacement knockout and precursor constructs
advertisement

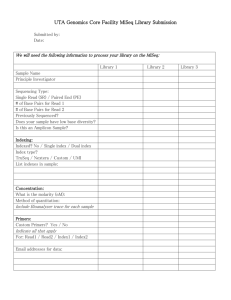
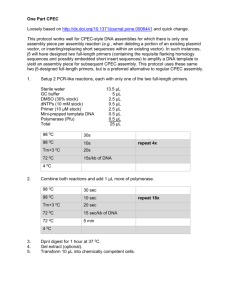
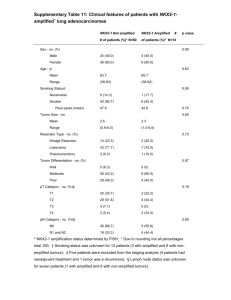
S2. Manufacture of replacement knockout and precursor constructs PLUG3-2. pLUG3-2 was made by amplifying the HPT gene with transcriptional terminator and pUC19 sequence from pLUG3 using primers hygrSpeI (5 GGGATGACTAGTGGGCAATGAGATATG - 3) TCATGGAAGCTTGGCGTAATCATGGTC – 3). and puc9HindIII (5 - A partially duplicated CaMV (cauliflower mosaic virus) 35S promoter (Kay R, Chan A, Daly M, McPherson J (1987) Science 236:1299-1302) fused to an AMV (alfalfa mosaic virus) leader sequence (Datla RSS, Bekkaoui F, Hammerlindl JK, Pilate G, Dunstan DI, Crosby WL (1993) Plant Sci 94:139-149) was amplified from pBI426 (Bommineni VR, Datla RSS, Tsang EWT (1994) J Exp Bot 45:491-495) GGCAACACCTATGACCATGATTACGC with - 3) primers and puc9MKN1 AMVSpeI (5 (5 - GCGAGAACTAGTGGTGGAAGTATTTGAAAG - 3). Since a Hind III site exists in the pUC-derived sequence of pBI426 immediately prior to the partially duplicated CaMV 35S promoter, engineering a restriction site into puc9MKN1 was unnecessary. Both PCR fragments were purified using a QIAquick PCR Purification kit (Qiagen) and digested with Hind III and Spe I. The restriction products were resolved electrophoretically and bands of the proper sizes were excised and purified using a QIAquick Gel Extraction kit (Qiagen). The two chosen DNA fragments were directionally ligated and the resulting vector was propagated in high efficiency JM109 E. coli competent cells (Promega, Fisher Scientific, Nepean, ON, Canada). Plasmid clones were isolated using Wizard Plus Minipreps (Promega) and partially sequenced to verify that the desired plasmid had been produced. pLUG3-2 is a precursor plasmid that provided the HPT selection cassette needed for the manufacture of some MKN knockout constructs. Knockout constructs MKN1-3. A 2.2 kb DNA fragment was amplified from MKN1-3 (GenBank accession number AF285148) with primers MKN1-3PA and MKN1-3PC and introduced into pGEM-T. A 5.0 kb segment of the resulting plasmid (pMKN1-3PAPC) was amplified using primers MKN1-3NheI and MKN1-3AflII. This step served to remove 244 bp, corresponding to a 3΄ portion of the GSE-box and the 5΄ portion of the ELK region with 59 bp of the following intron. A 3.6 kb plant-active selection cassette (GUS::NPT-II fusion gene flanked upstream by a partially duplicated CaMV 35S promoter and AMV translational enhancer and initiation codon, and downstream by a NOS (NOPALINE SYNTHASE) transcriptional terminator) was amplified from pBI426 with primers puc9NheI and puc9AflII. Both PCR products were purified, digested with Nhe I and Afl II and ligated. The resulting plasmid (pMKN1-3kout2) was propagated and isolated as described above. The linear DNA fragment (approx. 5.6 kb) required for gene targeting was amplified from pMKN1-3kout2 with primers MKN1-3PA and MKN1-3PC. MKN1-3B. To facilitate the generation of double knockout strains, a second MKN1-3 knockout construct possessing an alternative selectable marker was manufactured. Primers MKN1-3HindIII and MKN1-3NheI2 were used to amplify a 5.0 kb region of pMKN1-3PAPC. A 1.8 kb plant–active selection cassette (HPT gene flanked upstream by a partially duplicated CaMV 35S promoter and AMV leader sequence and downstream by a polyadenylation signal) was amplified from pLUG3-2 using primers puc9MKN1 and puc9NheI2. Both PCR fragments were purified, digested with Hind III and Nhe I and ligated. The resulting plasmid (pMKN1-3k-outB3) was propagated and isolated as described before. The linear DNA fragment (approx. 3.8 kb) required for gene targeting was amplified from pMKN1-3k-outB3 with primers MKN1-3PA and MKN1-3PC. MKN2. A 2.2 kb DNA fragment was amplified from MKN2 (GenBank accession number AF285147) with primers MKN2PA and MKN2PB and introduced into pGEM-T. A 4.9 kb segment of the resulting plasmid was amplified using primers MKN2HindIII and MKN2NheI. This PCR served to remove 242 bp, corresponding to a short 3΄ portion of the GSE-box, the entire ELK region, the 5΄ portion of the homeobox and 74 bp of the following intron. The HPT selection cassette was directionally ligated to the MKN2derived DNA fragment as described for MKN1-3B. The linear DNA fragment (approx. 3.8 kb) required for gene targeting was amplified from the resulting plasmid with MKN2PA and MKN2PB. MKN4. A 3.3 kb DNA fragment was amplified from MKN4 (GenBank accession number AF284817) with primers MKN4PA and MKN4PB and introduced into pGEM-T (Promega). A 5.9 kb segment of the resulting plasmid was amplified with primers MKN4XhoI and MKN4AvrII and comprised the entire pGEM-T vector flanked on either side by MKN4 DNA. Following this step, which served to remove 311 bp of MKN4 corresponding to a 3΄ portion of the GSE-box, the entire ELK region, the 5΄ portion of the homeobox and 28 bp of the following intron, the DNA fragment was digested with Xho I and Avr II. The GUS::NPT-II cassette was amplified from pBI426 using primers puc9SalI and puc9SpeI and ligated into pGEM-T. The resulting cloned plasmid was digested with Sal I and Spe I. The MKN4- and pBI426-derived restriction fragments were resolved electrophoretically and DNA bands of the proper sizes excised, purified and directionally ligated. The resulting plasmid (pMKN4kout3) was propagated and isolated as described for pLUG3-2. The linear DNA fragment (approx. 6.6 kb) required for gene targeting was amplified from pMKN4kout3 with primers MKN4PA and MKN4PB.