Honors Algebra 2
advertisement

Name___________________________________ Date_____________ Block_______
Algebra 2
Chapter 2 Test Review
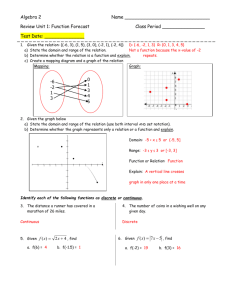
1. State the difference between a relation and a function.
There is only one y value for every x value.
2. State the difference between a linear equation and a linear function.
A linear equation can be written in Standard Form and a linear function can be
written in slope-intercept form.
State whether or not the relation is a function. Identify the domain and range of each.
3.
4.
5.
Function: yes no
Continuous or Discrete
Function: yes no
Continuous or Discrete
Function: yes no
Continuous or Discrete
y
–5
–4
–3
–2
y
y
5
5
5
4
4
4
3
3
3
2
2
2
1
1
–1
–1
1
2
3
4
x
5
–5
–4
–3
–2
1
–1
–1
1
2
3
4
–5
x
5
–4
–3
–2
–1
–1
–2
–2
–2
–3
–3
–3
–4
–4
–4
–5
–5
–5
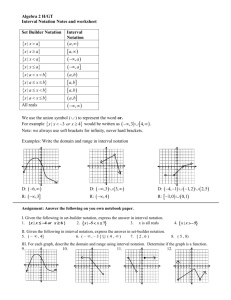
Set-Builder Notation:
D: {x|x=-3,-1,1,2,3}
R: {y|y=-3,-2,0,1,3,4
Set-Builder Notation:
D: {x|x=R}
R: {y|y=4}
6.
7.
Function: yes no
Continuous or Discrete
Function: yes no
Continuous or Discrete
1
2
3
4
x
5
Set-Builder Notation:
D: {x|x=R}
R: {y|y=Z}
8.
Function: yes no
Continuous or Discrete
y
y
5
4
y
9
5
8
4
7
3
6
2
5
1
3
2
1
4
–5
–4
–3
–2
–1
–1
1
2
3
4
5
x
–5
Interval Notation:
D: [-3,3]
R: [-4,4 ]
–4
–3
–2
–1
–1
1
2
3
–2
2
–3
1
–3
–4
–5
3
–2
–4
–5
–4
–3
–2
–1
–1
1
2
3
Interval Notation
D: (-∞, ∞)
R: [1, ∞)
4
5
x
–5
Interval Notation:
D: (-∞, ∞)
R: (-∞, ∞)
4
5
x
Name___________________________________ Date_____________ Block_______
Algebra 2
Find each value if f ( x)
10. f (a 5)
9. f (2)
x2 4x
6 x
81r 2 36r
6 9r
a 2 6a 5
1 a
3
2
1
12. f
2
11. f (9r )
7
22
13. What is the standard form of a linear equation? What are the restrictions?
Ax + By = C
Restrictions: A and B cannot be fractions, A must be positive, A and B cannot be
zero at the same time, No exponents other than 1
Write each equation in standard form and slope-intercept form. Then graph each.
7
14
2
14. x y
15. 5 x 6 y 5 x 6
16. y x 1
3
2
3
y
y
–10 –8
–6
–4
10
10
8
8
8
6
6
6
4
4
4
2
2
2
–2
–2
2
4
6
8
10
x
–10 –8
–6
–4
–2
–2
2
4
6
8
10
x
–10 –8
–6
–4
–2
–2
–4
–4
–4
–6
–6
–6
–8
–8
–8
–10
–10
–10
Std .: 3 x 7 y 21
x : (7, 0), y : (0, 3)
3
x3
7
3
m : , b : 3
7
SI : y
y
10
2
4
6
8
Std .: 2 x 3 y 3
Std .: y 1
x : none, y : (0, 1)
SI : y 1
m : 0, y : (0, 1)
3
x : , 0 , y : (0,1)
2
2
SI : y x 1
3
2
m : , y : (0,1)
3
10
x
Name___________________________________ Date_____________ Block_______
Algebra 2
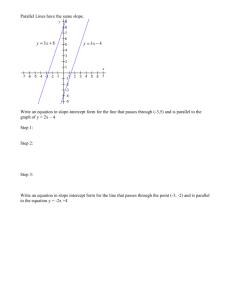
Write the equation of a line in slope-intercept form that satisfies each condition.
3
17. slope , passes through (6,9)
18. passes through (3, 8) and (3, 2)
4
3
27
5
y x
y x3
4
2
3
19. slope 2, y-intercept
y 2 x
3
2
3
2
20. y-intercept 4, x-intercept 5
y
4
x4
5
21. passes through 1,2 and is parallel to y 3x 7
y 3x 5
22. passes through 3,2 and is perpendicular to 4 x 3 y 12
3
17
y x
4
4
23. Given the function f ( x) 6 x 3 1 , explain why the vertex is (-3,1) and not (3,1).
Since the original form for an absolute value function is a|x-h|+k, you need to determine
which value is being subtracted from x and which value is being added to the absolute
value.
24. Describe the type of shifts that occurred between f ( x) 6 x 3 1 and f ( x) 6 x 4 1 .
The second graph shifted the first graph to the left 1 unit and down 2 units.
25. Explain why the value of [4.3] is 4, but the value of [-4.3] is -5.
The greatest integer of -4.3 is -5 because -5 is the integer that is less than or equal to -4.3.
-4 is greater than -4.3.
Name___________________________________ Date_____________ Block_______
Algebra 2
Identify each equation as either an absolute value or greatest integer function. Then
graph each function. Show all work for how you graphed each.
Keep in mind for the greatest integer function graphs, the steps should not be connected.
Also, the left side of the step should be a closed circle leading to an open circle on the right.
The graphing program used graphs these functions as actual steps.
26. f ( x) x 4
27. f ( x) x 2
28. f ( x) 2 x 1
y
–10 –8
–6
–4
a: 1
10
10
8
8
8
6
6
6
4
4
4
2
2
2
–2
–2
2
4
6
8
10
x
–10 –8
–6
–4
–2
–2
a: 1
6
8
10
x
–10 –8
–6
–4
–2
–2
–4
–4
–6
–6
–8
–8
–8
–10
–10
–10
a: 1
(h,k): (0,-2)
a: 2
2
x6 2
3
30. f ( x)
10
8
8
8
6
6
6
4
4
4
2
2
2
4
6
8
10
x
–10 –8
–6
–4
–2
–2
2
4
6
8
10
x
–10 –8
–6
–4
–2
–2
–4
–4
–4
–6
–6
–6
–8
–8
–8
–10
–10
–10
(h,k): (1,7)
Graph each inequality.
1
32. y x 5
3
a: 1
(h,k): (9,-2)
33. y x 2
6
8
10
x
y
10
2
4
31. f ( x) 3x 3 2
10
–2
–2
2
(h,k): (-1/2,0)
y
y
–4
4
–6
(h,k): (0,4)
–6
2
–4
29. f ( x) x 1 7
–10 –8
y
y
10
a: 1
2
4
6
(h,k): (-1,-2)
34. 2 y 3x 6
8
10
x
Name___________________________________ Date_____________ Block_______
Algebra 2
–10 –8
–6
–4
y
y
y
10
10
10
8
8
8
6
6
6
4
4
4
2
2
2
–2
–2
2
4
6
8
10
x
–10 –8
–6
–4
–2
–2
2
4
6
8
10
x
–10 –8
–6
–4
–2
–2
–4
–4
–4
–6
–6
–6
–8
–8
–8
–10
–10
–10
2
4
6
8
10
x