nph12062-sup-0001-FiguresS1-S7-TableS1-S4
advertisement

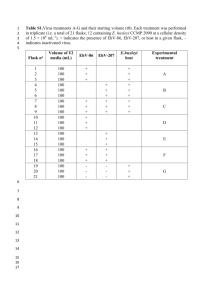
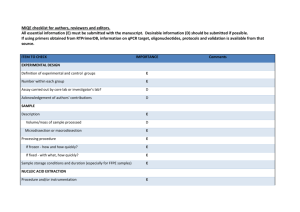
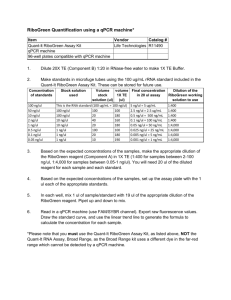
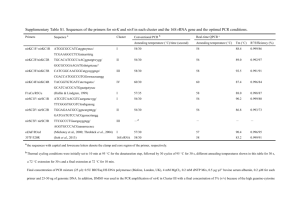
Supporting Information Table S1. Voucher information. Specimen C. amoena ssp. huntiana (Jepson) H. Lewis & M. E. Lewis* C. arcuata (Kellogg) A. Nelson & J. F. Macbride* C. gracilis ssp. albicaulis (Jepson) H. Lewis & M. E. Lewis Voucher/Location LDG 8872 C. gracilis ssp. gracilis (Piper) A. Nelson & J. F. Macbride TRM 039 (from population 8908, collected by L. Gottlieb) C. gracilis ssp. sonomensis (C. L. Hitchcock) H. Lewis & M. E. Lewis TRM 041 (population 8513 in Sonoma County, CA, same population used in Gottlieb and Ford, 1988) C. gracilis ssp. tracyi (Jepson) AbdelHameed & Snow TRM 042 (Highway 128 and Chiles Pope Valley Rd., collected by B. Barringer) C. franciscana H. Lewis and P. H. Raven* C8 EC Oakland Hills LDG 8812 TRM 040 (Centerville Road, 1.1 miles S of Nimshew Rd, Butte County, CA, collected by B. Barringer) C. lassenensis (Eastwood) H. Lewis & M. NFW 152 E. Lewis * C. rubicunda (Lindley) H. Lewis & M. E. LDG 8870 Lewis* C. breweri (A. Gray) Greene NFW 103 * DNA kindly provided by Ken Sytsma (UW-Madison, Botany Department) Table S2. Primers used for quantitative (qPCR) and qualitative (RT) gene expression assays. * Primers designed and kindly provided by V. Eckhart. Gene F3h Primer (V. Eckhart)* (V. Eckhart)* F3’h 1 qF3’H1 F qF3’H1 R F3’5’h 1A F3'5'H1a-q3F F3’5’H-q2R F3’5’h 1B F3'5'H1b-q3F F3’5’H-q1R Dfr1 A DFR1-q2F DFR1a-q2R Dfr1 B DFR1-q2F DFR1b-q2R Dfr2 DFR2-q1F DFR2-q2R Dfr3 DFR3-q1F DFR2-q2R Ans (V. Eckhart)* (V. Eckhart)* Actin ACT-q4F ACT qR Sequence (5’-3’) TCTCATACCCGATCCGAAAC GTCAGAGCCTCCTTGTCGAG TTATTTCTCTCACTGATGAC CCGGAAGGTCTCCTTGATTA AAGGCGGCATGAAGAAACTACAC TTTCGGCTAGGGACCATTCGATG AAGGTGGTATGAAGAAGCTACAT CCATTCGATGATGCTTGATG CACTAG CAGAACAAGCTG TCGGATGCTCGTATAGGTAA CACTAGCAGAACAAGCTG TCGGATGCTCGTAAAGATAT AGCTCGTCTTCACGTCATCA TAGGGTGGGTATGATACTGATC CGTTCAGAAACCCGTCTAT TAGGGTGGGTATGATACTGATC AGCTGTTCTACGAGGGCAAA GACAGCCCAAGAAATCCTGA CATGTATGTTGCGATCCAG TGAACATGTAACCTCTCTCRGT Assay RT RT qPCR, RT qPCR, RT qPCR, RT qPCR, RT qPCR, RT qPCR, RT qPCR, RT qPCR, RT qPCR, RT qPCR, RT qPCR, RT qPCR, RT qPCR, RT qPCR, RT RT RT qPCR, RT qPCR, RT Table S3. Primers used in Dfr2 genotyping assay of F2 plants from the P cross and expected fragment sizes. For Dfr2-A, alleles were differentiated by running fluorescently labeled samples alongside a 500 bp ladder in a ABI 3730XL DNA Analyzer. Primers amplify portions of exon 2 and intron 2. Length polymorphism is due to indel in intron. For Dfr2-B, PCR products were digested with AseI and products were run on an agarose gel. Primers amplify a portion of intron 2. Gene Method Dfr2-A FLA Allele A Allele B Dfr2-B Allele A Allele B variation (cut sight bold) Forward primer (5’-3’) Reverse Primer (5’-3’) FAMATAACATGAAGAAGGTG AAGCA CATTTTTGGATTGGTCCT TGC Expected sizes (bp) 424 434 RDAseI AAACACCCATTCCCGTGA GAGA CTAGCTCCTTGTGTACGT GGTG AAAATTA ATTGA AAAATTA TTTGA 298, 75 391 Table S4. Primers used in Dfr2 genotyping assay of F2 plants from the I cross and expected fragment sizes. Fragment lengths were determined by running fluorescently labeled samples alongside a 500 bp ladder in an ABI 3730XL DNA Analyzer. Primers amplify intron 3 and partial sequences of exons 3 and 4. Length variation is due to indels present in the intron. Gene Dfr2-A Forward primer (5’-3’) FAMAGCTCGTCTTCACGTCATCA Reverse Primer (5’-3’) TAGGGTGGGTATGATACTGATC Allele A Allele B Dfr2-B Allele A Allele B Expected sizes (bp) 299 288 FAMAGCTCGTCTTCACGTCATCA TAGGGTGGGTATGATACTGATC 300 304 Figure S1. Petal sections corresponding to top (T), center (C) and base (B) of the mature petal used in HPLC analyses for unspotted, central spotted, basal spotted, and double spotted plants, from left to right. Figure S2. Age of petals for basal, central, and double spotted flowers when dissections were performed for qualitative RT-PCR assays. Gray lines indicate proximate site of dissections. T, C, and B refer to top, center, and base, respectively. Figure S3. Stages of C. gracilis petal development. Double-spotted individual shown. Central spot appears before basal spot, and both spots appear before background color. Petals are shown to scale. B B A A P P I I = B B P A P P II = C C A A P P I I C C P A P P II = C C P P P P II C B A A P P I I B B P P P P II = C B P A C B P P P P II P P II = = Figure S4. Genotypes at the P and I loci and expected phenotypes. Figure S5. Phylogenetic trees of anthocyanin pathway genes in section Rhodanthos. C. gracilis homeologs are indicated as (A) or (B). Note that absence of a species from a particular cluster does not imply that a species does not have a gene corresponding to that cluster because we did not exhaustively search for genes in species other than C. gracilis. C. gracilis sequences represent those from all four subspecies. Values above branches show bootstrap support (100 replicates). All trees obtained using the GTR model of nucleotide evolution as implemented in ML analyses in PAUP*. A single optimal maximum likelihood tree was recovered for each gene. a, F3h (-lnL= 407.19313, 120 bp included characters—sites111-125 and 174-183 in alignment were excluded); b, F3’h (lnL= 1473.04082, 287 bp included characters); c, F3’5’h (-lnL= 860.47633, 288bp included characters); d, Ans (-lnL= 307.13268, 141bp included characters); e, Dfr (-lnL= 2377.47274, 559bp included characters). F3h x labeled as such because it is unclear if the two divergent sequences are homologous. denotes sequences with stop codons and/or frameshift mutations. Intraspecific allelic variants were combined into a single sequence and polymorphisms were coded as ambiguous characters. All sequences were obtained from genomic DNA with the exception of all Dfr sequences from C. gracilis, Dfr2 from C. lassenensis and C. franciscana, and F3’h1-A from C. gracilis. Arabidopsis thaliana sequences used are AT5G07990 (F3’h), AT4G22880 (Ans), and AT5G42800 (Dfr). albic. son_uns son_spo trac. T C B T C B T C B T C B Dfr2-A/B Actin Figure S6. Dfr2-A/B expression and Actin control in C. gracilis plants derived from seeds collected in natural populations. albic., son_uns, son_spo, trac, refer to C.g. albicaulis (3 replicates), C.g. sonomensis (unspotted plant, 3 replicates), C.g. sonomensis (spotted, 2 replicates), and C.g. tracyi (1 replicate). Spot phenotypes are indicated in cartoon, petal base is on the right. Figure S7. Alignment of all Dfr sequences from C. gracilis. Boxed-in region shows AA translation for active site. * denotes AA133, which has been repeatedly implicated in changes in substrate specificity. See attached txt file (Notes S1) for alignments used for phylogenetic analyses. Note that alignments only show characters included in phylogenetic analyses. Sequences isolated in this study are found under Genbank accession numbers KC019211-KC019249.