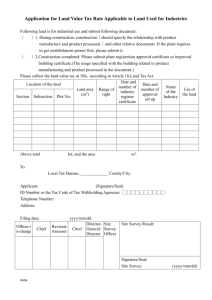
H.5. EF(ID#Photo)
advertisement
Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Belpic Chip Specifications Change History Version Date 1.0 16/10/01 1.1 06/11/02 page 1 of 77 Description Final version for publication Minor corrections (typos, explanations) 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Table des matières Partie A. Scope .......................................................................................................... 6 A.1. Terms and definitions......................................................................................... 6 A.2. Symbols, abbreviated terms and document conventions ................................... 8 A.2.1. Symbols.................................................................................................. 8 A.2.2. Abbreviated terms .................................................................................. 8 Partie B. Communication-related characteristics ...................................................... 9 B.1. Answer-to-reset .................................................................................................. 9 B.2. Negotiation of transmission parameters ............................................................. 9 B.3. Transmission protocols ...................................................................................... 9 Partie C. PINs, Keys and Certificates ..................................................................... 10 C.1. PIN codes ......................................................................................................... 10 C.1.1. BELPIC ................................................................................................ 10 C.1.2. PIN merge algorithms .......................................................................... 11 C.1.3. Cardholder Verification (CHV) ........................................................... 13 C.2. Keys and Certificates ....................................................................................... 14 C.2.1. BELPIC ................................................................................................ 14 C.2.2. Certificates and role identifiers ............................................................ 14 C.2.3. Certificate Verification (CTV) ............................................................. 15 C.2.4. External authentication (EXA) ............................................................ 15 C.2.5. Mutual authentication and Secure Messaging ..................................... 15 Partie D. Files .......................................................................................................... 17 D.1. File types .......................................................................................................... 17 D.2. Files in the EID card ........................................................................................ 17 D.3. BELPIC File relationships ............................................................................... 18 D.4. File structure .................................................................................................... 19 D.5. File access methods and conditions ................................................................. 21 D.6. File identifiers .................................................................................................. 22 D.7. File permissions ............................................................................................... 22 D.8. The PKCS #15 application selection ............................................................... 25 D.9. AID for the PKCS #15 application .................................................................. 25 Partie E. Signature-based Authentication Processes .............................................. 26 E.1. (Internal) Card Authentication ......................................................................... 26 E.2. External Authentication without certificate verification .................................. 27 E.3. External Authentication with certificate verification ....................................... 28 E.4. Mutual Authentication with certification verification and secure messaging .. 29 E.5. User Authentication .......................................................................................... 30 Partie F. MF directory contents .............................................................................. 32 F.1.1. Description ........................................................................................... 32 F.1.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 32 F.2. EF(Authentication Object #1) (PIN2) .............................................................. 32 F.2.1. Description ........................................................................................... 32 F.2.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 32 F.3. EF(DIR) ............................................................................................................ 33 F.3.1. Description ........................................................................................... 33 F.3.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 33 Partie G. DF(BELPIC Application) directory contents .......................................... 34 G.1.1. Description ........................................................................................... 34 G.1.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 34 page 2 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip G.2. EF(TokenInfo) ................................................................................................. 34 G.2.1. Description ........................................................................................... 34 G.2.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 34 G.3. EF(ODF) .......................................................................................................... 34 G.3.1. Description ........................................................................................... 34 G.3.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 34 G.4. EF(AODF) ....................................................................................................... 35 G.4.1. Description ........................................................................................... 35 G.4.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 35 G.4.3. PIN-code settings ................................................................................. 35 G.5. EF(PrKDF) ....................................................................................................... 35 G.5.1. Description ........................................................................................... 35 G.5.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 35 G.6. EF(PuKDF) ...................................................................................................... 36 G.6.1. Description ........................................................................................... 36 G.6.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 36 G.7. EF(CDF)........................................................................................................... 36 G.7.1. Description ........................................................................................... 36 G.7.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 36 G.8. EF(UnusedSpace)............................................................................................. 37 G.8.1. Description ........................................................................................... 37 G.8.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 37 G.9. EF(EmptyArea) ................................................................................................ 37 G.9.1. Description ........................................................................................... 37 G.9.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 37 Partie H. DF(ID) directory contents ........................................................................ 38 H.1. EF(ID#RN)....................................................................................................... 38 H.1.1. Description ........................................................................................... 38 H.1.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 38 H.2. EF(SGN#RN) ................................................................................................... 38 H.2.1. Description ........................................................................................... 38 H.2.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 38 H.3. EF(ID#Adresse) ............................................................................................... 39 H.3.1. Description ........................................................................................... 39 H.3.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 39 H.4. EF(SGN#Adresse) ........................................................................................... 39 H.4.1. Description ........................................................................................... 39 H.4.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 39 H.5. EF(ID#Photo) ................................................................................................... 39 H.5.1. Description ........................................................................................... 39 H.5.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 39 H.6. EF(SGN#Photo) ............................................................................................... 40 H.6.1. Description ........................................................................................... 40 H.6.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 40 H.7. EF(ID#Commune) ........................................................................................... 40 H.7.1. Description ........................................................................................... 40 H.7.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 40 H.8. EF(SGN#Commune) ........................................................................................ 40 H.8.1. Description ........................................................................................... 40 H.8.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 40 H.9. EF(ID#Preference) ........................................................................................... 41 page 3 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip H.9.1. Description ........................................................................................... 41 H.9.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 41 Partie I. Data Objects ............................................................................................. 42 I.1. Data objects in the EID card .............................................................................. 42 I.2. Object classes .................................................................................................... 42 I.3. Accessing objects .............................................................................................. 42 I.4. Authentication objects ....................................................................................... 44 I.4.1. Authentication Object #1 (PIN 2) ........................................................ 44 I.5. Key objects ........................................................................................................ 45 I.5.1. Private RSA Key #1 ............................................................................. 45 I.5.2. Private RSA Key #2 ............................................................................. 45 I.5.3. Private RSA Key #3 ............................................................................. 46 I.5.4. Public RSA Key #5 .............................................................................. 46 I.5.5. Public RSA Key #6 .............................................................................. 47 I.5.6. Public RSA Key #7 .............................................................................. 47 I.6. Certificate objects .............................................................................................. 48 I.6.1. Certificate #2 ........................................................................................ 48 I.6.2. Certificate #3 ........................................................................................ 48 I.6.3. Certificate #4 ........................................................................................ 49 I.6.4. Certificate #8 ........................................................................................ 49 Partie J. Command interface .................................................................................. 50 J.1. Activate File ...................................................................................................... 50 J.1.1. Definition and scope ............................................................................ 50 J.1.2. Conditional usage and security ............................................................ 51 J.1.3. Command message .............................................................................. 51 J.1.4. Response message (nominal case) ....................................................... 51 J.1.5. Status conditions .................................................................................. 51 J.2. Deactivate File ................................................................................................... 52 J.2.1. Definition and scope ............................................................................ 52 J.2.2. Conditional usage and security ............................................................ 52 J.2.3. Command message .............................................................................. 52 J.2.4. Response message (nominal case) ....................................................... 52 J.2.5. Status conditions .................................................................................. 52 J.3. Select File .......................................................................................................... 53 J.3.1. Definition and scope ............................................................................ 53 J.3.2. Conditional usage and security ............................................................ 53 J.3.3. Command message .............................................................................. 53 J.3.4. Response message (nominal case) ....................................................... 54 J.3.5. Status conditions .................................................................................. 55 J.4. Read Binary ....................................................................................................... 55 J.4.1. Definition and scope ............................................................................ 55 J.4.2. Conditional usage and security ............................................................ 55 J.4.3. Command message .............................................................................. 55 J.4.4. Response message (nominal case) ....................................................... 56 J.4.5. Status conditions .................................................................................. 56 J.5. Update Binary.................................................................................................... 56 J.5.1. Definition and scope ............................................................................ 56 J.5.2. Conditional usage and security ............................................................ 56 J.5.3. Command message .............................................................................. 57 J.5.4. Response message (nominal case) ....................................................... 57 J.5.5. Status conditions .................................................................................. 57 page 4 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip J.6. Erase Binary ...................................................................................................... 57 J.6.1. Definition and scope ............................................................................ 57 J.6.2. Conditional usage and security ............................................................ 58 J.6.3. Command message .............................................................................. 58 J.6.4. Response message (nominal case) ....................................................... 58 J.6.5. Status conditions .................................................................................. 58 J.7. Get response ...................................................................................................... 59 J.7.1. Definition and scope ............................................................................ 59 J.7.2. Conditional usage and security ............................................................ 59 J.7.3. Command message .............................................................................. 59 J.7.4. Response message (nominal case) ....................................................... 59 J.7.5. Status conditions .................................................................................. 59 J.8. Manage Verification Process............................................................................. 60 J.8.1. Introduction .......................................................................................... 60 J.8.2. Manage Verification Process: VERIFY ............................................... 60 J.8.3. Manage Verification Process: CHANGE REFERENCE DATA ........ 62 J.8.4. Manage Verification Process: RESET RETRY COUNTER ............... 64 J.9. Manage security environment ........................................................................... 66 J.9.1. Definition and scope ............................................................................ 66 J.9.2. Conditional usage and security ............................................................ 66 J.9.3. Command message .............................................................................. 66 J.9.4. Response message (nominal case) ....................................................... 68 J.9.5. Status conditions .................................................................................. 68 J.10. Perform security operation .............................................................................. 68 J.10.1. Definition and scope ............................................................................ 68 J.10.2. Conditional usage and security ............................................................ 68 J.10.3. Perform Security Operation: COMPUTE DIGITAL SIGNATURE ... 69 J.10.4. Perform Security Operation: VERIFY DIGITAL SIGNATURE ........ 71 J.10.5. Perform Security Operation: VERIFY CERTIFICATE ...................... 72 J.10.6. Generate Public Key Pair ..................................................................... 73 Partie K. Example: FedPKI DF in EmptySpace ..................................................... 75 K.1. DF(FedPKI) ..................................................................................................... 75 K.1.1. Description ........................................................................................... 75 K.1.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 75 K.2. Private RSA Key #9 ......................................................................................... 75 K.2.1. Description ........................................................................................... 75 K.2.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 75 K.3. Certificate #9 .................................................................................................... 76 K.3.1. Description ........................................................................................... 76 K.3.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 76 K.4. Certificate #10 .................................................................................................. 76 K.4.1. Description ........................................................................................... 76 K.4.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 76 K.5. Public RSA Key #11 ........................................................................................ 77 K.5.1. Description ........................................................................................... 77 K.5.2. Access conditions................................................................................. 77 page 5 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Partie A. Scope This standard describes the specifications of the Electronic Identification Card microprocessor. A.1. Terms and definitions For the purposes of this document, the following definitions apply: application application identifier application protocol data unit application provider authentication object directory file binary coded decimal cardholder card issuer certificate directory file command data object directory file dedicated file directory (DIR) file page 6 of 77 15-10-2001 the data structure, data elements and program modules needed for a specific functionality to be satisfied data element that identifies an application in a card message between the card and the interface device, e.g. host computer entity that provides an application optional elementary file containing information about authentication objects known to the PKCS #15 application Number representation where a number is expressed as a sequence of decimal digits and then each decimal digit is encoded as a four bit binary number. Example – Decimal 92 would be encoded as the eight bit sequence 1001 0010. person for whom the card was issued organization or entity that issues smart cards and card applications optional elementary file containing information about certificate known to the PKCS #15 application message that initiates an action and solicits a response from the card optional elementary file containing information about data objects known to the PKCS #15 application file containing file control information, and, optionally, memory available for allocation, and which may be the parent of elementary files and/or other dedicated files optional elementary file containing a list of applications supported by the card and optional related data elements version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip elementary file set of data units or records that share the same file identifier, and which cannot be a parent of another file 2-byte binary value used to address a file on a smart card file identifier function master file message object directory file password path personal identification number (PIN) private key directory file provider public key directory file record secret key directory file template page 7 of 77 15-10-2001 process accomplished by one or more commands and resultant actions that are used to perform all or part of a transaction mandatory unique dedicated file representing the root of the structure NOTE – The MF typically has the file identifier 3F0016 string of bytes transmitted by the interface device to the card or vice versa, excluding transmission-oriented characters elementary file containing information about other directory files in the PKCS #15 application data that may be required by the application to be presented to the card by its user before data or functions can be processed concatenation of file identifiers without delimitation NOTE – If the path starts with the MF identifier (3F0016), it is an absolute path; otherwise it is a relative path. A relative path shall start with the identifier ‘3FFF16’ or with the identifier of the current DF. 4 to 8 digit number entered by the cardholder to verify that the cardholder is authorized to use the card optional elementary file containing information about private keys known to the PKCS #15 application authority who has or who obtained the right to create the MF or a DF in the card optional elementary file containing information about public keys known to the PKCS #15 application string of bytes which can be handled as a whole by the card and referenced by a record number or by a record identifier optional elementary file containing information about secret keys known to the PKCS #15 application value field of a constructed data object, defined to give a logical grouping of data objects version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip token portable device capable of storing persistent data A.2. Symbols, abbreviated terms and document conventions A.2.1. Symbols DF(x) Dedicated file x EF(x) Elementary file x A.2.2. Abbreviated terms For the purposes of this document, the following abbreviations apply: AID application provider identifier AODF authentication object directory file APDU application protocol data unit BCD binary-coded decimal CDF certificate directory file DF dedicated File DODF data object directory file EF elementary file IFD interface device (e.g. reader) MF master file ODF object directory file PIN personal identification number PrKDF private key directory file PuKDF public key directory file RID registered application provider identifier SKDF secret key directory file TPDU transmission protocol data unit URL uniform resource locator page 8 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Partie B. Communication-related characteristics B.1. Answer-to-reset The contents of the Answer-to-Reset (ATR) message shall conform to [ISO/IEC 7816-3], clause 6. The historical bytes are not defined by this standard and may be coded at the issuer’s discretion. B.2. Negotiation of transmission parameters To obtain a reasonable performance, the EID card should be able to support one or both of the mechanisms: cold/warm reset (as defined in ISO/IEC 7816-3, sub-clause 5.3.2 and 5.3.3), see also [EMV ’96, ICC], sub–clause 2.1.3; protocol and parameter selection (PPS) as defined in ISO/IEC 7816-3, clause 7. B.3. Transmission protocols The EID card shall use direct convention as defined in ISO/IEC 7816-3, sub–clause 6.4.1. The EID card shall support the T=0 transmission protocol. An EID card supporting the T=0 transmission protocol shall comply with ISO/IEC 7816-3, clause 8. It is recommended to have an input buffer size in the card of at least 128 bytes to avoid performance penalties when large commands are sent to the card. The mapping of APDUs onto T=0 TPDUs shall conform to ISO/IEC 7816-4, Annex A. page 9 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Partie C. PINs, Keys and Certificates C.1. PIN codes C.1.1. BELPIC Concerning PIN and PUK (PIN Unblocking Keys) codes following conventions are applied in this document - - PIN and PUK codes as defined in the BELPIC specifications are denoted as PINBELPIC, PUK1BELPIC, PUK2BELPIC and PUK3BELPIC: o PINBELPIC is used by the cardholder to execute a private key based authentication and non-repudiation signature o PUK1BELPIC, PUK2BELPIC is used by respectively the cardholder and the registration authority to execute following card commands: the ACTIVATE card command to activate the card after issuing the RESET RETRY COUNTER card command to unblock the PINBELPIC code after a 3 unsuccessful attempts o PUK1BELPIC, PUK3BELPIC is used by respectively the cardholder and the registration authority to execute the CHANGE REFERENCE DATA card command for the modification of the PINBELPIC code PIN and PUK codes as defined in the card are denoted as PINactivate, PINcardholder, PINreset and PUKunblock: o PINactivate is the code used by the card to activate the MF file after card issuing. This code can only be used ones. After activation of the MF this code can never been used. Three unsuccessful attempts blocks the card for ever. This PIN code does not have an unblocking key. This code is a combination of two codes respectively owned by the registration authority and cardholder and needs to be presented to the card before any application will be supported by the EID card. o PINcardholder is the code used by the card to verify the cardholder and to grant access to a number of DF(BELPIC) application files. Three unsuccessful attempts blocks the card for temporary. Unblocking is possible by means of the PUKcardholder key. This is the code that needs to be used by the cardholder to get access to the electronic signature application in the EID card. o PINreset is the code used by the card to grant access to the CHANGE REFERENCE DATA card command that presets the PINcardholder code to a random value. Ten unsuccessful attempts blocks the card for ever. This PIN code does not have an unblocking key. page 10 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip This code is a combination of two codes respectively owned by the registration authority and the cardholder and needs to be presented to the card to preset the PINcardholder code to a random value and to reset the PIN retry counter. This code is useful if the cardholder forgot his PINcardholder o PUKunblock is the code used by the card to grant access to the RESET RETRY COUNTER card command for unblocking the PINcardholder code. Twelve unsuccessful attempts blocks the card for ever. This PIN code does not have an unblocking key. This is the code that needs to be used by the cardholder to unblock the card after three unsuccessful PIN entries and to reset the PIN retry counter. This code is only useful if the cardholder stil knows his PINcardholder. The relation between the PIN/PUK codes in the BELPIC application and in the card are shown in table C1. Table C1 – BELPIC PIN relationships PIN/PUK PIN code in BELPIC Ref. Application PIN1 PUK1 BELPIC 1 PUK2 BELPIC PIN2 PINBELPIC Card Equivalent PINactivate PINcardholder PUK1 PUK1 BELPIC 2 PUK 2 BELPIC PUKunblock PIN3 PUK1 BELPIC 1 PUK 3 BELPIC PINreset Unblocking PUKunblock Application Activate EID card Modify PINcardholder Authentication & Non-repudiation signature Unblock PINcardholder Set PINcardholder to random code The 1, 2 and 3 algorithms merge key parts to create a PIN code. From now on only the PIN reference is used in this document to indicate the abovementioned PIN and PUK codes. C.1.2. PIN merge algorithms C.1.2.1. Activation PINactivate A six digit PINactivate is derived from PUK1 BELPIC and PUK2 BELPIC by means of a permutation algorithm. To explain the permutation algorithm, the following example is used: PUK1BELPIC =250901 and PUK2BELPIC =311201. The input buffer is then constructed as follows: page 11 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip SOURCE POSITION D1 2 D2 5 PUK1BELPIC D3 D4 0 9 D5 0 D6 1 D7 3 D8 1 PUK2BELPIC D9 D10 D11 1 2 0 D12 1 All digits from the input buffer are sorted from left to right in ascending order as follows: D3 0 D5 0 PUK1BELPIC D11 D6 0 1 D8 D9 D12 D1 1 1 1 2 DESTINATION POSITION PUK2BELPIC D10 D7 2 3 D2 5 D4 9 D11 0 D12 3 The first digit D1 =2 is then moved to the byte position D3. The second byte D2 =5 is then moved to the byte position D5, etc. D1 1 D2 0 D3 2 D4 1 D5 5 D6 9 D7 2 D8 0 D9 1 D10 1 The 6-byte permutation value is then calculated as a mathematic addition of the first 6 digits with the last 6 digits limited to the 6 least-significant digits PINactivate =(D1…D6) + (D7…D12) PINactivate =102159 + 201103 PINactivate =303262 C.1.2.2. Unblocking PINunblock A six digit PINunblock is derived from PUK1 BELPIC and PUK2 BELPIC by means of a permutation algorithm. To explain the permutation algorithm, the following example is used: PUK1BELPIC =250901 and PUK2BELPIC =311201. The input buffer is then constructed as follows: SOURCE POSITION D1 2 D2 5 PUK1BELPIC D3 D4 0 9 D5 0 D6 1 D7 3 D8 1 PUK2BELPIC D9 D10 D11 1 2 0 D12 1 All digits from the input buffer are sorted from right to left descending order as follows: D4 9 D2 5 PUK1BELPIC D7 D10 3 2 page 12 of 77 15-10-2001 D1 D12 D9 D8 2 1 1 1 DESTINATION POSITION version 2.4 PUK2BELPIC D6 D11 1 0 D5 0 D3 0 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip The first digit D1 =2 is then moved to the byte position D4. The second byte D2 =5 is then moved to the byte position D2, etc. D1 0 D2 5 D3 1 D4 2 D5 0 D6 1 D7 0 D8 1 D9 3 D10 9 D11 2 D12 1 The 6-byte permutation value is then calculated as a mathematic addition of the first 6 digits with the last 6 digits limited to the 6 least-significant digits PINunblock =(D1…D6) + (D7…D12) PINunblock =051201 + 013921 PINunblock =065122 C.1.2.3. Resetting PINreset For the calculation of the PINreset code the same calculation as for the PINactivate is used except that PUK3 BELPIC is used instead of PUK2 BELPIC. C.1.3. Cardholder Verification (CHV) The cardholder verification is the process whereby the EID card verifies the PIN code from an external application against the reference data stored into the EID card. If this verification process succeeds then the external card application can get access to the authorized files and functions in the EID card. page 13 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip C.2. Keys and Certificates C.2.1. BELPIC Table C2 shows all the keys and certificates that are applicable in the EID card. Table C2 – BELPIC keys and certificates relationships Private Key Public Key Basic PrK#1 Authentication PrK#2 In Cert#2 Non-repudiation PrK#3 In Cert#3 Certification In Cert#4 Authority (CA) Commune PuK#5 Root PuK#6 Role Puk#7 RN Certificates (+PuK) Cert#2 Cert#3 Cert#4 Cert#8 Each key or certificate is indicated by means of a reference number (#). Some keys do not have a corresponding private/public key or certificate. C.2.2. Certificates and role identifiers In compliance with ISO/IEC FDIS 7816-9 (sub–clause 7.4) card verifiable certificates will be applied in public key based authentication procedures. Such certificates contain certificate holder authorisations (e.g. role identifiers). This role identifier is used in the security conditions to be fulfilled for access to data or functions. In the BELPIC application following roles are defined: - Role R01 In this role the card architecture can be remotely updated and extended. This role is applied to delete and create respectively old and new keys and certificates for signature applications or to delete and create respectively old and new application files in the EmptyArea of the EID card. - Role R02 In this role the card architecture can be remotely updated and extended. This role is applied only to create new keys and certificates for signature applications or to create new application files in the EmptyArea of the EID card. - Role R03 In this role the card can be instructed to generate new keys pair for authentication (PrK#2 and Puk#2) and/or non-repudiation (PrK#3 and PuK#3) and to store the generated private keys (Prk#2 and PrK#3) in the EID card. page 14 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip - Role R04 In this role the card can be instructed to store new certificates for authentication (Cert#2) non-repudiation (Cert#3) and CA (Cert#4) in the EID card. - Role R05 In this role the card can be instructed to store a new root key PuK#6 in the EID card. - Role R06 In this role the card can be instructed to change the Public Key PuK#5 (commune) in the EID card. - Role R07 In this role the card can be instructed to update the ID files EF(ID#Adresse), EF(SGN#Adresse) in the EID card. - Role R08 In this role the card can be instructed to store a new role key PuK#7 in the EID card. The roles are retrieved from the certificates after an external authentication with certificate verification. Except for R021, a mutual authentication with secure messaging is required. C.2.3. Certificate Verification (CTV) The certificate verification is the process whereby the EID card verifies the digital signature of a certificate coming from an external application and retrieves the public key and the role identifier from the certificate. If the role identifier retrieved from the certificate corresponds with one that is programmed in the EID card then external card application will get access to the corresponding files and functions in the EID card. The public key retrieved from the certificate can be used for an external or mutual authentication process. C.2.4. External authentication (EXA) The external authentication is the process whereby the EID card authenticates the external application by means of a signature based challenge/response authentication scheme. If this verification process succeeds then the external card application will get access to the authorized files and functions in the EID card. C.2.5. Mutual authentication and Secure Messaging The mutual authentication is the process whereby the EID card authenticates the external application and visa versa by means of a signature based challenge/response authentication scheme. If this verification process succeeds then the external card application will get access to the authorized files and functions in the EID card. 1 Because the external application does not know about the base key page 15 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip In the EID card this process can be proceeded by a certificate verification process. A successful mutual authentication causes also the setup of a secure message channel between the external application and the EID card. page 16 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Partie D. Files D.1. File types The following EF file types as defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4, sub–clause 5.1.3 will be supported by the EID card: - transparent EF; linear EF with records of fixed size; linear EF with records of variable size (optional); cyclic EF with records of fixed size (optional). D.2. Files in the EID card The electronic signature and electronic identification applications are separated in the card by means of two application directories: DF(BEPLIC) and DF(ID). Files in the EID card shall be organized into a hierarchical structure according to ISO/IEC 7816-4. The actual content of the DF(BELPIC) application directory files shall be according to PKCS#15 v1.1. On the EID card resides a directory file, EF DIR, containing the AIDs (ISO/IEC 7816-5) for each application in the EID card. The PKCS#15 AID, and other AIDs, shall also be directly selectable. page 17 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip D.3. BELPIC File relationships EF(DIR) Update: R01 EF(TokenInfo) Update: R01 EF(AODF) Update: R01 PIN2 UpdateCHV(PIN3) PrK#1 Basic Update:NEV EF(PrKDF) Update:R01 PrK#2 Authentication Update:R03 PrK#3 Non-repudiation Update:R03 Puk#5 ODF Commune Update:R06 EF(PuKDF) Update:R01 Puk#6 Root Update:R05 Puk#7 Role Update:R08 ODF AODF PrKDF PuKDF CDF PIN PrK Puk Cert Object Directory File Authentication Object Directory File Private Key Directory File Public Key Directory File Certificate Directory File Personal Identification Number Private Key Public Key Certificate Cert#2 Authentication Update:R04 Cert#3 EF(CDF) Update:R01 Non-repudiation Update:R04 Cert#4 CA Update:R04 Cert#8 RN Update:NEV The purpose of the figure above is to show the relationship between certain files EF(ODF), EF(AODF), EF(PrKDF) and EF(CDF) in the DF(BELPIC Application). Directory. EF(ODF) points to other EFs. page 18 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip EF(PrKDF) contains cross-reference pointers to authentication objects (PINs) used to protect access to the keys. Arrows between PINs and PrKs indicate this. Some certificates (#2 & #3) contain a public key whose private key also resides on the card, so this certificates contain the same identifier as the corresponding private key. Arrows between Certs and PrKs indicate this. D.4. File structure The file structure of the card is described in the figure below. In this table only PIN2 is shown because that’s the only PIN code that is considered as an authentication object for the PKCS#15 BELPIC application. All other PIN codes are store as data elements or directly store in the file control information or store in a separate secret code file depending of the card operating system. Because PIN2 can need to be used also for other application then the PKCS#15 BELPIC application, this PIN code is not a part of the PKCS#15 file structure. Although the authentication object directory file contains a pointer to this external authentication object. page 19 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip EF(DIR) MF EF(AO#1) (PIN2) DF(BELPIC Application) DF(ID) EF(TokenInfo) EF(ID#RN) EF(ODF) EF(SGN#RN) EF(AODF) EF(ID#Adresse) EF(PrKDF) EF(SGN#Adresse) Private Key PrK#1 (basic) EF(ID#Photo) Private Key PrK#2 (authentication) EF(SGN#Photo) Private Key PrK#3(non-repudiation) EF(ID#Commune) EF(PukDF) EF(SGN#Commune) Public Key PuK#5 (commune) Public Key PuK#6 (root) Public Key PuK#7 (role) EF(CDF) Cert#2 (authentication) Cert#3 (non-repudiation) Cert#4 (CA) Cert#8 RN) EF(DODF) (optional) EF(UnusedSpace) (optional) EF(EmptyArea) (optional) page 20 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 EF(ID#Preferences) Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip D.5. File access methods and conditions Table D1 – File Access Methods MF/DF Activate File Deactivate File Create File Delete File EF Activate File Deactivate File Read Binary Update Binary Erase Binary Compute Digital Signature * Verify Signature * Verify Certificate. * Generate Public Key Pair * File type Access method Meaning The MF or DF can be activated. The MF ore DF can be deactivated In the MF or DF files can be created. In the MF or DF files can be deleted. The EF can be activated The EF can be deactivate The content of the EF can be read. The content of the EF can be updated. The content of the EF can be erased. The content of the EF can be used to compute a digital signature. The content of the EF can be used to verify a digital signature. The content of the EF can be used to verify a digital signature The content of the EF can be used to store key values In the table, a “*” indicates that the access method is only relevant for files containing keys (in this case, Private RSA). Each access method can have the conditions shown in table D2. Table D2 – File Access Conditions Type Meaning NEV The operation is never allowed ALW The operation is always allowed CHV The operation is only allowed after a successful cardholder verification. CTV The operation is only allowed after a successful certificate verification EXA The operation is only allowed after a successful signature based external authentication. This external authentication can be part of a mutual authentication. page 21 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip D.6. File identifiers The following file identifiers are defined for the PKCS#15 files. Table D3 – File Identifiers File MF DIR BELPIC ODF TokenInfo UnusedSpace AODFs PrKDFs PuKDFs CDFs Other EFs - (Reserved) DF X File Identifier (relative to nearest DF) 3F0016 (ISO/IEC 7816-4) 2F0016 (ISO/IEC 7816-4) Decided by application issuer (AID is RID || “PKCS-15”) 503116 by default 503216 by default 503316 by default Decided by application issuer Decided by application issuer Decided by application issuer Decided by application issuer Decided by application issuer 503416 - 510016 (Reserved for future use) X D.7. File permissions Some file in the EID card can be freely accessed for different functions. Other files do have a controlled access by means of the following processes or a combination thereof: - cardholder verification certificate verification external authentication Following tables D4 to D6 shown the different permissions. page 22 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Generate Public Key Pair NA NA NA NA NA NA ALW NEV CTV(R01) CHV(PIN3) CTV(R01) NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV CTV(R01) NA NA NA NA NA NA NA ALW ALW ALW ALW ALW CTV(R01) CTV(R02) NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA ALW ALW ALW ALW NEV CTV(R01) CTV(R01) CTV(R01) CTV(R01) NEV CTV(R01) CTV(R01) CTV(R01) CTV(R01) NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV ALW NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV CTV(R03) ALW NA NA NEV NEV NEV CHV(PIN2) NEV NEV CTV(R03) CTV(R04) CTV(R03) ALW NA NA NEV NEV NEV CHV(PIN2)* NEV NEV CTV(R03) NEV NEV NEV NEV ALW ALW NA NA NA NA NEV ALW CTV(R01) CTV(R06) CTV(R01) CTV(R06) NEV NEV NEV ALW NEV NEV NEV NEV CTV(R05) CTV(R05) ALW NA NA ALW CTV(R05) CTV(R05) NEV ALW NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NA NA ALW CTV(R08) CTV(R08) NEV ALW NEV NEV NEV CTV(R04) NEV CTV(R03) ALW ALW NA NA NA NA ALW ALW CTV(R01) CTV(R04) CTV(R01) CTV(R04) NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV Select File ALW EF(DIR) EF(AO#1) (PIN2) DF(BELPIC) NEV NEV NEV NEV ALW ALW NEV NEV ALW EF(TokenInfo) EF(ODF) EF(AODF) EF(PrKDF) EF(PrK#1) (basic) EF(PrK#2) (authentication) EF(PrK#3) (non-repudiation) EF(PukDF) (PuK#5) (commune) (PuK#6) (root) (PuK#7) (role) EF(CDF) (Cert#2) (authentication) NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV CTV(R04) page 23 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Verify Digital Certificate Erase Binary NA NEV Verify Digital Signature Update Binary NA CHV(PIN1) Delete File NA MF Create File CTV(R01) Deactivate File CTV(R01) CTV(R02) NA NA Activate File Read Binary Comput Digital Signature Table D4 – Access rules Generate Public Key Pair Verify Digital Certificate Verify Digital Signature Comput Digital Signature Erase Binary Read Binary CTV(R04) CTV(R03) ALW NA NA ALW CTV(R04) CTV(R04) NEV NEV NEV NEV CTV(R04) NEV NEV CTV(R03) NEV NEV ALW ALW ALW NA NA NA NA NA NA ALW ALW ALW CTV(R04) NEV CTV(R01) CTV(R04) NEV CTV(R01) NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV ALW ALW ALW NA NA CTV(R01) ALW ALW NA CTV(R01) CTV(R01) NA CTV(R01) CTV(R01) NA NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV EF(ID#RN) EF(SGN#RN) EF(ID#Adresse) EF(SGN#Adresse) EF(ID#Photo) EF(SGN#Photo) EF(ID#Commune) EF(SGN#Commune) EF(ID#Preferences) NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV ALW ALW ALW ALW ALW ALW ALW ALW ALW NA NA CTV(R01) CTV(R02) NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA ALW ALW ALW ALW ALW ALW ALW ALW ALW NEV NEV CTV(R07) CTV(R07) NEV NEV EXAcommune EXAcommune CHV(PIN2) NEV NEV CTV(R07) CTV(R07) NEV NEV EXAcommune EXAcommune NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV NEV Select File Deactivate File (Cert#3) (non-repudiation) (Cert#4) (CA) (Cert#8) (RN) EF(DODF) (optional) EF(UnusedSpace) EF(EmptyArea) DF(ID) Activate File Delete File Update Binary Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Create File Annex 5 Remark *: PIN2 need to be presented for each non-repudiation signature. page 24 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip D.8. The PKCS #15 application selection PKCS #15 compliant IC cards should support direct application selection as defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4 Section 9 and ISO/IEC 7816-5, Section 6 (the full AID is to be used as parameter for a ‘SELECT FILE’ command). The operating system of the card must keep track of the currently selected application and only allow the commands applicable to that particular application while it is selected. When several PKCS #15 applications resides on one card, they shall be distinguished by their object identifier in their application template in EF(DIR). It is recommended that the application label (tag ‘50’H) also be present to simplify the man-machine interface (e.g. vendor name in short form). D.9. AID for the PKCS #15 application The Application Identifier (AID) data element consists of 12 bytes and its contents is defined below. The AID is used as the filename for DF(BELPIC) in order to facilitate direct selection of the PKCS #15 application on multi-application cards with only one PKCS #15 application present. The AID is composed of RID || PIX, where ‘||’ denotes concatenation. RID is the 5 byte globally “Registered Application Provider Identifier” as specified in ISO/IEC 7816-5.. The RID need to be registered at ISO. PIX (Proprietary application Identifier eXtension) should be set to “PKCS-15”. page 25 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Partie E. Signature-based Authentication Processes E.1. (Internal) Card Authentication EID Card External Application Generate Challenge: CHLapplication (CHLapplication) Calculate Response: REScard = Sign( CHLapplication,PrKbasic ) (REScard) Verify signature: CHLapplication ?= Verify( REScard, PuKbasic ) During the internal authentication process the external application generates a challenge CHLapplication that is send to the EID card. The EID card receives the challenge CHLapplication from the external application, computes a digital signature on the received challenge CHLapplication with private basic key PrKbasic stored in the EID card and creates a response REScard which is returned to the external application. The external application verifies the received response REScard and the transmitted challenge CHLapplication using the public basic key PuKbasic The EID card will never know if the verification process in the external application is successful. This criteria can thus never been used to obtain access to card files and functions in the EID card. In this case there is no secure message channel established between the external application and the EID card. There are no security conditions to fulfil to execute the internal authentication process. Remark: Only the RN can execute this internal card authentication function because this is the only party that knows the public basic key PuKbasic. page 26 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip E.2. External Authentication without certificate verification External Application EID Card Generate Challenge: CHLcard CHLcard Calculate Response: RESapplication = Sign(CHLcard,PrKapplication) RESapplication Verify signature: CHLcard ?= Verify( RESapplication, PuKapplication ) During the external authentication process the EID card generates a challenge CHLcard that is send to the external application. The external application receives the challenge CHLcard from the EID card, computes a digital signature on the received challenge CHLcard with private key PrKapplication from the external application and creates a response RESapplication which is returned to the EID card. The EID card verifies the received response RESapplication and the transmitted challenge CHLcard using the public key PuKapplication stored in the card. If the verification process on the EID card is successful then the EID card will grant access to the card files and functions corresponding the EXA criteria. In this case there is no secure message channel established between the external application and the EID card. There are no security conditions to fulfill to execute the internal authentication process. Remarks: This function needs to be used to update EF(ID#Commune) and EF(SGN#Commune) files in the EID card using the public key PuKcommune in the card. A CHV(PIN2) must have been performed before using this function page 27 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip E.3. External Authentication with certificate verification External Application EID Card Generate Challenge: CHLcard CHLcard Calculate Response: RESapplication = Sign(CHLcard,PrKapplication) (RESapplication + Certapplication) Verify signature: (Attributes+PuKapplication) ?= Verify( Certapplication, PuKrole ) Retrieve Role Identifier from certificate attributes Retrieve PuKapplication from certificate Verify signature: CHLcard ?= Verify( RESapplication, PuKapplication ) During the external authentication process the EID card generates a challenge CHLcard. The external application needs to read in advance the public role key PUKrole from the EID card to use a certificate signed by this key (in case there has been several versions). The external application receives the challenge CHLcard from the EID card, computes a digital signature on the received challenge RESapplication with private application key PrKapplication from the external application and creates a response RESRN. This response RESapplication together with an application certificate Certapplication are returned to the EID card. The EID card verifies the received application certificate Certapplication and the role identifier in this certificate and retrieves the public key PuKapplication .The retrieved public key can be used to execute an additional internal authenticate so a mutual authentication is occurred. If the verification process on the EID card is successful then the EID card will grant access to the card files and functions corresponding the CTV criteria. In this case there is no secure message channel established between the external application and the EID card. There are no security conditions to fulfil to execute the internal authentication process. Remarks: This function needs to be used to execute all roles defined in the application certificates. A CHV(PIN2) must have been performed before using this function page 28 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip E.4. Mutual Authentication with certification verification and secure messaging EID Card External Application Generate Challenge CHLapplication (CHLapplication) Calculate Response: REScard = Sign( CHLapplication,PrKbasic ) (REScard, CHLcard) Verify signature: CHLapplication ?= Verify( REScard, PuKbasic ) Calculate Response: RESapplication = Sign( CHLcard,PrKapplication ) (RESapplication + Certapplication) Verify signature: (Attributes+PuKapplication) ?= Verify( Certapplication, PuKrole ) Retrieve Role Identifier from certificate attributes Retrieve PuKapplication from certificate Verify signature: CHLcard ?= Verify( RESapplication, PuKapplication ) The mutual authentication process combines an (internal) card authentication and an external authentication with certificate verification. The result of a mutual authentication process is the setup of a secure messaging channel based on symmetric 3DES algorithm and a session key randomly constructed with the responses RESapplication and REScard generated by the authentication process itself. The session key should be generated by an algorithm like Diffie-Hellmann or equivalent. Remark: A CHV(PIN2) must have been performed before using this function page 29 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip E.5. User Authentication External Application EID Card Generate Challenge CHLapplication (CHLapplication) Calculate Response: REScard = Sign( CHLapplication,PrKauth ) (REScard, Certauth, CertCA) Retrieve PuKauth from Certauth Verify signature: CHLapplication ?= Verify( REScard, PuKauth ) Retrieve PuKCA from CertCA Verify Certificate Certauth with PuKCA Verify Certificate CertCA with PuKroot During the user authentication process the external application generates a challenge CHLapplication which is send to the EID card. The EID card receives the challenge CHLapplication from the external application, computes a digital signature on the received challenge CHLapplication with private authentication key PrKauth and creates a response REScard which is returned to the external application together with the authentication Certauth and CA certificates CertCA. The external application retrieves the public authentication key PuKauth from the received authentication certificate Certauth and verifies the received response REScard and the transmitted challenge CHLapplication using the retrieved public authentication key PuKauth. The external application retrieves the public CA key PuKCA from the received CA certificate CertCA and verifies the received authentication certificate Certauth with the retrieved CA public key PuKCA. The EID card will never know if the verification process in the external application is successful. This criteria can thus never been used to obtain access to card files and functions in the EID card. In this case there is no secure message channel between the external application and the EID card. This user authentication process is only possible after a successful PIN2 presentation. page 30 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Remark The CA certificate (CertCA) may not be transmitted. In this case, the application must get it itself. This is the case with some existing protocols, like SSL or TLS, for example. The choice to transmit or not the CA certificate is highly dependant on the server’s environment: if a directory server is available, the application may want to get it there because it’s reliable if it is already present in a local cache, it is the quickest way if no other mean to get it is available, it may request it to the application – although it is quite slow to read it on the card and transmit in on the line page 31 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Partie F. MF directory contents F.1.1. Description The access conditions of MF must be set so that: - PIN 2 (Authentication Object #1) can never be read or removed and DATA (i.e. change PIN) and RESET RETRY COUNTER (i.e. unblock PIN) commands. F.1.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: CHV(PIN1) NEV F.2. EF(Authentication Object #1) (PIN2) F.2.1. Description This elementary file contains the authentication object to enable the authentication and non-repudiation signature. F.2.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV NEV CHV(PIN3) NEV page 32 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip F.3. EF(DIR) F.3.1. Description This file shall contain one or several application templates as defined in ISO/IEC 7816-5. The application template (tag ‘61’H) for a PKCS15 application shall at least contain the following DOs: - Application Identifier (tag ‘4F’H), value supplied by application issuer - Path (tag ‘51’H), value supplied by application issuer Other tags from ISO/IEC 7816-5 may, at the application issuer’s discretion, be present as well. In particular, it is recommended that application issuers include both the “Discretionary ASN.1 data objects” data object (tag ‘73’H) and the “Application label” data object (tag ‘50’H). The application label shall contain an UTF-8 encoded label for the application, chosen by the card issuer. The “Discretionary ASN.1 data objects” data object shall, if present, contain a DER-encoded value. F.3.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW CTV(R01) CTV(R01) page 33 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Partie G. DF(BELPIC Application) directory contents G.1.1. Description DF(BELPIC Application) is the directory of the BELPIC application. The value for the AID (Application Identifier) shall be registered. G.1.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Create: Delete: NEV NEV CTV(R01) CTV(R01) G.2. EF(TokenInfo) G.2.1. Description The TokenInfo file contains generic information about the token (in this case IC Card) as such and it’s capabilities. This information includes the token serial number, file types for object directory files, algorithms implemented on the token etc. G.2.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW CTV(R01) CTV(R01) G.3. EF(ODF) G.3.1. Description The Object Directory File (ODF) is a transparent elementary file, which contains pointers to other elementary files (PrKDFs, PuKDFs, CDFs, AODFs) of the EID card. The information is presented in ASN.1 syntax according to PKCS #15. An application using the EID card shall use this file to determine how to perform security services with the card. G.3.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW CTV(R01) CTV(R01) page 34 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip G.4. EF(AODF) G.4.1. Description This elementary file (Authentication Object Directory File) contains generic authentication object attributes such as allowed characters, PIN length, PIN padding character, etc. It also contains the pointers to the authentication objects themselves (in the case of PINs, pointers to the DF in which the PIN file resides). The authentication objects are used to control access to other objects such as keys. The content of this file is according to PKCS#15. G.4.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW CTV(R01) CTV(R01) G.4.3. PIN-code settings PIN codes need to respect following rules: - PIN-codes shall contain only numbers (ascii-numeric PIN encoding) - Minimum PIN length shall be 4 characters - Maximum PIN length shall be 8 characters - Card shall support PIN changing - The content of the actual PIN files is card specific. G.5. EF(PrKDF) G.5.1. Description This transparent elementary file (Private Key Directory File) contains general key attributes such as labels, intended usage, identifiers etc. It also contains the pointers to the keys themselves. The keys reside in the BELPIC application directory on the card. G.5.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW CTV(R01) CTV(R01) page 35 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip G.6. EF(PuKDF) G.6.1. Description This transparent elementary file (Public Key Directory File) can be regarded as directories of public keys known to the PKCS #15 application. They contain general key attributes such as labels, intended usage, identifiers, etc. When applicable, it contains cross-reference pointers to authentication objects used to protect access to the keys. Furthermore, they contain pointers to the keys themselves. Private keys corresponding to public keys must share the same identifier. The keys reside in the BELPIC application directory on the card. G.6.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW CTV(R01) CTV(R01) G.7. EF(CDF) G.7.1. Description This transparent elementary file contains attributes and pointers to the authentication certificate (Cert #2), non-repudiation signature certificate (Cert #3) and CA certificate (Cert#4). Information in this file contains certificate attributes such as labels, key identifiers, pointers to certificate files etc. The format of the file is specified in PKCS #15. G.7.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW CTV(R01) CTV(R01) page 36 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip G.8. EF(UnusedSpace) G.8.1. Description This transparent elementary file is used to keep track of unused space in empty files of the card. Initially this file will contain a pointer to the empty transparent file EF(EmptyArea). The format of the file is specified in PKCS #15. G.8.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEC NEV ALW CTV(R01) or CTV(R02) CTV(R01) or CTV(R02) G.9. EF(EmptyArea) G.9.1. Description This transparent elementary file contains empty space for additional certificates or data objects that are not stored into the card during centralized personalization. Pointers in EF(UnusedSpace) keep track of used areas inside this file. Originally this file is empty. G.9.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW CTV(R01) or CTV(R02) CTV(R01) or CTV(R02) page 37 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Partie H. DF(ID) directory contents H.1. EF(ID#RN) H.1.1. Description This transparent elementary file contains all permanent information about the ID-card and the ID-cardholder that is managed by the National Register, such as issuing country, issuing authority, issuing data, validity period, name, address, birth date, etc. This is known as the ‘ID file’. This file contains also all information that is graphically personalized on the card plastic. A signature – by the National Register – of this file with the card serial number and the picture will be also included in the file. H.1.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW NEV NEV H.2. EF(SGN#RN) H.2.1. Description This transparent elementary file contains the signature – by the National Register – of the EF(ID#RN) file with the card serial number. H.2.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW NEV NEV page 38 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip H.3. EF(ID#Adresse) H.3.1. Description This transparent elementary file contains all information about the ID-cardholder ‘s residence. H.3.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW CTV(R07) CTV(R07) H.4. EF(SGN#Adresse) H.4.1. Description This transparent elementary file contains the signature – by the National Register – of the EF(ID#Adresse) file with the signature if the EF(ID#RN) included. H.4.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW CTV(R07) CTV(R07) H.5. EF(ID#Photo) H.5.1. Description This transparent elementary file contains the ID-cardholder’s picture. H.5.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW NEV NEV page 39 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip H.6. EF(SGN#Photo) H.6.1. Description This transparent elementary file contains the signature – by the National Register – of the EF(ID#Photo) with the signature if the EF(ID#RN) included. H.6.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW NEV NEV H.7. EF(ID#Commune) H.7.1. Description This transparent elementary file contains the ID-cardholder’s picture. H.7.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW EXA EXA H.8. EF(SGN#Commune) H.8.1. Description This transparent elementary file contains the signature – by the commune – of the EF(ID#Commune) with the signature if the EF(ID#RN) included. H.8.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW EXA EXA page 40 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip H.9. EF(ID#Preference) H.9.1. Description This transparent elementary file contains additional information belonging to the ID-cardholder such as language preference, disabilities, , etc…. This file can be updated on request of the ID-cardholder. H.9.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW CHV(PIN2) NEV page 41 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Partie I. Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Data Objects I.1. Data objects in the EID card Data objects shall be according to PKCS#15 v1.1. I.2. Object classes This document defines four general classes of objects (check PKCS#15 for additional information): - Authentication Objects, - Key Objects, - Certificate Objects, and - Data Objects. All these object classes have sub-classes, e.g. Private Key is a sub-class of the Key Object. Objects can be private, meaning that they are protected against unauthorized access, or public. In the bBELPIC card case, access to private objects is defined by Access Conditions. Conditional access is usually achieved with PINs. Public objects are not protected from read-access. I.3. Accessing objects The flowchart below describes a solution for accessing objects and fulfilling the authentication requirements (PIN verifications) of these objects. page 42 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Begin Yes Is Object PINprotected? No No Check if user consent required? Yes Lock Card (prevent other applications accessing the card) Yes Has PIN been already verified? No Ask Pin from user (dialog) Lock Card (prevent other applications accessing the card) Object-specific operations Verify PIN Unlock Card (prevent other applications accessing the card) End page 43 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip The verification status of a PIN may be dropped automatically to state ‘not verified’ by the card operating system after performing e.g. a private key operation. This is indicated by the userConsent element of the private key object. E.g. userConsevt value set to one for a private key object indicates that the cardholder must manually enter the PIN for each private key operation. Requiring user interaction for all operations done with a specific private key is a trade-off between usability and security. It is anticipated that this feature will be used for performing legally binding non-repudiable digital signatures only. Verification status for ‘local’ one-time PINs is dropped automatically to state ‘not verified’ by the card operating system after performing the private key operation. I.4. Authentication objects All objects (private keys, certificates etc.) can be protected with authentication objects (i.e. PINs). Each object may contain a pointer to an authentication object e.g. a private key object may contain a pointer to a PIN object. This means that the private key operation (sign) can be done only after successful verification of the PIN code. An object cannot be protected with multiple authentication objects in PKCS#15. Furthermore, the specific access type (operation on the object) cannot be specified. The following table lists the operations that can be protected with authentication objects in the PKCS#15 sense. Object type Private key Private key operations Public key Public key operations Certificate Data object Authentication object Operations protected with the authentication object sign (PSO: COMPUTE DIGITAL SIGNATURE) verify (PSO: VERIFY DIGITAL SIGNATURE) Reading the contents of the certificate Reading the contents of data the object The authentication object can be used to unblock this authentication object (e.g. unblocking PIN is used) which is not applied in the BELPIC application . I.4.1. Authentication Object #1 (PIN 2) I.4.1.1. Description The Authentication Object #1 file contains the common PIN-code (basic PIN2) of the EID card. All applications (including the BELPIC application) will use the PIN2 as an access condition for their files. Rules for PIN2: ever Read: Update: Erase: I.4.1.2. Access conditions NEV CHV(PIN3) NEV page 44 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip I.5. Key objects Table C2 shows the different key objects that are stored into the card. I.5.1. Private RSA Key #1 I.5.1.1. Description This file contains the private RSA basic key. No PIN must be verified before RSA transformation can be performed. I.5.1.2. Access conditions Read: NEV Update: NEV Erase: NEV Compute Digital Signature: ALW Verify Digital Signature: NEV Verify Certificate: NEV Generate Public Key Pair: NEV2 I.5.2. Private RSA Key #2 I.5.2.1. Description This file contains the private RSA authentication key. PIN2 must be verified before RSA transformation can be performed. PIN2 verification status remains unaffected after the RSA transformation is performed. I.5.2.2. Access conditions Read: NEV Update: NEV Erase: NEV Compute Digital Signature: CHV(PIN2) Verify Digital Signature: NEV Verify Certificate: NEV Generate Public Key Pair: CTV(R03) 2 During personalization, no security is enforced page 45 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip I.5.3. Private RSA Key #3 I.5.3.1. Description This file contains the private RSA non-repudiation key. PIN 2 must be verified every time before RSA transformation can be performed. PIN2 verification status is dropped to state ‘not verified’ automatically by the card after each RSA transformation performed with this key. The userConsent element in PrKDF contains value 1 for this key i.e. the cardholder must manually enter the corresponding PIN for each private key operation. I.5.3.2. Access conditions Read: NEV Update: NEV Erase: NEV Compute Digital Signature: CHV(PIN2) Verify Digital Signature: NEV Verify Certificate: NEV Generate Public Key Pair: CTV(R03) I.5.4. Public RSA Key #5 I.5.4.1. Description This file contains the public RSA commune key. No PIN is required before RSA transformation can be performed. I.5.4.2. Access conditions Read: ALW Update: CTV(R06) Erase: CTV(R06) Compute Digital Signature: NEV Verify Digital Signature: ALW Verify Certificate: NEV Generate Public Key Pair: NEV page 46 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip I.5.5. Public RSA Key #6 I.5.5.1. Description This file contains the public RSA root key. No PIN is required before RSA transformation can be performed. I.5.5.2. Access conditions Read: ALW Update: CTV(R05) Erase: CTV(R05) Compute Digital Signature: NV) Verify Digital Signature: NEV Verify Certificate: NEV Generate Public Key Pair: NEV I.5.6. Public RSA Key #7 I.5.6.1. Description This file contains the public RSA role key used for external and mutual authentication. No PIN is required before RSA transformation can be performed. I.5.6.2. Access conditions Read: ALW Update: CTV(R08) Erase: CTV(R08) Compute Digital Signature: NEV Verify Digital Signature: NEV Verify Certificate: NEV Generate Public Key Pair: NEV page 47 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip I.6. Certificate objects Table C2 shows the different certificate objects that are stored into the card. All certificate objects contain the corresponding public key object. I.6.1. Certificate #2 I.6.1.1. Description This file contains the cardholder’s .authentication certificate containing the public key corresponding to the private RSA authentication key (Private RSA Key #2). The certificate in this file is DER encoded. I.6.1.2. Access conditions Read: ALW Update: CTV(R04) Erase: CTV(R04) Compute Digital Signature: NEV Verify Digital Signature: NEV Verify Certificate: NEV Generate Public Key Pair: NEV I.6.2. Certificate #3 I.6.2.1. Description This file contains the cardholder’s non-repudiation signature certificate containing the public key corresponding to the private RSA ‘signature key’ (Private RSA Key #3). The certificate in this file is DER encoded. I.6.2.2. Access conditions Read: ALW Update: CTV(R04) Erase: CTV(R04) Compute Digital Signature: NEV Verify Digital Signature: NEV Verify Certificate: NEV Generate Public Key Pair: NEV page 48 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip I.6.3. Certificate #4 I.6.3.1. Description This file contains the trusted CA certificate. The certificate in this file is DER encoded. I.6.3.2. Access conditions Read: ALW Update: CTV(R04) Erase: CTV(R04) Compute Digital Signature: NEV Verify Digital Signature: NEV Verify Certificate: NEV Generate Public Key Pair: NEV I.6.4. Certificate #8 I.6.4.1. Description This file contains the RN certificate. The certificate in this file is DER encoded. I.6.4.2. Access conditions Read: ALW Update: NEV Erase: NEV Compute Digital Signature: NEV Verify Digital Signature: NEV Verify Certificate: NEV Generate Public Key Pair: NEV page 49 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Partie J. Command interface This chapter describes the commands (and their parameters) that shall be supported by BELPIC cards. Additional commands may be supported by the card but they are not normally used by host applications utilizing the BELPIC cards. The defined commands in are based on either ISO/IEC 7816-4 or ISO/IEC DIS 7816-8. The format of APDU is defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4. Table J1 – EID application related commands Command ACTIVATE FILE DEACTIVATE FILE Standard ISO/IEC FDIS 7816-9 ISO/IEC FDIS 7816-9 ISO/IEC 7816-4 Functionality Activate a file form the card’s file system Deactivate a file from the card’s file system MVP: CHANGE REFERENCE DATA MVP: RESET RETRY COUNTER MSE: RESTORE ISO/IEC 7816-8 Select a file from the card’s file system Read the content of a transparent (binary) file Update the content of a transparent (binary) file Erase the content of a transparent (binary) file Get response data from the card (in T=0 protocol) Verify reference data presented by user (e.g. PIN) with the reference data stored inside the card. The current verification status can also be queried with this command. Change the current reference data (e.g. PIN) ISO/IEC 7816-4 Unlock locked reference data (e.g. PIN) ISO/IEC 7816-8 MSE: SET ISO/IEC 7816-8 PSO: COMPUTE DIGITAL SIGNATURE ISO/IEC 7816-8 PSO: VERIFY DIGITAL SIGNATURE ISO/IEC 7816-8 PSO: VERIFY CERTIFICATE ISO/IEC 7816-8 GENERATE PUBLIC KEY PAIR ISO/IEC 7816-8 Restore a pre-defined (or empty) security environment Set the security environment (algorithms, keys) that shall be used in the following PERFORM SECURITY OPERATIONJ (PSO) commands. Compute a digital signature with a private key. The algorithm and key are specified with the MSE command. Verify the digital signature of a signed message a public key. The algorithm and key are specified with the MSE command. Verify the digital signature of a certificate with the public key of the certification authority. The algorithm is specified with the MSE command. Generate and store a public key pair in the card. SELECT FILE READ BINARY UPDATE BINARY ERASE BINARY GET RESPONSE MVP:VERIFY ISO/IEC 7816-4 ISO/IEC 7816-4 ISO/IEC 7816-4 ISO/IEC 7816-4 MVP: Manage Verification Process MSE: Manage Security Environment PSO: Perform Security Operation J.1. Activate File J.1.1. Definition and scope The ACTIVATE FILE command initiates the transition of a from: page 50 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip - the creation state or the initialisation state or the operational (deactivated) state to the operational state (activated). J.1.2. Conditional usage and security Activating a correctly created file is always allowed. Activating a deactivated file can only be performed if the security status satisfies the security attributes defined for this file for the activation function. J.1.3. Command message When the system wants to activate a file, the format defined in table J2 shall be used. Table J2 – ACTIVATE FILE command APDU (Select an EF by file id) CLA As defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4, sub–clause 5.4.1 INS ‘44’ (Activate File) P1 As defined for the SELECT FILE command P2 ‘0C’ (No FCI to be returned) Lc ‘02’ (Length of the file id) File id The (relative) file id of the file to be activated Le Empty J.1.4. Response message (nominal case) The response message to ACTIVATE FILE shall be as defined in table J3 Table J3 – ACTIVATE FILE response APDU Data field Empty SW1-SW2 Status bytes. See the following two tables for possible values of status bytes. J.1.5. Status conditions The warning conditions listed in table J4 may occur. Table J4 – Warning conditions for SELECT FILE ‘6283’ Selected file invalidated ‘6284’ FCI not formatted according to ISO/IEC 7816-4, sub–clause 5.1.5 The error conditions listed in table J5 may occur. page 51 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Table J5 – Error conditions for SELECT FILE ‘6400 Created file could not be activated ‘6982’ Security status not satisfied J.2. Deactivate File J.2.1. Definition and scope This command initiates a reversible deactivation of a file. J.2.2. Conditional usage and security The command can be performed if the security status satisfies the security attributes defined for this command. J.2.3. Command message When the system wants to deactivate a file the format defined in table J6 shall be used. Table J6 – DEACTIVATE FILE command CLA As defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4, sub–clause 5.4.1 INS ‘04’ (Deactivate File) P1 As defined for the SELECT FILE command P2 ‘0C’ (No FCI to be returned) Lc ‘02’ (Length of the file id) File id The (relative) file id of the file to be activated Le Empty J.2.4. Response message (nominal case) The response message to DEACTIVATE FILE shall be as defined in table J7. Table J7 – DEACTIVATE FILE response APDU Data field Empty SW1-SW2 Status bytes. See the following two tables for possible values of status bytes. J.2.5. Status conditions The warning conditions listed in table J8 may occur. Table J8 – Warning conditions for SELECT FILE page 52 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip ‘6283’ Selected file invalidated ‘6284’ FCI not formatted according to ISO/IEC 7816-4, sub–clause 5.1.5 The error conditions listed in table J9 may occur. Table J9 – Error conditions for SELECT FILE ‘6982’ Security status not satisfied ‘6A80’ Incorrect parameters in data field J.3. Select File J.3.1. Definition and scope The SELECT FILE command selects a file from the card’s file system according to file identifier, file path or application identifier (AID). A successful SELECT FILE sets a current file within a logical channel. Subsequent commands may implicitly refer to the current file through that logical channel. Selecting a DF (which may be the MF) sets it as current DF. After such a selection, an implicit current EF may be referred to through that logical channel. Selecting an EF sets a pair of current files: the EF and its parent file. After the answer to reset, the MF is implicitly selected through the basic logical channel, unless specified differently in the historical bytes or in the initial data string. NOTE: A direct selection by DF name can be used for selecting applications registered according to ISO/IEC 7816-5. J.3.2. Conditional usage and security The following conditions shall apply to each open logical channel. Unless otherwise specified, the correct execution of the command modifies the security status (see ISO/IEC 7816-4, sub–clause 5.2.1) according to the following rules: When the current EF is changed, or when there is no current EF, the security status, if any, specific to a former current EF is lost. When the current DF is a descendant of, or identical to the former current DF, the security status specific to the former current DF is maintained. When the current DF is neither a descendant of, nor identical to the former current DF, the security status specific to the former current DF is lost. The security status common to all common ancestors of the previous and new current DF is maintained. J.3.3. Command message When an EF is to be selected by its file id relative to the currently selected DF, the command format defined in Table J10 shall be used. Table J10 – SELECT FILE command APDU (Select an EF by file id) page 53 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 CLA INS P1 P2 Lc File id Le Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip As defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4, sub–clause 5.4.1 ‘A4’ (Select File) ‘02’ (EF selection) ‘0C’ (No FCI to be returned) ‘02’ (Length of the file id) The (relative) file id of the file to be selected Absent or maximum length of data expected in the response When a DF is to be selected by file name (equal to the AID), the command format defined in Table J11 shall be used. Table J11 – SELECT FILE command APDU (Select a DF by file name) CLA As defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4, sub–clause 5.4.1 INS ‘A4’ (Select File) P1 ‘04’ (DF selection by file name) P2 ‘0C’ (No FCI to be returned) Lc ‘05’…’10’ (Length of the full or partial AID) AID Full or partial AID of the DF to be selected Le Absent or maximum length of data expected in the response When an EF is to be selected by use of the absolute path from the MF, the command format defined in Table J12 shall be used. Table J12 – SELECT FILE command APDU (Select an EF by path from MF) CLA As defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4, sub–clause 5.4.1 INS ‘A4’ (Select File) P1 ‘08’ (EF selection) P2 ‘0C’ (No FCI to be returned) Lc Length of the absolute path File id Absolute path without the identifier of the MF Le Absent or maximum length of data expected in the response Other options defined by ISO/IEC 7816-4, sub–clause 6.11 may be supported by the EID card. J.3.4. Response message (nominal case) When an EF is to be selected, the response format defined in Table J13 shall be used. Table J13 – SELECT FILE response APDU (Select an EF by file id) Data field Empty SW1-SW2 Status bytes. See the following two tables for possible values of status bytes. page 54 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip J.3.5. Status conditions The warning conditions listed in Table J14 may occur. Table J14 – Warning conditions for SELECT FILE ‘6283’ Selected file invalidated ‘6284’ FCI not formatted according to ISO/IEC 7816-4, sub–clause 5.1.5 The error conditions listed in Table J15 may occur. Table J15 – Error conditions for SELECT FILE ‘6A81’ Function not supported ‘6A82’ File not found ‘6A86’ Incorrect parameters P1-P2 ‘6A87’ Lc inconsistent with P1-P2 J.4. Read Binary J.4.1. Definition and scope The READ BINARY command is used to read consecutive bytes from the current (transparent) elementary file. J.4.2. Conditional usage and security When the command contains a valid short EF identifier, it sets the file as current EF. The command is processed on the currently selected EF. The command can be performed only if the security status satisfies the security attributes defined for this EF for the read function. The command shall be aborted if it is applied to an EF without transparent structure. J.4.3. Command message When a transparent file is to be read using the READ BINARY command, the format defined in Table J16 shall be used. Table J16 – READ BINARY command APDU CLA As defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4, sub–clause 5.4.1 INS ‘B0’ (Read Binary) P1 See text below P2 See text below Le Number of bytes to be read. If Le=‘00’ then read until end-of-file. P1-P2 specifies the offset of the data to be read. page 55 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip J.4.4. Response message (nominal case) The response message to READ BINARY shall be as defined in Table J17. Table J17 – READ BINARY response APDU Data field The byte string read from the selected file SW1-SW2 Status bytes. See the following two tables for possible values of status bytes. J.4.5. Status conditions The warning conditions listed in Table J18 may occur. Table J18 – Warning conditions for READ BINARY ‘6281’ Part of the returned data may be corrupted ‘6282’ End of file reached before reading Le bytes The error conditions listed in Table J19 may occur. Table J19 – Error conditions for READ BINARY ‘6700’ Wrong length (wrong Le field) ‘6981’ Command incompatible with file structure ‘6982’ Security status not satisfied ‘6986’ Command not allowed (no current EF) ‘6A81’ Function not supported ‘6A82’ File not found ‘6B00’ Wrong parameters (offset outside the EF) ‘6CXX’ Wrong length (wrong Le field; ‘XX’ indicates the exact length) J.5. Update Binary J.5.1. Definition and scope The UPDATE BINARY command is used update the contents of the current (transparent) elementary file. J.5.2. Conditional usage and security When the command contains a valid short EF identifier, it sets the file as current EF. The command is processed on the currently selected EF. The command can be performed only if the security status satisfies the security attributes defined for this EF for the read function. The command shall be aborted if it is applied to an EF without transparent structure. page 56 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip J.5.3. Command message When a transparent file is to be updated using the UPDATE BINARY command, the format defined in Table J20 shall be used. Table J20 – UPDATE BINARY command APDU CLA As defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4, sub–clause 5.4.1 INS ‘D6’ (Update Binary) P1 See text below P2 See text below Lc Length of the subsequent data field Data field Data to be updated Le Empty P1-P2 specifies the offset of the data to be update. J.5.4. Response message (nominal case) The response message to UPDATE BINARY shall be as defined in Table J21 Table J21 – UPDATE BINARY response APDU Data field Empty SW1-SW2 Status bytes. See the following table for possible values of status bytes. J.5.5. Status conditions The error conditions listed in Table J22 may occur. Table J22 – Error conditions for UPDATE BINARY ‘6981’ Command incompatible with file structure ‘6982’ Security status not satisfied ‘6986’ Command not allowed (no current EF) ‘6A81’ Function not supported ‘6A82’ File not found ‘6B00’ Wrong parameters (offset outside the EF) J.6. Erase Binary J.6.1. Definition and scope The ERASE BINARY command is used to erase the contents of a (transparent) elementary file. Erasing is done starting from the address specified in bytes P1 and P2 until the end of file page 57 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip J.6.2. Conditional usage and security When the command contains a valid short EF identifier, it sets the file as current EF. The command is processed on the currently selected EF. The command can be performed only if the security status satisfies the security attributes defined for this EF for the read function. The command shall be aborted if it is applied to an EF without transparent structure. J.6.3. Command message When a transparent file is to be erased using the READ BINARY command, the format defined in Table J23 shall be used. Table J23 – READ BINARY command APDU CLA As defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4, sub–clause 5.4.1 INS ‘0E’ (Erase Binary) P1 See text below P2 See text below Data field Empty Le Empty P1-P2 specifies the offset of the data to be erased. J.6.4. Response message (nominal case) The response message to UPDATE BINARY shall be as defined in Table J24 Table J24 – READ BINARY response APDU Data field Empty SW1-SW2 Status bytes. See the following table for possible values of status bytes. J.6.5. Status conditions The error conditions listed in Table J25 may occur. Table J25 – Error conditions for READ BINARY ‘6981’ Command incompatible with file structure ‘6982’ Security status not satisfied ‘6986’ Command not allowed (no current EF) ‘6A81’ Function not supported ‘6A82’ File not found ‘6B00’ Wrong parameters (offset outside the EF) page 58 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip J.7. Get response J.7.1. Definition and scope The GET RESPONSE command returns response data from the card in T=0 protocol. This command is used in to get response data from commands - SELECT FILE READ BINARY PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION: COMPUTE DIGITAL SIGNATURE GENERATE PUBLIC KEY PAIR J.7.2. Conditional usage and security No condition. J.7.3. Command message When issuing the GET RESPONSE command, it shall have the format defined in Table J26. Table J26 – GET RESPONSE command APDU CLA As defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4, sub–clause 5.4.1 INS ‘C0’ (Get response) P1 ‘00’ P2 ‘00’ Le Maximum length of the data expected in response J.7.4. Response message (nominal case) If the Le field contains only zeroes, then within the limit of 256, all available bytes should be returned. The response message to GET RESPONSE shall be as defined in Table J27. Table J27 – GET RESPONSE response APDU (restore) Data field (Part of) APDU according to Le SW1-SW2 Status bytes. See the following three tables for possible values of status bytes. J.7.5. Status conditions The specific normal processing defined in Table J28 may occur. Table J28 – Normal processing conditions for GET RESPONSE ‘61XX’ Normal processing: more data bytes are available (‘XX’ indicates a number of extra data bytes still available by a subsequent GET RESPONSE). The warning conditions listed in table J29 may occur. Table J29 – Warning conditions for GET RESPONSE page 59 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip ‘6281’ Part of the returned data may be corrupted The error conditions listed in Table J30 may occur. Table J30 – Error conditions for GET RESPONSE ‘6700’ Wrong length (incorrect Le field) ‘6A86’ Incorrect parameters P1-P2 ‘6CXX’ Wrong length (wrong Le field; ‘XX’ indicates the exact length) J.8. Manage Verification Process J.8.1. Introduction The following commands belong to the manage verification process: - VERIFY, as defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4 CHANGE REFERENCE DATA RESET RETRY COUNTER Further options as defined in ISO/IEC FDIS 7816-8 may be supported by the EID card, but the IFD shall not rely on such support. J.8.2. Manage Verification Process: VERIFY J.8.2.1. Definition and scope The VERIFY command is used to authenticate the user. Verification data (e.g. PIN) is compared with the reference data stored internally by the card. J.8.2.2. Conditional usage and security The security status may be modified as a result of a comparison. Unsuccessful comparisons may be recorded in the card (e.g., to limit the number of further attempts of the use of the reference data). J.8.2.3. Command message When the cardholder has to authenticate himself to the card using the VERIFY command, the format defined in Table J31 shall be used. Table J31 – VERIFY command APDU CLA As defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4, sub–clause 5.4.1 INS ‘20’ (Verify) P1 ‘00’ (Other values are RFU) P2 Qualifier of the reference data, see Table J32 Lc Length of the subsequent data field Data field Verification data page 60 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Table J32 – Coding of the reference control P2 B8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 Meaning 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 No information is given 0 - - - - - - - Global reference data (e.g. card password) 1 - - - - - - - Specific reference data (e.g. DF specific password) x x - - - - - ’00’ (Other values are RFU) - - x x x x x Reference data number page 61 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip J.8.2.4. Response message (nominal case) The response message to VERIFY shall be as defined in Table J33. Table J33 – VERIFY response APDU Data field Empty SW1-SW2 Status bytes. See the following two tables for possible values of status bytes. J.8.2.5. Status conditions The warning conditions listed in Table J34 may occur. Table J34 – Warning conditions for VERIFY ‘6300’ No information given (verification failed) ‘63CX’ Counter (verification failed; X indicates the number of further allowed retries) The error conditions listed in Table J35 may occur. Table J35 – Error conditions for VERIFY ‘6983’ Authentication method blocked ‘6984’ Referenced data invalidated ‘6A86’ Incorrect parameters P1-P2 ‘6A88’ Referenced data not found J.8.3. Manage Verification Process: CHANGE REFERENCE DATA J.8.3.1. Definition and scope The CHANGE REFERENCE DATA command is used to change the current internally stored reference data into a new value. Current reference data is first compared with verification data presented by the user. J.8.3.2. Conditional usage and security The command can be performed only if the security status satisfies the security attributes valid for this command. page 62 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip J.8.3.3. Command message When the cardholder (or the system operator) wants to change the reference data (such as a PIN), the format defined in Table J36 shall be used. Table J36 – CHANGE REFERENCE DATA command APDU CLA As defined in ISO/IEC 7816-8, sub–clause 12.2 INS ‘24’ (Change reference data) P1 ‘00’: Exchange reference data ‘01’: Change reference data P2 Qualifier of the reference data, see Table J37 Lc Length of the subsequent data field Data field P1=’00’: Existing reference data followed by new reference data P1=’01’: New reference data NOTE: The length of the existing reference data is known by the card. Therefore, no delimiter between existing and new reference data is present. Table J37 – Coding of the reference control P2 B8 b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 Meaning 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 No information is given 0 - - - - - - - Global reference data (e.g. card password) 1 - - - - - - - Specific reference data (e.g. DF specific password) x x - - - - - ’00’ (Other values are RFU) - - x x x x x Reference data number NOTE 1: P2 = ‘00’ is reserved to indicate that no particular qualifier is used, in those cards where the command references data unambiguously. NOTE 2: The reference data number may be, for example, a password number or short EF identifier. J.8.3.4. Response message (nominal case) The response message to CHANGE REFERENCE DATA shall be as defined in Table J38. Table J38 – CHANGE REFERENCE DATA response APDU Data field Empty SW1-SW2 Status bytes. See the following two tables for possible values of status bytes. J.8.3.5. Status conditions The warning conditions listed in table J39 may occur. Table J39 – Warning conditions for CHANGE REFERENCE DATA ‘6300’ No information given (verification failed) page 63 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip ‘63CX’ Counter (verification failed; X indicates the number of further allowed retries) The error conditions listed in Table J40 may occur. Table J40 – Error conditions for CHANGE REFERENCE DATA ‘6581’ Memory failure (unsuccessful changing) ‘6700’ Wrong length (empty LC field) ‘6982’ Security status not satisfied ‘6983’ Authentication method blocked ‘6984’ Reference data invalidated ‘6A81’ Function not supported ‘6A82’ File not found ‘6A86’ Incorrect parameter P1-P2 ‘6A88’ Reference data not found J.8.4. Manage Verification Process: RESET RETRY COUNTER J.8.4.1. Definition and scope The RESET RETRY COUNTER command is used when a PIN code has been locked due to too many consecutive unsuccessful verifications. Unlocking a PIN requires a resetting code (a.k.a. PIN Unlocking Key, PUK) to be presented to the card by the user. J.8.4.2. Conditional usage and security This command can be performed only if the security status satisfies the security attributes valid for this command. J.8.4.3. Command message When the reference retry counter is to be reset, the command defined in Table J41 shall be used. Table J41 – RESET RETRY COUNTER command APDU CLA As defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4, sub–clause 5.4.1 INS ‘2C’ (Reset retry counter) P1 ‘00’: Reset retry counter and set new reference data ‘01’: Reset retry counter, resetting code in data field ‘02’: Reset retry counter and set new reference data (no resetting code) ‘03’: Reset retry counter, data field empty P2 Qualifier of the reference data, see Table J42 Lc Length of the subsequent data field Data field P1=’00’: Resetting code followed by new reference data page 64 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip P1=’01’: Resetting code P1=’02’: New reference data P1=’03’: Absent NOTE: When P1 = ‘00’ the length of the resetting data is known by the card. Therefore no delimiter between resetting code and new reference data is present. Table J42 – Coding of the reference control P2 b8 b7 b6 b5 B4 b3 b2 b1 Meaning 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 No information is given 0 - - - - - - Global reference data (e.g. card password) 1 - - - - - - Specific reference data (e.g. DF specific password) - x x - - - - ’00’ (Other values are RFU) - - - x x x x x Reference data number J.8.4.4. Response message (nominal case) The response message to RESET RETRY COUNTER shall be as defined in table 43. Table 43 – RESET RETRY COUNTER response APDU Data field Empty SW1-SW2 Status bytes. See the following two tables for possible values of status bytes. J.8.4.5. Status conditions The warning conditions listed in table 44 may occur. Table 44 – Warning conditions for RESET RETRY COUNTER ‘6300’ No information given (verification failed) ‘63CX’ Counter (verification failed; X indicates the number of further allowed retries) The error conditions listed in table 45 may occur. Table 45 – Error conditions for RESET RETRY COUNTER ‘6581’ Memory failure (unsuccessful changing) ‘6700’ Wrong length (empty LC field) ‘6982’ Security status not satisfied ‘6983’ Authentication method blocked ‘6984’ Reference data invalidated ‘6A81’ Function not supported ‘6A82’ File not found ‘6A86’ Incorrect parameter P1-P2 ‘6A88’ Reference data not found page 65 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip J.9. Manage security environment J.9.1. Definition and scope The MANAGE SECURITY ENVIRONMENT command supports the following functions: - replacing the current Security Environment by a Security Environment stored in the card (RESTORE) ; setting, or replacing, one component of the current Security Environment (SET); Further options as defined in ISO/IEC FDIS 7816-8 may be supported by the EID card, but the IFD shall not rely on such support. J.9.2. Conditional usage and security None. J.9.3. Command message When the security environment is to be modified, the command defined in table 46 shall be used. page 66 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Table 46 – MANAGE SECURITY ENVIRONMENT command APDU CLA As defined in ISO/IEC 7816-8, clause 10 INS ‘22’ (Manage security environment) P1 See Table J47. P2 See Table J48. Lc Length of the subsequent data field Data field Concatenation of CRDOs (in the case of SET) Table J47 – Coding of P1 b8 B7 b6 b5 B4 b3 b2 - - 1 - - 1 - - - 1 - - - 1 - - - - - - 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 b1 1 0 0 0 Meaning SM command SM response Computation, encryption and internal authentication Verification, decryption and external authentication SET STORE RESTORE ERASE Table J48 – Coding of P2 b8…b1 Meaning In the case of STORE, RESTORE and ERASE ‘xy’ SE number In the case of SET ‘B4’ Value of CCT in data field, optional ‘B6’ Value of DST in data field. CRDOs File reference (‘81’ file path) Key reference (‘84’ for referencing a private key) Algorithm reference (‘80’) may be used. ‘AA’ Value of HT in data field, optional page 67 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip ‘B8’ Value of CT in data field. CRDOs File reference (‘81’ file path) Key reference (‘84’ for referencing a private key) Algorithm reference (‘80’) may be used. ‘A4’ Value of AT in data field, optional J.9.4. Response message (nominal case) The response message to MANAGE SECURITY ENVIRONMENT shall be as defined in table J49. Table J49 – MANAGE SECURITY ENVIRONMENT response APDU Data field Empty SW1-SW2 Status bytes. See the following table for possible values of status bytes. J.9.5. Status conditions The error conditions listed in Table J50 may occur. Table J50 – Error conditions for MANAGE SECURITY ENVIRONMENT ‘6600’ The environment cannot be set or modified, no further information. ‘6987’ Expected SM data objects missing. ‘6988’ SM data objects incorrect. ‘6A88’ Reference data not found. J.10. Perform security operation J.10.1. Definition and scope The PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION initiates the following security operations: - computation of a digital signature; verification of a digital signature verification of a certificate Further options as defined in ISO/IEC FDIS 7816-8 may be supported by the EID card, but the IFD shall not rely on such support. J.10.2. Conditional usage and security The PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION command may be preceded by a MANAGE SECURITY ENVIRONMENT command. The successful execution of the page 68 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip command may be subject to successful completion of prior commands (e.g. VERIFY before computation of a digital signature). The key reference as well as the algorithm reference shall be: either implicitly known or specified in a CRT in a MANAGE SECURITY ENVIRONMENT command (see ISO/IEC FDIS 7816-8). If present, a header list defines the order and the data items which form the input for the security operations. J.10.3. Perform Security Operation: COMPUTE DIGITAL SIGNATURE J.10.3.1. Definition and scope The PSO: COMPUTE DIGITAL SIGNATURE command calculates a digital signature. The private key and algorithm to be used must be specified using the MANAGE SECURITY ENVIRONMENT command. The input to the command may be either - a hash code (e.g. SHA-1 hash value 20 bytes), a DigestInfo ASN.1 structure encapsulating the hash code, or a full modulus size input buffer (padding done by host application) according to the selected algorithm reference value. J.10.3.2. Conditional usage and security The command can be performed only if the security status satisfies the security attributes for this operation. J.10.3.3. Command message When a digital signature needs to be calculated by the EID card, the command defined in Table J51 shall be used. Table J51 – PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION command APDU (compute digital signature) CLA As defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4 and ISO/IEC 7816-8 INS ‘2A’ (Perform security operation) P1 ‘9E’: digital signature data object is returned in response P2 ‘9A’: data field contains non BER-TLV coded data to be signed Lc Length of the subsequent data field page 69 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Data field If algorithm reference in SE = 00h - Data to be signed (e.g. encapsulated hash code). Padding is done to the full modulus length by the host application. If algorithm reference in SE = 02h: - Hash code encapsulated by the host application into DigestInfo structure. Padding is done internally by the card. If algorithm reference in SE = 12h or 22h - Card encapsulates the hash into DigestInfo structure and pads it internally according to PKCS#1 v1.5 into full modulus length. Le Maximum length of the data expected in response J.10.3.4. Response message (nominal case) The response message to PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION (compute digital signature) shall be as defined in Table J52. Table J52 – PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION response APDU (compute digital signature) Data field Digital signature SW1-SW2 Status bytes. See the following two tables for possible values of status bytes. J.10.3.5. Status conditions The warning conditions listed in Table J53 may occur. Table J53 – Warning conditions for PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION (compute digital signature) to be defined later by the card supplier The error conditions listed in Table J54 may occur. Table J54 – Error conditions for PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION (compute digital signature) to be defined later by the card supplier page 70 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip J.10.4. Perform Security Operation: VERIFY DIGITAL SIGNATURE J.10.4.1. Definition and scope The PSO: VERIFY DIGITAL SIGNATURE initiates the verification of a digital signature. The key and algorithm to be used must be specified using the MANAGE SECURITY ENVIRONMENT command. J.10.4.2. Conditional usage and security The command can be performed only if the security status satisfies the security attributes for this operation. J.10.4.3. Command message When a digital signature needs to be verified by the EID card, the command defined in Table J55 shall be used. Table J55 – PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION command APDU (verify digital signature) CLA As defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4 and ISO/IEC 7816-8 INS ‘2A’ (Perform security operation) P1 ‘00’: no data object is returned in response P2 ‘A8’: Input template for digital signature verification Lc Length of the subsequent data field Data field Signature to be verified Le Empty J.10.4.4. Response message (nominal case) The response message to PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION (verify digital signature) shall be as defined in Table J56. Table J56 – PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION response APDU (verify digital signature) Data field Empty SW1-SW2 Status bytes. See the following two tables for possible values of status bytes. J.10.4.5. Status conditions The warning conditions listed in Table J57 may occur. Table J57 – Warning conditions for PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION (verify digital signature) page 71 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip to be defined later by the card supplier The error conditions listed in Table J58 may occur. Table J58 – Error conditions for PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION (verify digital signature) to be defined later by the card supplier J.10.5. Perform Security Operation: VERIFY CERTIFICATE J.10.5.1. Definition and scope The PSO: VERIFY CERTIFICATEDIGITAL SIGNATURE command s the verification of a certificate. The public key and algorithm to be used must be specified using the MANAGE SECURITY ENVIRONMENT command. J.10.5.2. Conditional usage and security The command can be performed only if the security status satisfies the security attributes for this operation. J.10.5.3. Command message When a certificate needs to be verified by the EID card, the command defined in Table J59 shall be used. Table J59 – PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION command APDU (verify certificate) CLA As defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4 and ISO/IEC 7816-8 INS ‘2A’ (Perform security operation) P1 ‘00’: no data object is returned in response P2 ‘92’: Non BER-TLV coded certificates ‘AE’ or ‘BE’: Input templates for BER-TLV coded certificates Lc Length of the subsequent data field Data field Certificate to be verified Le Empty J.10.5.4. Response message (nominal case) The response message to PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION (verify certificate) shall be as defined in Table J60. Table J60 – PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION response APDU (verify certificate) Data field Empty SW1-SW2 Status bytes. See the following two tables for possible values of status page 72 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip bytes. J.10.5.5. Status conditions The warning conditions listed in Table J61 may occur. Table J61 – Warning conditions for PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION (verify certificate) To be defined later by the card supplier The error conditions listed in Table J62 may occur. Table J62 – Error conditions for PERFORM SECURITY OPERATION (verify certificate) To be defined later by the card supplier J.10.6. Generate Public Key Pair J.10.6.1. Definition and scope The GENERATE PUBLIC KEY PAIR command initiates the generation and storing of a public key pair in the card. The key generation related parameters must specified using the MANAGE SECURITY ENVIRONMENT command. J.10.6.2. Conditional usage and security The command can be performed only if the security status satisfies the security attributes for this operation. page 73 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip J.10.6.3. Command message When a key pair need s to be generated by the EID card, the command defined in Table J63 shall be used. Table J63– GENERATE PUBLIC KEY PAIR command APDU CLA As defined in ISO/IEC 7816-4 and ISO/IEC 7816-8 INS ‘46’ P1 ‘00’ P2 ‘00’ Lc Empty Data field Empty Le Empty J.10.6.4. Response message (nominal case) The response message to GENERATE PUBLIC KEY PAIR shall be as defined in Table J64 Table J64– GENERATE PUBLIC KEY PAIR response APDU Data field Public key SW1-SW2 Status bytes. See the following two tables for possible values of status bytes. J.10.6.5. Status conditions The warning conditions listed in Table J65 may occur. Table J65 Warning conditions for GENERATE PUBLIC KEY PAIR To be defined later by the card supplier The error conditions listed in Table J66 may occur. Table J66 – Error conditions for GENERATE PUBLIC KEY PAIR To be defined later by the card supplier page 74 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip Partie K. Example: FedPKI DF in EmptySpace A role R09 would correspond to the FedPKI e-ID administrator K.1. DF(FedPKI) K.1.1. Description This directory file contains all files belonging to FedPKI. K.1.2. Access conditions Activate: Deactivate: Read: Update: Erase: NEV NEV ALW NEV CTV(R09) K.2. Private RSA Key #9 K.2.1. Description This file contains the private RSA non-repudiation key. PIN 2 must be verified every time before RSA transformation can be performed. PIN2 verification status is dropped to state ‘not verified’ automatically by the card after each RSA transformation performed with this key. K.2.2. Access conditions Read: Update: Erase: Compute Digital Signature: Verify Digital Signature: Verify Certificate: Generate Public Key Pair: NEV NEV NEV CHV(PIN2) NEV NEV CTV(R09) page 75 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip K.3. Certificate #9 K.3.1. Description This file contains the non-repudiation certificate containing the public key corresponding to the private RSA authentication key (Private RSA Key #9). The certificate in this file is DER encoded. K.3.2. Access conditions Read: Update: Erase: Compute Digital Signature: Verify Digital Signature: Verify Certificate: Generate Public Key Pair: ALW CTV(R09) CTV(R09) NEV NEV NEV NEV K.4. Certificate #10 K.4.1. Description This file contains the FedPKI CA certificate. The certificate in this file is DER encoded. K.4.2. Access conditions Read: Update: Erase: Compute Digital Signature: Verify Digital Signature: Verify Certificate: Generate Public Key Pair: ALW CTV(R09) CTV(R09) NEV NEV NEV NEV page 76 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4 Annex 5 Technical specification for the BelPIC electronic identity card chip K.5. Public RSA Key #11 K.5.1. Description This file contains the public RSA FedPKI role key. No PIN is required before RSA transformation can be performed. K.5.2. Access conditions Read: Update: Erase: Compute Digital Signature: Verify Digital Signature: Verify Certificate: Generate Public Key Pair: ALW CTV(R09) CTV(R09) NEV ALW NEV NEV page 77 of 77 15-10-2001 version 2.4