Surveying II
advertisement

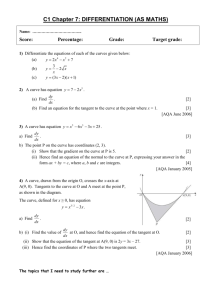
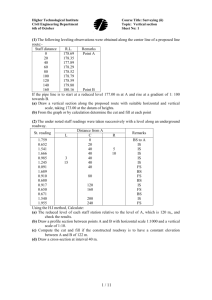
POKHARA UNIVERSITY Semester – Spring Level: Bachelor Programme: BE Course: Surveying II Year : 2009 Full Marks : 100 Pass Mark : 45 Time : 3 hrs Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable. The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Attempt all the questions. 1. a. b. Explain characteristics of contours with suitable examples. What are the factors which controls choosing of proper contour interval? Explain various method of contouring. 2. a. Explain stadia and tangential systems of techeometry. Write the working principle of a subtense bar. b. A tachometer was set up at station an M and the following readings were observed on a vertically held staff : Station Staff station Vertical angle Hair reading Remarks M BM N - 2º28’ + 7º13’ 2.225 2.550 2.875 1.648 2.516 3.393 7 8 7 8 RL of BM=1375.324 Calculate the horizontal distance from M to N and R.L. of N, if the constant of the instrument were 100 and 0.1. 3. a. b. Find elements of simple circular curves. Two tangents intersect at chainage (59+10.3), the deflection angle being 50030''. Calculate the necessary data for setting out a curve of 15 chains radius to connect the two tangents if it is intended to set out the curve by offsets from tangents. Take peg interval equal to 1 chain, length of chain being equal to 20 metres. 6 9 4. a. How do you find the discharge of a river? Describe at least two methods. What do you mean by sounding? Explain three methods of locating sounding positions. Define any four : i. Vertical photograph ii. Oblique photograph iii. Flying height 8 b. 5. a. 1 7 8 b. 6. 7. iv. Nadir point v. Forward and side overlap Derive an expression to find the scale of a vertical photograph. a. b. What do you mean by GIS? Explain their uses in civil engineering. What are active and passive remote sensing? Write the methods of image interpretation. Write short notes on (Any Two): a. Transition curve b. Stereoscopic vision and stereoscope c. Use of computer software in surveying and contouring 2 7 8 7 2×5