HELP SHEET
advertisement
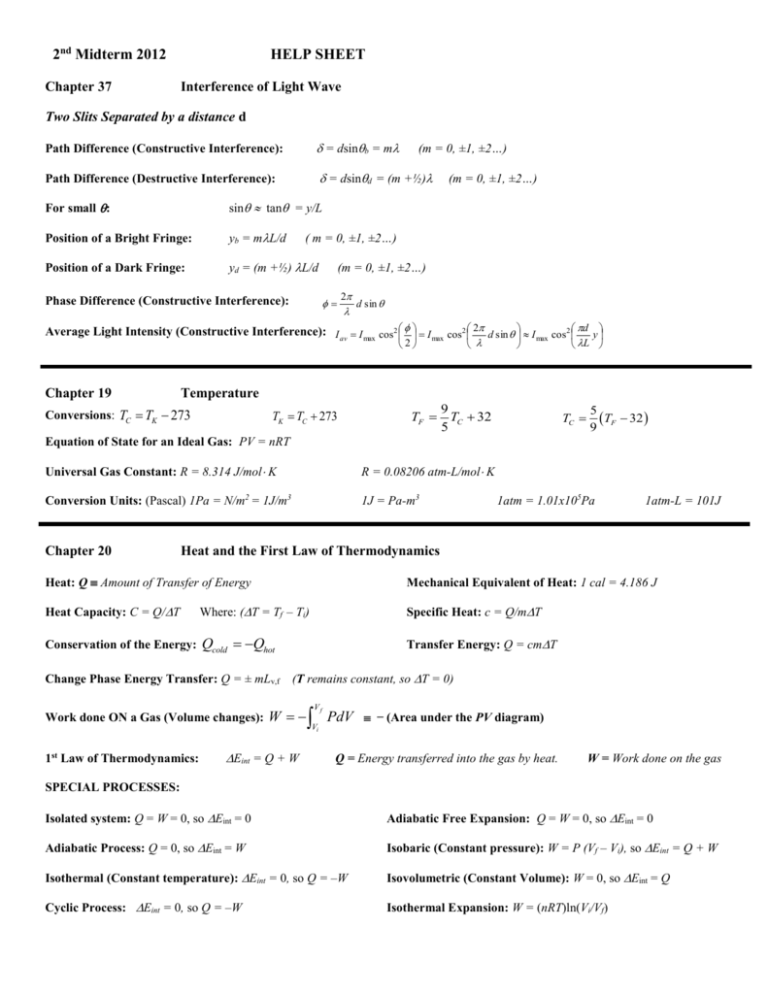
2nd Midterm 2012 Chapter 37 HELP SHEET Interference of Light Wave Two Slits Separated by a distance d Path Difference (Constructive Interference): = dsinb = m Path Difference (Destructive Interference): = dsind = (m +½) For small : sin tan = y/L Position of a Bright Fringe: yb = mL/d Position of a Dark Fringe: yd = (m +½) L/d (m = 0, ±1, ±2…) (m = 0, ±1, ±2…) ( m = 0, ±1, ±2…) (m = 0, ±1, ±2…) Phase Difference (Constructive Interference): 2 d sin Average Light Intensity (Constructive Interference): I av I max cos2 I max cos2 2 d sin I max cos2 d y 2 Chapter 19 L Temperature Conversions: TC TK 273 TK TC 273 TF 9 TC 32 5 TC 5 TF 32 9 Equation of State for an Ideal Gas: PV = nRT Universal Gas Constant: R = 8.314 J/mol K R = 0.08206 atm-L/mol K Conversion Units: (Pascal) 1Pa = N/m2 = 1J/m3 1J = Pa-m3 Chapter 20 1atm = 1.01x105Pa 1atm-L = 101J Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics Heat: Q Amount of Transfer of Energy Mechanical Equivalent of Heat: 1 cal = 4.186 J Heat Capacity: C = Q/T Where: (T = Tf – Ti) Specific Heat: c = Q/mT Conservation of the Energy: Qcold Qhot Transfer Energy: Q = cmT Change Phase Energy Transfer: Q = ± mLv,f (T remains constant, so T = 0) Work done ON a Gas (Volume changes): W 1st Law of Thermodynamics: Eint = Q + W Vf Vi PdV ̶ (Area under the PV diagram) Q = Energy transferred into the gas by heat. W = Work done on the gas SPECIAL PROCESSES: Isolated system: Q = W = 0, so Eint = 0 Adiabatic Free Expansion: Q = W = 0, so Eint = 0 Adiabatic Process: Q = 0, so Eint = W Isobaric (Constant pressure): W = P (Vf – Vi), so Eint = Q + W Isothermal (Constant temperature): Eint = 0, so Q = –W Isovolumetric (Constant Volume): W = 0, so Eint = Q Cyclic Process: Eint = 0, so Q = –W Isothermal Expansion: W = (nRT)ln(Vi/Vf) Chapter 21 The Kinetic Theory of Gases Pressure of N Particles (Ideal Gas): P 2 3 N V 1 2 mv 2 Average Translational Kinetic Energy per molecule: Root-Mean-Square Speed: vrms v 2 1 2 mv 2 23 k BT or 3kBT m 1 2 2 mv rms 32 k B T Boltzmann’s Constant: kB R 1.4 10 23 J / K NA Monatomic Gas (Ideal Gas): Internal Energy (N molecules or n mole): Eint =3/2(NkBT) = 3/2(nRT) Change in Internal Energy: Eint = nCVT Molar Specific Heat (Volume Constant): CV = (3/2)R Molar Specific Heat (Pressure Constant): CP = (5/2)R Ratio of Specific Heats: = CP / CV =5/3 Adiabatic Expansion or Compression: PV = Constant P V i i P f V f or PT -1 = Constant P T i i 1 P f V f 1