Tips for Equipment Design - CSIP Cornell
advertisement

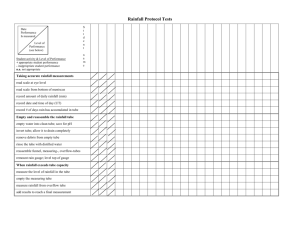
Runoff and Infiltration Equipment Design 1. Rainfall Simulator This is the Cornell Rainfall Simulator (Rainmaker) and Infiltrometer, used for research by the Soil Health Team at Cornell. Your goal is to design a simpler version of this $1000 piece of equipment. Here are the key characteristics of the rainfall simulator: A large enough volume to allow for about 10 min of rain There must be a way to measure changes in volume without moving the rainfall simulator (i.e. by reading the change in volume from a scale on the side of the rainfall simulator as the water level is dropping; the Cornell version is graduated on one side, A) Very small holes at the bottom that allow for rain-like drops (B) The tube (C) must be able to reach almost to the bottom, about 5-15 cm from the bottom. The level of the bottom of the tube controls the rate at which water is raining out of the rainmaker (i.e. keeps it constant). It will rain faster when the tube is higher off the bottom. The tube must stay in place during measurement. The rainmaker can be opened to add water (D) When it is closed (D, a rubber stopper works, depending on the design), the seal must be airtight. (Thus the airspace (E) is closed in, so this slight vacuum, holds up the water above the bottom of the tube. Atmospheric pressure now pushes on the water only at the bottom of the tube, not at the changing water level, so that raindrops fall constantly and more slowly.) It must fit over the Infiltrometer Ring or Sample Container so that all rain falls inside the ring. D E A ~10cm, C B 2. Infiltrometer Ring for Outdoor Measurement Total Rainfall Soil Surface Rubber Stopper Outflow Tube Runoff Infiltration 3. Sample Container for Indoor Measurement B A D Infiltrometer base could be either a ring, or could also be 4 sided wooden box The outflow tube (or whatever outflow channel can be attached to either a slot or hole (A or B, B is the type of outflow used on the Cornell set-up) Soil is filled into the bucket/ring/box up to the soil line (D), such that runoff can flow out of the holes Holes or a mesh in the bottom allow water to pass through, but soil to remain in container (C) C Option 1 A For outdoor experiments: Infiltrometer ring should be strong enough to be able to be pushed or hammered into the soil so that the outflow hole (A or B) is at the level of the soil (D) No mesh/holes (C) needed outdoors B Option 2 D C This material was developed through the Cornell Science Inquiry Partnership program (http://csip.cornell.edu), with support from the National Science Foundation’s Graduate Teaching Fellows in K-12 Education (GK-12) program (DGE # 0231913 and # 9979516) and Cornell University. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the NSF.