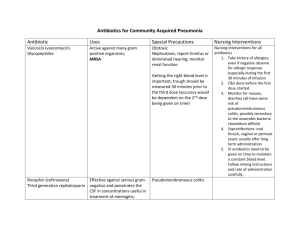
Clinical Antibiotic Use
advertisement
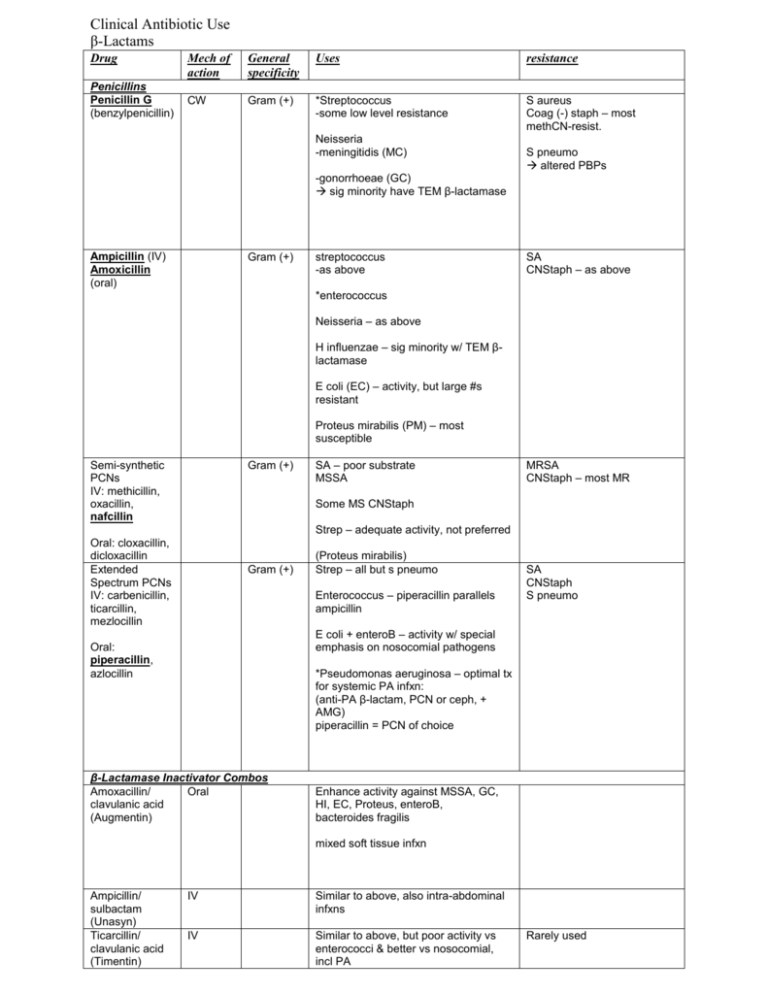
Clinical Antibiotic Use β-Lactams Drug Penicillins Penicillin G (benzylpenicillin) Mech of action General specificity Uses resistance CW Gram (+) *Streptococcus -some low level resistance S aureus Coag (-) staph – most methCN-resist. Neisseria -meningitidis (MC) S pneumo altered PBPs -gonorrhoeae (GC) sig minority have TEM β-lactamase Ampicillin (IV) Amoxicillin (oral) Gram (+) streptococcus -as above SA CNStaph – as above *enterococcus Neisseria – as above H influenzae – sig minority w/ TEM βlactamase E coli (EC) – activity, but large #s resistant Proteus mirabilis (PM) – most susceptible Semi-synthetic PCNs IV: methicillin, oxacillin, nafcillin Gram (+) SA – poor substrate MSSA MRSA CNStaph – most MR Some MS CNStaph Strep – adequate activity, not preferred Oral: cloxacillin, dicloxacillin Extended Spectrum PCNs IV: carbenicillin, ticarcillin, mezlocillin Gram (+) (Proteus mirabilis) Strep – all but s pneumo Enterococcus – piperacillin parallels ampicillin SA CNStaph S pneumo E coli + enteroB – activity w/ special emphasis on nosocomial pathogens Oral: piperacillin, azlocillin *Pseudomonas aeruginosa – optimal tx for systemic PA infxn: (anti-PA β-lactam, PCN or ceph, + AMG) piperacillin = PCN of choice β-Lactamase Inactivator Combos Amoxacillin/ Oral clavulanic acid (Augmentin) Enhance activity against MSSA, GC, HI, EC, Proteus, enteroB, bacteroides fragilis mixed soft tissue infxn Ampicillin/ sulbactam (Unasyn) Ticarcillin/ clavulanic acid (Timentin) IV Similar to above, also intra-abdominal infxns IV Similar to above, but poor activity vs enterococci & better vs nosocomial, incl PA Rarely used Piperacillin/ tazobactam (Zosyn) Cephalosporins 1st generation IV: cefazolin, cephalothin, cephradine Oral: cephradine, cephalexin, cefadroxil IV Similar to above, but adequate vs enterococci & even better vs nosocomials, incl PA Gram (+) Also some gram (-) MSSA (similar to nafcillin) MS-CNStaph MRSA Strep – similar to PCN G, but not active vs PCN-resist S pneumo EC, PM – more strains EC than amp, some resistance Klebsiella – many susceptible **clinical use: 1. surgical prophylaxis 2. PCN allergies w/o hx of anaphylaxis 3. poor penetration of BBB c-tetan & c-mzole have MTT 2nd generation Cefoxin Gp: cefoxin, cefotetan, cefmetazole Staph – poor S pneumo strep – ok vs PCN-susceptible GC – superb enteroB – good vs EC, PM, kleb, serratia, some citroB & enterobacter anaerobes, including B frag poor penetration of BBB MSSA – fair Strep – good Cefuroxime Gp MRSA Poor-fair vs PCN-resis s pneumo *HI – good enteroB – good vs EC, PM, kleb, more **penetration of BBB! MSSA – fair Strep – good vs PCN-intermediate s pneumo, fair vs some PCN-res strains 3rd generation Standard: cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, ceftizoxime GC, MC – superb HI – superb enteroB – superb penetration of BBB MSSA – cefe > cefta Strep – cefe > cefta ***incl. s pneumo Ceftazidime, cefepime GC, MC – superb HI – superb EnteroB – superb *PA – excellent Penetration into BBB Monobactams Aztreonam Pyelonephritis – some ceftriaxone resistance probs Broad spectrum gram (-) Gram (-) similar to ceftazidime NO activity vs gram (+) aerobes NO activity vs anaerobes NO cross-hypersens w/ PCNs or cephs **can be used for PCN allergy w/ hx of anaphylaxis Some probs w/ resistance MSSA – excellent Strep – excellent Enterococci – similar to amp GC, MC, HI – superb enteroB, PA – superb anaerobes, incl B frag – superb Carbapenems Imipenem, meropenem Can be used w/ β-lactam resistant bacteria *imipenem admin w/ cilastatin (inh imipenem inact by renal dehydropeptidase) Seizures: I >M, esp in pts w/ impaired renal fcn Ertapenem Glycopeptide Drug Mech of action Vancomycin Parenteral (gen) General specificity Uses resistance *all* aerobic gram (+) All aerobic gram (+) cocci & bacilli Staph Strep Enterococcus Corynebacterium Clostridium ˚˚can be used for MRSA!! Oral vanco for c diff but metranidazole preferred for resistance reasons Oral (≠ absorb) Slightly less efficacious than βlactams (eg. MSSA) Resistance w/ enterococci (VRE), some VRSA… Little toxicity by itself, but synergistic effect of nephrotoxicity w/ AMG ***use restricted to situations when βlactams can’t be used Aminoglycosides Drug Streptomycin Gentamycin Mech of action General specificity Uses Broad gram (+) & gram (-) aerobes 2nd line agent for M tuberculosis (MTB) Adjunctive therapy w/ amp or vanco for systemic enterococcal infxns **Gram (+) aerobes – adjunctive w/ anti-CW for systemic enterococcal infxns Hardware associated infxns (SA) Gram (-) aerobes – excellent vs enteroB and PA (use w/ β-lactam) Tobramycin Gram (-) aerobes – similar to gent More active vs PA (use w/ β-lactam) Amikacin 2nd line agent for MTB, gen active vs streptomycin-resistant strains Gram (-) aerobes – similar to gent and tobra, but active vs more strains (use w/ β-lactam) resistance Clindamycin Drug Mech of action General specificity Uses resistance Clindamycin IV or oral Aerobic gram (+) Most strep Many staph SA – only if susceptible to BOTH clinda AND erythro MRSA PCN-resist s pneumo Anaerobes, incl B frag Good penetration into bone and abscesses **MUST check for erythro resistance b/c mech of resistance for erythro can also confer resistance to clinda!! Diarrhea probs canNOT cross BBB Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole Drug Mech of action TMP/SMX Oral & IV General specificity Uses resistance Staph – many strains, incl some MRSA (good oral alternative) Strep – fair/poor NO activity vs enterococcus Enterococcus – humans take exogenous folate 20-25% EC are resistant HI – fair enteroB – excellent pneumocystis carinii nocardia Probs w/ hypersens (esp in HIV/AIDS pts) toxoplasmosis UTIs – EC resis precludes empiric use for pyelo **penetrates into prostate (TMP) Macrolides Drug Mech of action Erythromycin Oral & IV Clarithromycin Oral General specificity Uses resistance Strep – alt to PCN Legionella Mycoplasma pneumoniae Campylobacter Similar to erythro, fewer GI side effects S pneumo H pylori Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) Azithromycin Oral, IV Similar to erythro, fewer GI side effects Chlamydia trachomatis (1x dose) used w/ ceftriaxone to tx gono/clap MAC Diarrhea, cramping Fluoroquinolones Drug Mech of action General specificity Uses Norfloxacin Oral UTIs Aerobic gram (-) rods, incl PA Ciprofloxacin Levofloxacin Oral & IV Aerobic gram (-) rods, incl PA (cipro>levo for PA) Aerobic gram (+) cocci, incl S pneumo (levo >cipro) MTB (levo) GC M pneumo Legionella C pneumo Gatifloxacin Oral & IV Moxifloxacin Oral Similar to levofloxacin, but MORE active vs S pneumo Similar to gati, but better against anaerobes, incl B frag Resistance POOR vs gram (-), incl PA NOT for UTIs Community-acquired pneumonia Better for S pneumo than levo Only FQ w/ indication for intraabdominal infxn New Agents Drug Mech of action Synercid IV Linezolid Daptomycin Tigecycline Glycylcycline (NEW CLASS) Oral, IV IV only IV only General specificity Uses resistance Synergy of 2 streptogramins Broad spectrum gram (+) MRSA VRSA VRE faecium Rx-resistant S pneumo Broad spectrum gram (+) MRSA VRSA VRE Rx-resistant S pneumo BacterioSTATIC Broad spectrum gram (+) MRSA VRSA VRE Rx-resistant S pneumo Broad spectrum Staph Strep Enterococcus enteroB anaerobes, incl B frag acinobacter indicated for complicated skin/soft tissue & intra-abdom infxns used for sulbactam resistance Arthralgia-myalgia syndrome Resistance w/ enterococcus and SA strains bacterioSTATIC reversible thrombocytopenia w/ tx 2+ weeks resistance w/ enterococcus and SA bacterioCIDAL NOT indicated for pneumonia binds surfactant Resistance?? bacterioSTATIC side effects : nausea, vomiting