THEORY INTO PRACTICE MODEL OF INSTRUCTION
advertisement

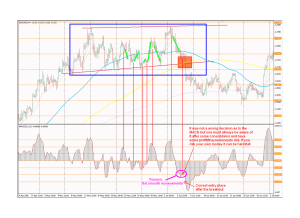
THEORY INTO PRACTICE MODEL OF INSTRUCTION Source: Becoming a Teacher:Parkay,Stanford,Vaillancourt, Stephens, 2nd. ed.:Pearson, 2005 Using the Theory into Practice Model of Instruction, teachers make decisions about: 1. the content to be taught 2. how students will learn 3. the behaviours the teacher will use in the classroom The effectiveness of the teaching is related to the quality of the decisions the teacher makes in these areas. In this model, the teacher follows seven steps in the classroom. These steps align with the Phases of Instruction (Motivation, New Learning, Consolidation, Application) and follows the Nipissing University GPF Lesson Planning Format. The teacher: MOTIVATION 1. Orients the students to the material to be learned. 2. Tells the students what they will learn and why it is important. NEW LEARNING 3. Presents new material that consists of knowledge, skills, or processes students are to learn. 4. Models what students are expected to do. CONSOLIDATION 5. Checks for students’ understanding. 6. Gives students opportunities for practice under the teacher’s guidance. APPLICATION 7. Makes assignments that give students opportunities to practice what they have learned with greater independence.