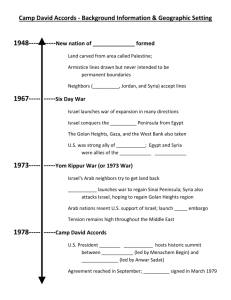
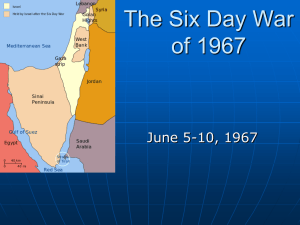
Persian Gulf and Interior
advertisement

Persian Gulf and Interior People and Language • Islam is the main religion of this region. • Arabic is the most common language because the Qur’an is written in Arabic. • Other ethnicities of the region: Kurds, Baloch, Bakhtiari, and Hazara. People and Languages • Kurds are Muslim, just not Arabic. • Farsi is the language used by most of Iran’s Persians. • Kurds, Baloch, Bakhtiari, and Hazara speak languages related to Farsi. • • • • • • • • • People and Languages Because the ethnicities of Iran and Afghanistan are so different, the cultural diversity is complex. Afghanistan’s main ethnic group is the Pastritan, which are tribes that speak Pushtu Focus on Culture; Religion and Society Sunni choose their Imams, religious leaders, mainly to lead prayers. Shia only allow those related to Muhammad the prophet to be their Imams. Focus on Culture; Religion and Society 90% of all Muslims are Sunnis, 10% are Shia. Sunni is found anywhere Islam is practiced. Shi’ism is only found in Iran, southern Iraq, Yemen, Syria, and Lebanon. What is the difference between Sunni and Shi’ite? After the Death of Muhammad (632) – Elected the Caliph – Four were elected • Ali was the only related to Muhammad Among Arabs = More Shi’i that Sunni What is the difference between Sunni and Shi’ites? • Sunni – Believe succession was legitimate – Upheld the tradition – Keep order throughout the Muslim World – Seveners – recognized the 7th leader Isma’it – Conformity and social stability – Held political power • Shi’I – Believed Ali was the only legitimate Caliph – – – – • • • • • He was relate to Muhammad Twelvers = 12 leaders after Ali Equality, social justice, and dignity of the individual History is of persucution The Region Today Economic Development Oil and Gas Production are the main economic industries along the Persian Gulf. It is hard to farm the area because of the dry, rugged landscape. Barley and wheat are the most common crops. Economic Development Bedouins are nomadic herders that move their camels, goats, or sheep when the seasons change. Modern manufacturing is limited but focuses on building materials, food products, and other supplies. The Region Today Urban Environments • Old- narrow streets for walking, market places called bazaar, and a neighborhood mosque near the city. • New- air conditioned shopping malls, modern styled buildings, and cars are used. The Region Today Governments, Issues, and Challenges • Saudi Arabia is a vital member of OPEC (organization of Petroleum Exporting countries), which influences oil prices by controlling supply. Government, Issues, and Challenges • In 1979, Iran’s monarchy was ruled over by ayatollahs, religious leaders of the highest authority among Shia Muslims and is now a theocracy. • Iraq was dictated by Saddam Hussein, who used the country’s oil revenues to build a large military. Government, Issues, and Challenges • Under Hussein’s rule, Iraq invaded Iran in 1980 and Kuwait in 1990 wanting oil. • A group of countries led by the U.S. pushed back Iraqi forces in 1991, which was known as the Persian Gulf War. Government, Issues, and Challenges • In 2003, the U.S. led an invasion of Iraq, because of its continued resistance to • • • • • • inspections and violations of UN rules. The Iraqi forces were defeated and Saddam Hussein was captured Government, Issues, and Challenges A group called the Taliban came to power in the 1990’s and were driven by an extreme version of Sunni Islam. The U.S. and allied forces attacked terrorist camps and Taliban military targets after September 11th (because they aided the terrorists) Government, Issues, and Challenges A loyal jirga, a traditional council, with representatives from all ethnic groups was held in June 2002. Hamid Karzai was elected as Afghanistan’s president. The loyal jirga adopted a new presidential system of government with a parliament. Government, Issues, and Challenges • Now, women have more educational and economical opportunities. • As a result, population growth rates are often high and large families are common • The importance of oil in global trade has given the oil-rich countries much economic and political power • • • • • The Eastern Mediterranean Palestine and Modern Israel Zionism was established in the late 1800’s. After World War I Jews moved to Palestine. Today Jews make up 80% of Israel’s population. In 1947 the UN voted to divide Palestine into Jewish and Arab states. Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon, and Syria invaded Israel. Palestine and Modern Israel • In 1967 Israel gained land west of the Jordan River (West Bank), the Gaza Strip, and a small amount of land on the Mediterranean Coast. • Thousands of Jews have moved form the West Bank to the Gaza Strip. • Israelis took the Golan Heights from Syria in 1967. • In Israel, troops guard the Jordan River, a very important water source. Economic Development: Turkey • • • • Turkey is the second most developed industry. Earthquakes interrupt economic growth. Political Conflict is a big problem. It has modern urban factories and small sale industries. • • • • • • • • Economic Development: Israel Israel economy is based on agriculture. Israel is the most developed technological country in the Eastern Mediterranean. Polished diamonds are Israel’s leading export. Tourism is high in Bethlehem and Jerusalem for the religious sites. Economic Development: Jordan and Syria Palestinians live as refugees in Jordan. Population increase strains its resources It has an undeveloped economy and high unemployment They have a lack of resources, a weak educational system, and undeveloped technology. Urban Environments in Eastern Mediterranean • Population – The houses of the eastern Mediterranean are small and cramped because of population – Traffic congestion and smog keep getting worse each year Urban Environments in Eastern Mediterranean • Damascus , Syria – Damascus, Syria is probably the oldest city in the world Urban Environments in Eastern Mediterranean • Souks – Souks are open air markets in the Arab world – Souks are common in the older cities Urban Environments in Eastern Mediterranean • New an Old Parts of the Cities – Usually, the newer parts of the city surround the older parts – Most service oriented businesses and government offices are in the newer parts Urban Environments in Eastern Mediterranean • Beirut – Beirut has been damaged by war – Lebanon’s government has worked hard to rebuild its center – It was built into a thriving and modern commercial zone Issues and Challenges • The PLO wants Palestine to have control of the West Bank and Gaza Strip. • The Kurds say that Turkeys government treats them unfairly. • The Turkish government has limited the religious freedom of Muslims. Issues and Challenges • In 1975 the Greeks and Turks started a feud that lasted 15 years. • Overgrazing has damaged semiarid grasslands in parts of Jordan and Syria. • • • • North Africa The Arabs and Islam Under Arab rule North African cities became great canters of Islamic culture and education. Cities like Marrakech (Morocco) became centers of trade between central and western Africa, Europe, and Arabia. They grew rich trading gold, ivory, and spices as well as slaves. However in the 1500s Ottomans took control first of Egypt and then of Libya, Tunisia, and Algeria. Colonialism The Ottoman Empire ruled much of North Africa until the late 1800s. Western European powers began to take over parts of the region. Beginning in the 1830s, France moves to control Tunisia, Algeria, and part of Morocco. • Spain took control of northern Morocco. • Thousands of French, Spaniards, and Italians settled in North Africa in the decades that followed. • • • • • • • • • • • • • Colonialism In 1882 Great Britain took over Egypt. They wanted to control the Suez Canal. The canal was an important trade link between Europe and Britain’s colony of India. Italy completed the European conquest of North Africa by taking Libya from the Ottomans in 1912. Independence North Africans resented European rule. They worked for their independence. In 1922 Egypt gained limited independence from Great Britain. In 1952 a group of Egyptian military officers led a revolution that brought complete independence from Britain. Independence France granted Tunisia and Morocco their independence in 1956. The French fought a bloody war in order to hold on to Algeria. • Algeria finally won Independence in 1962. • All of the French population in Algeria left. Independence • Libya became and independent kingdom in 1951. • In 1969 military officers overthrew the monarchy. • Gadhafi (military officer) declared the country a socialist republic and adopted anti-Western policies. Culture People • Many people consider themselves Arab or Arab-Berbers • Berber- culture group that lived in North Africa before Arabs • Small group of desert nomads called Bedouins Culture Languages • Arabic is the official language (Different variations) • Colonization's outcome was many other languages. ex: French, Italian, English Culture Settlement • Many people live along The Mediterranean coast and Atlas Mountain foothills Culture Land Use • 99% of Egypt's pop. live along the Nile. • Only makes up 3% of Egypt’s land Culture Land Use • Cities are becoming overcrowded • People are coming form the countryside to work • Casablanca receives 30 thousand new migrants a year Culture The Medina • Many old cities develop inside a casbah • Casbah- protective fort Culture The Medina • As pop. grew buildings were built higher and closer. • Space was narrow and limited as possible Culture The Medina • Europeans took over and created European style homes • People didn’t abandon medinas • Many medinas still remain lively Culture Religion • Majority are Muslim except Jewish, Christian minorities • Islam is important in life Ex: 5 daily prayers, Fridays are when Muslims meet in mosques Culture Religion • Business are closed on religious holidays’ • Businesses close on Thursday and Friday and reopen on Saturday Culture Religion • Holidays are based lunar calendar • They change each year depending on the moon. Culture Traditions and Customs • Many wear traditional clothing (long, loose, ideal for hot climate) • Women's clothes cover everything except for face and hands Culture Religion • Greet by touching hands then touching heart • Families and close friends will kiss the cheek Culture Traditions and customs • Family is central in Arab culture • Celebrations are very important Ex: marriages • Celebrations can last several days Economic and Urban Environments • Many North African countries face issues of developing countries Ex: government spending, inflation down, foreign trade • Free port- no taxes are place on imported goods Economic and Urban Environments Economic Activities • Oil and natural gas are backbone to Libya, Algeria, Tunisia, Egypt High prices=benefit Low prices=weak economies Economic and Urban Environments Economic Activities • Agriculture is important to this region • Fellahin-peasant farmers in Nile river valley • They make up 40% of Egyptian workforce Economic and Urban Environments Economic Activities • Libyan imports 75% of food • Tourism is important to this region Economic and Urban Environments Economic Activities • Not enough jobs, rapid pop growth makes problems worse • Many skilled and educated leave the region Economic and Urban Environments Urban Environments • Largest city: Casablanca, Morocco • All the capitals are large too • Cities have old and new buildings • Large cities are expanding Economic and Urban Environments Urban Environments • In Cairo people set up tents • Communities are developing in cemeteries Issues And Challenges • North African countries relate to each other greatly when it comes to issues and challenges. • Two of the most important of them are poverty and political unrest. Issues and Challenges • North Africa also has similar political/social problems as Arab countries in Southwest Asia. Political Issues • Islam is very important in North Africa’s politics. • A vast number of Islamic fundamentalists want the government to be based strictly on the laws of Islam, leading the government into giving Islam a very small role. • Violence is sometimes followed when the government interrupts what fundamentalists want. Political Issues • The U.S. has been trying to help North Africa and gives much aid to Egypt. • Mu`ammar Gadhafi, of Libya, has labeled him self as a defender of Arab causes and has many anti-American policies. Political Issues • Gadhafi, later on in 2004, then agreed to open Libya to arms inspectors and has currently been trying to work his way to improving relations to the U.S. Environmental Challenges • Pollution from oil refining, desertification, and polluted water supplies are only three of the many environmental issues that North Africa faces. • The Nile River is one major concern. The Aswan High Dam (constructed in 1960) is currently used for an important source of hydroelectric power. Environmental Challenges • Even though the dam is a major energy source, it has also caused the annual flooding of the Nile to not exist anymore. Environmental Challenges • The flooding is very important because every year silt was deposited on to the banks of the Nile. • since it doesn't flood farmers fertilize it themselves. Environmental Challenges • Fertilizers have polluted the Nile. • The river is shrinking in size. • The fishing industry is slowly dying out.