File
advertisement

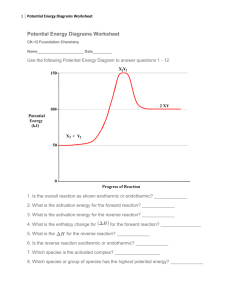
Honors Chemistry I Quarter 1 Test Objectives Be able to: Identify the appropriate separation technique for a specified mixture. Identity the differences in physical properties of a mixture’s components, allowing those components to be separated. Classify crude oil as a mixture and discuss how to separate it into its components. Identify uses of petroleum products. Interpret models of chemical, physical and nuclear changes. Define organic compounds. Write the balance chemical equation for the combustion of fuel. Apply the concept of endothermic and exothermic to chemical reactions. What does it mean to say water has a high specific heat? Interpret an energy profile for a reaction. Determine the activation energy and the heat of reaction using the energy profile diagrams. Identify reactants, products and activated complex. Understand the importance of collision in initiating reactions. Use sign convention for endothermic and exothermic. Identify diatomic gases. Use and interpret models of chemical, physical and nuclear changes. Describe all of the components of the water cycle. Discuss some important characteristics of pure water. Identify important properties that must be tested to ensure that water is potable. How do ions get in the soil? Why does salt water conduct electricity but solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity? Explain the dissociation of salt in water. What are anions and cations? Balance and interpret chemical equations. Understand Law of Conservation of matter at the level of chemical reactions. Understand subatomic structure of the atom. Know names and symbols of 40 elements listed in class. Important Terms Specific heat Heat of reaction (+/-) Sublimation as a separation Technique reactant product Physical change Chemical change Specific heat Separation Technique methane combustion Diatomic gas Activation energy Chalogens Activation energy Activated Complex Fractional distillation Crude oil Magnetic separation Distillation Extraction Centrifuging Filtration Decanting Chromatography Re-crystalization Halogens Reactant Law of conservation of mass Charcoal Filtration precipitation evaporation condensation percolation transpiration respiration Photosynthesis Alkali metals Alkaline Earth Metals Noble Gases Product