Microscope Cell Study Notes: Compound Light Microscope
advertisement

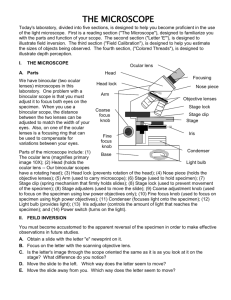
Aim: How do we study cells? MICROSCOPE I. Compound Light Microscope (optical microscope) Uses light to produce an enlarged view of object Uses 2 lenses One lens produce an enlarged image & is further magnified by the second lens Lenses cause light rays to bend producing an enlarged image Made up of 3 systems: optical, mechanical and light. Image: what we see when we use a microscope to examine an object Magnification: the ratio of image size to object size 1.Optical System: the lenses Eyepiece (ocular) Objectives: Low power objective - used to locate the region of the specimen High power objective - moved into position if further magnification is wanted 2. Mechanical System: Structural parts that hold the specimen and lenses and permit focusing of the image Base: Support the microscope Arm: Used to hold the microscope Stage: Platform on which specimen is placed Stage clips: Hold the slide in place Body tube: Holds lenses- eyepiece on top and objectives on the bottom Revolving nosepiece: Holds the objective lenses; rotates so that different objective lenses can be moved Coarse adjustment: Large knob used for approximate focusing under LOW POWER only Fine adjustment: Small knob; final focusing of low power and all focusing under high power. 3. Light System: Mirror and Substage illuminator: directs light up through the specimen Diaphragm: Regulates the amount of light reaching the specimen Total Magnification: Ocular x Objective = Total Magnification (10x) (43x) = 430x The greater the magnification, the smaller the field of vision of the specimen. RESOLUTION: Sharpness of image The ability of a microscope to show 2 points that are close together as separate images What does the microscope do to the image? It makes the image UPSIDE DOWN and REVERSED e Low Power Vs. Less detail Field is brighter Image smaller Field of view is bigger High Power More detail Field is darker Image larger Field of view is smaller