Name: AP Environmental Science Marine and Coastal Ecosystems
advertisement

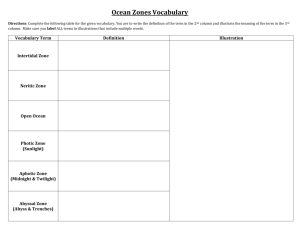
Name: _________________________ AP Environmental Science Marine and Coastal Ecosystems 26 February 2014 Chapter 16 – pp 438-444 _____ 1. In which of the following ecosystems would you find the least species diversity? a. reef b. pelagic zone c. benthic zone d. estuary e. salt marsh 2. Draw an open ocean food chain. Include organisms in at least five levels. _____ 3. True or False: All marine ecosystems rely on sunlight for energy. 4. Match the ecosystem in Column A with its description in Column B. Column A _____ rocky intertidal zone _____ salt marsh _____ estuary _____ mangroves _____ reef _____ kelp bed _____ pelagic zone _____ sandy intertidal zone Column B A. Underwater outcrop of rock, sand, or calcium carbonate upon which living things make their homes. B. Open water area between the ocean’s surface and floor C. Rocks and boulders strewn along a shoreline between the uppermost reach of the high tide and the lowest limit of the low tide. D. Broad, flat, sandy areas that form a gradual transition throughout the tidal range from high to low tide. E. Area where tides overwash gently sloping sandy or silty substrates upon which salt-tolerant grasses, rushes, or shrubs grow. F. Salt tolerant trees with unique and elaborate prop root networks that stabilize shorelines in subtropical and tropical regions. G. Partially enclosed water bodies where rivers flow into the ocean, mixing salt and fresh water. H. Dense stands of large brown algae found on continental shelves along temperate coastlines. Estuary Mangroves Salt marsh Intertidal Reef Kelp bed 5. Read each statement. In the grid, check the boxes for all of the ecosystems to which it applies. You may make more than one check mark per statement. a. Described as a “forest.” b. Location with high primary productivity. c. Protect shorelines from erosion by absorbing wave energy. d. Provide complex physical structure or habitats. e. Host tremendous biodiversity. f. Negatively affected by increasing ocean acidification. g. Associated with important fisheries. h. Provide shelter for small organisms or nursery areas for juveniles i. Threatened by coastal development. j. Considered transitional between aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. 6. What are zooxanthellae? Why are they important to corals? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Write the correct chemical reaction described to the right of the description. Description Chemical Reaction Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere reacts with ocean water to form carbonic acid. Carbonic acid dissociates into a proton and a bicarbonate ion. Protons combine with carbonate ions to form bicarbonate. Calcium carbonate shells of marine creatures dissolve into calcium ions and carbonate ions. 8. Give two pieces of evidence that suggest to scientists that coral reefs may disappear by the middle of this century if ocean acidification continues at current rates. _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. List three consequences for people, if coral reef communities collapse. i. ______________________________________________________________________ ii. _______________________________________________________________________ iii. _______________________________________________________________________