Unit 6 Vocabulary Flashcards
advertisement

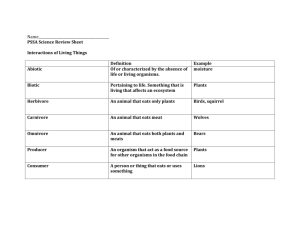
Unit 6 Vocabulary Flash Cards Ecology Biotic factor Abiotic factor Population Species Community Ecosystem Biome Habitat Niche Herbivore Producer Decomposer Consumer Living things and how they interact with other living things; ex: squirrel, tree, eagle, rabbit, groundhog, bee, worm, etc Study of how organisms interact with each other and with their environment Group of individual of the same species living in the same area at the same time; ex: cows in a field, robins in the tree, wolves in the mountains Nonliving part of the environment; ex: water, air, temperature, clouds, soil, sunlight, etc All the population of different species that live in an area; the biotic community or all the living things in that area; ex: birds in the trees, insects in the bush, dogs, cats, people, ants in the neighborhood Organisms that are closely related and can mate with each other and make fertile offspring (their babies can have babies) Large region or area that has the same climate and communities of species (plants & animals); ex: tropical rainforest, grassland, desert, ocean A community of organisms and their nonliving environment; all the biotic and abiotic in an area; all the living and nonliving things in an area; ex: ocean, field, pond, mountains, salt marsh Role a population plays in the ecosystem; how it gets food, interacts with others; ex: predator, competitor, producer, herbivore Place where organisms usually live and provides their water, shelter, food, etc Organisms that use energy, like sunlight, to make food; most do photosynthesis; also called an autotroph Type of consumer where the animal eats only plants to get energy; ex: giraffe, cow, squirrel, cricket Organism that eats or absorbs other organisms for food; can’t make their own food from energy; also called a heterotroph Organism that gets energy from breaking down the remains of other organisms; it eats dead things and breaks them down and returns the nutrients to the soil; ex: earthworm, fly, some bacteria Omnivore Carnivore Food chain Scavenger Energy pyramid Food web Third order consumer / tertiary consumer Biomass First order consumer / primary consumer Second order consumer / secondary consumer Carrying capacity Top predator or apex predator Predation Limiting factor Type of consumer where the animal eats only other animals to get energy; ex: cougar, wolf, tiger, hawk Type of consumer where the animal eats both plants and animals to get energy; ex: humans, bears, robins, foxes Type of consumer where the animal eats dead, sick, and dying organisms or steals food from other animals; it does not return the nutrients to the soil like decomposers; ex: vulture; hyena, crow Diagram that shows the path of energy transfer from producers to consumers; show the path that one piece of energy takes; usually a circle where a decomposer returns the nutrients to the soil for the producer to use again Diagram that shows the flow of energy in the ecosystem; has many different producers and consumers; shows how many different organisms eat each other to get energy Diagram that shows how energy is passed from one level to the next and is used up at each level; producers are always at the bottom with the highest level consumer at the top All the living organisms as a level in the energy pyramid; largest is at the bottom with the plants Third consumer, a carnivore, in a food chain, food web, or energy pyramid; gets about 0.1% of the energy made by the producer Second consumer, either an omnivore or carnivore, in a food chain, food web, or energy pyramid; gets less energy than the level before it; gets about 1% of the energy made by the producer First consumer, an herbivore, in a food chain, food web, or energy pyramid; gets about 10% of the energy the producer makes Last consumer in the food chain, food web, or energy pyramid; nothing but the decomposer gets its energy; gets the least amount of energy from the producer The maximum or largest number of individuals of one species that the environment can support or have enough food, shelter, water, for; when go over this limit animals and plants start to die off The biotic (living) or abiotic (nonliving) part of the environment that keeps a population size below the carrying capacity; ex: amount of water or shelter, number of predators, amount of food available, diseases, competition The relationship where one animal hunts down and eats another animal; predator eats prey Competition Cooperation Predator Prey Immigration Emigration Symbiosis Mutualism Commensalism Parasitism Parasite Host Behavior where individuals of the same species work together to get something done; ex: hunting together, watching out for predators together Behavior where two or more individuals or populations are trying to use the same limited resources, like food, water, shelter, sunlight, territory, mates An animal that is hunted down and eaten by another animal Animal that hunts, stalk, and kills another animal for food; ex: hawk, lion, wolf Behavior that happens when individuals move away from where they were currently living; individuals exit the population Behavior that happens when individuals move into a new location or territory; individuals are joining a new population Symbiotic relationship where organisms of different species work together and both are helped; ex: coral and algae, clownfish and sea anemone, sponge and brittle star A close long-term relationship between organisms in different species where at least one organism is helped Symbiotic relationship where one organism is helped and the other organism is harmed; the parasite feeds upon the host for energy; ex: tick and dog, flea and cat, leech and human Symbiotic relationship where one organism is helped and the other is not helped or harmed, it is unaffected; ex: osprey hawk and sparrow, robin and tree, shark and remora fish An organism that is fed upon by another but is not killed by it; ex: human fed on by tick; dog fed on by flea, tree fed on by mistletoe An organism that feeds upon another organism for energy but does not kill them; ex: tick, flea, leech, tapeworm, mistletoe