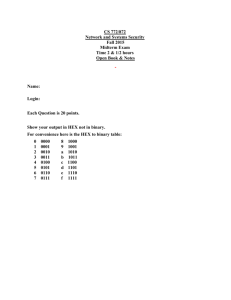
1932322Information Security and Privacy
advertisement

The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center COURSE Syllabus 4 5 6 7 8 9 Course title Course number Credit hours (theory, practical) Contact hours (theory, practical) Prerequisites/co requisites Program title Program code Awarding institution Faculty Department Information Security and Privacy 1932322 3 3 Introduction to Database Systems (1902223) Computer Information Systems 2 The University of Jordan King Abdullah II school for IT Computer Information Systems 10 Level of course Third year 11 12 Year of study and semester (s) Final Qualification Other department (s) involved in teaching the course 2014/2015 Second Semester B.Sc. 14 Language of Instruction English 15 16 Date of production/revision Required/ Elective 5/2015 Required 1 2 3 13 - 17. Course Coordinator: Loai Alnemer Office Hours: Sun- Wed 9-10, Phone Number: 22613 E-mail: l.nemer@ju.edu.jo 18. Other instructors: Office numbers, office hours, phone numbers, and email addresses should be listed. 19. Course Description: As stated in the approved study plan. Identify a range of methods, techniques and current issues of security and privacy problems associated with the use of CISs; Cryptology: Encryption and decryption, Steganography, Security models, Ways to minimize risks and losses, Apply the information security methods and management to the development and management of information system security within an organization, User Identification / Authentication, Digital Signature, Applications. 20. Course aims and outcomes: A- Aims: B- Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs): Upon successful completion of this course students will be able to … A1) Understand the meaning of information security. A2) Understand security threats, Security models, and building security functions. A3) Understand the Public key cryptography schema. A4) Understand the private key cryptography schema. A5) Understand the cryptographic hash functions. A6) Understand the steganography, watermarking and information hiding. A7) Understand database security B1) Distinguish between different security models. B2) Distinguish between public key and private key cryptography B3) Explain some classical encryption methods. B4) Explain the Hash functions, cryptographic hash functions with applied examples. B5) Distinguish between different information hiding schema. C- Subject specific skills- with ability to … C1) analyze simple mathematical formulae. C2) Analyze some computational aspects related to public cryptography schema. C3) Analyze some computational aspects related to Private cryptography schema. 21. Topic Outline and Schedule: Topic Week Instructor Achieved ILOs Evaluation Methods Overview Introduction to data security, attacks, services, Security models, Cryptology, and digital signature 1,2 Loai Alnemer A1,A2,B1 Homework Reference chapter 1 Cryptology Introduction to Cryptology Privacy, authenticity and integrity Keys Background on functions and Number Theory Symmetric Ciphers Symmetric cipher model, Caesar cipher, Monoalphabatic cipher, Polyalphabatic cipher, Vigenere Cipher, Transposition Cipher and ROTOR Machines Block Ciphers Playfair cipher, Hill cipher, Affine cipher and DES. Advanced Encryption Standard Key creation, Encryption, Decryption, and 3DES PSEUDORAND OM NUMBER GENERATION AND STREAM CIPHERS Public key encryption RSA cipher and 3 A3, B2,B3, C2, D1 Homework A3,B3,C2,D2 Quiz + Homework attendance, Discussion, handouts Loai Alnemer 4,5 6,7 8 Loai Alnemer Loai Alnemer Loai Alnemer A3,B3,C2,D2 A3,B3,C2,D2 9 A4,B3,C3,D2 10 A4,B3,C3,D2 Quiz + Homework Homework Chapters 4,7 attendance, discussion, reading: handout , Chapter 7 attendance, discussion, reading: handout , Chapter 9 others Project assignment Hashing Hash function, One-way functions,SHA1, MDs and Digital Signature INFORMATIO N HIDING Steganography, Watermarking, Text Hiding. DATABASE SECURITY AND WEB SECURITY SQL INJECTION, DATA ENCRYPTION, HTTPS, SSL, OTHERS Project Discussion 11,12 A5, B4, D3 13,14 A6,B5,C4,D2, D3 15 A7 16 D4 22. Teaching Methods and Assignments: Development of ILOs is promoted through the following teaching and learning methods: 23. Evaluation Methods and Course Requirements: Opportunities to demonstrate achievement of the ILOs are provided through the following assessment methods and requirements: Quizzes and homeworks through the semester. Midterm exam , Project and Final exam 24. Course Policies: A- Attendance policies: Students are allowed up to 7 absences. If you exceed this number, you will fail the class. B- Absences from exams and handing in assignments on time: All projects and assignments are to be uploaded to the course website. -mail and Moodle regularly. Students are responsible for information posted there. If critical information is posted in Moodle that you must read today, an announcement to check elearning will be sent to the mailing list. C- Health and safety procedures: D- Honesty policy regarding cheating, plagiarism, misbehavior: Discussion of the concepts and principles between students is fine and very welcomed. Also, students are allowed to debug each other’s code. However, Student cooperation should not result in identical or near identical answers/code/documentation. ALL THE MATERIAL SUBMITTED FOR GRADING MUST BE YOUR OWN EFFORT. If this policy is violated then the following steps may be taken: (1) reduction of points by dividing by the number of students involved in an incident, (2) assignment of a grade of ZERO for all students involved in an incident. E- Grading policy: Midterm Exam 30% Quizzes and assignments 10% Project 10% Final Exam 50% F- Available university services that support achievement in the course: 25. Required equipment: None 26. References: Required book (s), assigned reading and audio-visuals: Alfred Menezes, Paul van Oorschot and Scott Vanstone, Handbook of Applied Cryptography, CRC Press, 2001. ISBN: 0-8493-8523-7. Published online free for personal usage as per the copyright notice. Available online at http://www.cacr.math.uwaterloo.ca/hac/ Recommended books, materials, and media: The following books are recommended for the student who wants more material in algebra and number theory: 1. Wenbo Mao, Modern Cryptography: Theory and Practice. Prentice Hall 2004. 3. V. Shoup. A Computational Introduction to Number Theory and Algebra. An excellent source, written with Cryptographic applications in mind. Available online: http://www.shoup.net/ntb/ntb-v1.pdf 4. D. Anglian: Lecture Notes on the Complexity of Some Problems in Number Theory. L.N. Childs: A Concrete Introduction to Higher Algebra. 5. Ingemar J. Cox, Matthew L. Miller, Jeffrey A. Bloom, Digital watermarking, Morgan Kaufmann, 2002 27. Additional information: None Name of Course Coordinator: -------------------Signature: ------------------------- Date: ------------------------ Head of curriculum committee/Department: ------------------------- Signature: -------------------------------Head of Department: ------------------------- Signature: --------------------------------Head of curriculum committee/Faculty: ------------------------- Signature: -------------------------------Dean: ------------------------------------------- -Signature: --------------------------------- Copy to: Head of Department Assistant Dean for Quality Assurance Course File