pmic7952-sup-0002-FigureS1
advertisement

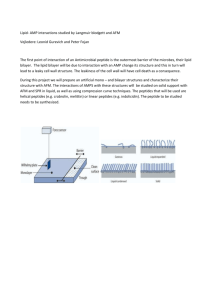
Supporting information Proteinase K improves quantitative acylation studies Benjamin Fränzel1, Frank Fischer2, Clemens Steegborn2, Dirk Andreas Wolters1* 1 Dept. of Analytical Chemistry, Biomolecular Mass Spectrometry, Institute of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Ruhr-Universität Bochum, 44801 Bochum Dept. Biochemistry, NW I, University of Bayreuth, 95447 Bayreuth *Corresponding author: Dirk A. Wolters Department of Analytical Chemistry Biomolecular Mass Spectrometry Ruhr University Bochum NC 4/72 Universitaetsstr. 150 44801 Bochum, Germany Tel + 49 (0) 234/32-25463 Fax + 49 (0) 234/32-14742 Email Dirk.Wolters@ruhr-uni-bochum.de METHODS Chemicals Ammonium bicarbonate (AmBic), ammonium carbonate, ammonium hydroxide, ammonium sulphate, ammonium acetate, formic acid (FA), trifluoric acid (TFA), hydrochloric acid, methanol, and HPLC grade acetonitrile (ACN) were purchased from Mallinckrodt Baker (Deventer, The Netherlands). Sequencing grade trypsin was procured from Promega (Madison, WI). Modified sequencing grade chymotrypsin was purchased from Princeton Separations INC. (Adelphia, NJ). Proteinase K was acquired from Roche Diagnostics (Mannheim, Germany). Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) was obtained from PAN-Biotech (Aidenbach, Germany). Histones, compounds for phosphate buffered saline (PBS), and TWEEN20 were from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Gallen, Switzerland) and anti acetyl-lysine antibodies were obtained from Immunechem (Burnaby, Canada). Stable isotope labeled amino acids were purchased from Silantes (Munich, Germany). Growth and Cell Lysis of HEK293 HEK293 were cultivated in 75 cm² cultivation flasks at 37°C in DMEM medium for at least 5 doubling times. Cells were harvested by centrifugation at 5,000 x g for 10 min, washed once with PBS buffer and re-suspended in PBS lysis buffer with 0.1 mL protease inhibitors (Sigma Aldrich, Germany). Sonification was used to disrupt the cells. Cell debris was removed at 500 x g for 10 min and discarded. Subsequently, proteins were precipitated in 80% acetone. At least three technical replicates were scrutinized for each experiment. For SILAC experiments, 13C-lysine and 13C/15N-arginine were utilized. Thereby, wild type was compared with a Sirtuin isoform 5 overexpressor cell line, kindly provided by Marcia Haigis (Harvard Medical School). This cell line was cultivated on heavy SILAC medium, whereas wild type was cultivated on light SILAC medium, respectively. Digestion Conditions For optimization of the digestion condition, test analyses were conducted with 1 mg purified histones (H1.1, H2A, H3.1, H3.3 and H4.1) from calf (Sigma) for each test, which were outlined in triplicates. LC-MS/MS experiments used linear increasing ACN-gradients over 90 minutes. Three technical replicates were analysed from each fraction. To 100 μg protein amount sequencing grade trypsin and chymotrypsin (1:50 w/w) were supplied in 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate buffer. The preparation was incubated at 37°C overnight, centrifuged at 15,000 x g and finally diluted in water and 0.1% formic acid. Proteinase K digestion was performed in 100 mM ammonium carbonate buffer for 1 hour at room temperature 1:100 w/w). Afterwards, digestion was stopped with 0.1% TFA and solvent was evaporated. For the direct analysis 100 μg whole cell proteins were precipitated with acetone and incubated in 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate buffer plus 20% methanol using sequencing grade trypsin (1:50 w/w) overnight at 37°C. After centrifugation at 15,000 x g peptides were finally diluted in water and 0.1% formic acid. Enrichment of Acetylated Peptides For enrichment of acetylated peptides, agarose coupled anti acetyl-lysine antibodies were used according to the supplier’s manual. Briefly, 20 µL agarose antibodies were washed with PBST buffer (PBS containing 0.02% TWEEN20). Binding of acetylated peptides from 1 mg protein mixture was achieved in 2 hours at room temperature. Subsequently, antibodies were washed and bound peptides were finally eluted using 0.5 N hydrochloric acid. For SILAC analysis, 1 mg of HEK cell lysate from wt and Sirt-5 overexpressor cells were each added to 100 mM ammonium carbonate buffer and 10 µg proteinase for 1 hour at room temperature. Afterwards, digestion was stopped with 0.1% TFA and solvent was evaporated. LC-MS/MS and MudPIT Analysis A quaternary Accela U-HPLC pump was connected to a Thermo LTQ Orbitrap Velos from Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (Waltham, MA) ion trap mass spectrometer. The digested samples were loaded onto a biphasic micro-capillary pre-column (diameter = 100 μm), which was equipped with an in-house manufactured frit, 5 cm strong cation exchange SCX material (Phenomenex, Germany) and with 5 cm of Luna C18 RP material (Phenomenex, Germany). The main chromatographic column was packed with 45 cm of Luna C18 RP material (Phenomenex, Germany) and held in a thermo-stated metal block at 45°C. The two columns were connected with a PEEK union. The joined columns were connected to a PEEK microcross to split the flow of the HPLC pump to an effective flow rate of 150 – 250 nL/ min and supply a spray voltage of 1.8 kV. The LTQ Orbitrap Velos was operated using instrument method files in the Sequence Setup window of Xcalibur. The heated desolvation capillary was set to 200°C. For a 10 step MudPIT experiment, each step was represented by one instrument method file with identical settings except for the gradient program for the HPLC pump. The instrument method files of the LTQ Orbitrap were set to detect a full MS scan between 400 and 2000 m/z for the precursor ion (resolution = 60,000) followed by full MS/MS scans of the top 20 ions from the preceding MS scan to detect fragment ions by the ion trap. Data Analysis To interpret MS/MS data we used the SEQUEST algorithm implemented in Proteome Discoverer 1.2. Data were searched against a Uniprot human database (2007) containing 17,482 protein entries. All accepted results had a false discovery rate (FDR) of 0.8 and lower determined by decoy database search. Singly, doubly, and triply charged peptides had a cross-correlation score (XCorr) above 1.8, 2.5 or 3.5. Furthermore, mass accuracy was set to 10 ppm and the oxidation of methionine was admitted as variable peptide modification. Additionally, the RSp value was set to 1. A protein was considered as present in the mixture when two or more unique peptides were identified by the previous criteria. For acetylation studies, acetylated lysine was set as variable modification. Unspecific database searches (no enzyme specification) for large datasets were performed using the SEQUEST algorithm implemented in the multi-thread compatible search engine ProLuCID. Protein quantification was performed using the ProRata 1.0 algorithm. We reported earlier how we performed the quantification using the ProRata algorithm (Fränzel B, Fischer F, Trötschel C, Poetsch A, Wolters D (2009) The two-phase partitioning system--a powerful technique to purify integral membrane proteins of Corynebacterium glutamicum for quantitative shotgun analysis. Proteomics 9(8):2263–2272). Briefly, the minimum log2 ratio was set to -7 the maximum log2 ratio to 7, respectively. Each protein was quantified by at least two different peptides and the left peak shift and the right peak shift were set to zero scans. We considered a protein as significantly regulated at a log2 value of at least 1 and -1 respectively. From four biological replicates at least two had to show regulation by the previous criteria to ascertain significance. a) b) c) Figure S1: The elution profile of peptides shown in Figure 4 of the main text are displayed. Light and heavy peptides are eluting simultaneously. Sequence Log2R Log2SNR Validity a)Y.SLKNQIGDKEKLGGK#L 2.17067 2.85496 true b)L.KNQIGDKEKLGGK#L.S 0 0 false c)L.KNQIGDKEKLGGK#LS.S 2.12134 2.13646 true