Name Period ______ Date Chapter 8 (sections 1
advertisement

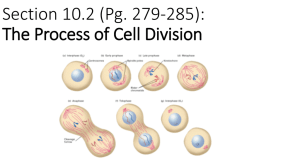
Name ________________________________________________ Period ___________ Date _______________________ Chapter 8 (sections 1-2) – Study Guide 1. What is the role of histones in the cell? Proteins that DNA wraps around tightly to make the chromosome shape. 2. Explain the difference between chromatids and chromosomes. Chromatids are halves of a chromosome. Chromosomes are made of two identical sister chromatids. 3. What is the difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes chromosomes? Prokaryotes have a faster replication process. Their chromosomes are circular. Eukaryotes have linear chromosomes. (Bacteria have 1 chromosome and humans have 46) 4. What is binary fission? The process of replication in bacteria. This is an asexual process. 5. What are the stages of the cell cycle in order? Interphase Mitosis Cytokinesis (Mitosis: prophase metaphase anaphase telophase) 6. What are the end products of the cell cycle? Two identical daughter cells 7. What is the advantage of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction? Sexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically different and allows for new babies to be able to adapt to new environments. 8. What happens during the three stages of interphase? During interphase, the cell is growing to mature size, DNA is copied, and the organelles are copied. G1: growth S: DNA replication G2: more growth, organelle repliecation 9. What do cyclins do? Cyclins check the cell for mutation and regulate the cell cycle. 10. What is the importance of chromosomes during cell division? Chromosomes hold the genetic information for the cell (DNA). Without chromosomes the new cells would not have genetic information or know what to do. 11. What do cancer cells look like? What can they develop into? Cancer cells have little cytoplasm, multiple or large nuclei, coarse chromatin and grow uncontrollably. A mass of cancer cells can develop into a tumor. 12. Fill in the follow tables. Stage of cell What’s happening? cycle Interphase Prophase Cell grows, DNA copied, organelles replicated Nucleus disappears, chromatin coils up into chromosomes Metaphase Chromosomes line up in the MIDDLE of cell Anaphase Chromatids are pulled to opposite poles (pulled APART) What cell looks like Telophase Cell begins to split into two, nuclei reappear, chromosomes break down into chromatin Plant: cell plate begins to form and a cell wall forms and cytoplasm splits equally Cytokinesis Animal: cell membrane pinches to create a cleavage furrow and cytoplasm splits equally