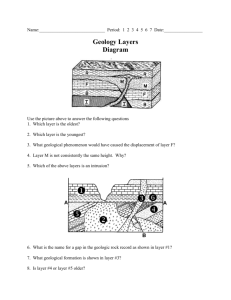
geological crust
advertisement

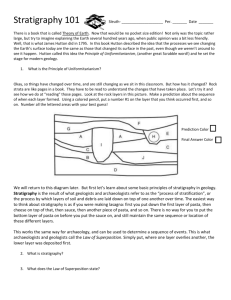
Unit 1- Earth Systems and Resources AP Environmental Science AIM: How have stratigraphy and radiometric dating been used to construct the geological time scale? Stratigraphy: • Stratigraphy- branch of geology that studies ______________________________________________ Rules of Stratification: 1) Rock layers (_________________) are laid down in ______________________________with each strata representing a “slice” of time 2) The principle of superposition- younger layers are on _________, older layers are on ____________________ Geology: • The _______________________________ of life on earth is captured in the rock layers of earth • The fossil record is our greatest source of information about the ____________________________ of life on earth The History of Earth: Using fossil evidence and the concepts of _________________________________, Earth’s history has been organized into various units according to _______________________________ that took place in each period. This is called the __________________________________________ • Earth’s history has been divided into 4 major ____________ which are furthers categorized into _________________________ Earth’s Eras: • ____________________________ Era • ____________________________ Era • _____________________________ Era • _____________________________ Era TODAY: • Today, we are in the _____________________ Era, in the ______________________________Period • Cenozoic Era (_________ mya)- begins after extinction of ___________________________; characterized by the evolution and diversification of ___________________________ • Quaternary Period (____________mya) - _____________________, evolution of _____________________ History of Earth: Scientists estimate that Earth is ___________________________ years old ______________________________ Dating- decay of radioactive elements in rocks are quantified to determine age in years __________________________________- rules of _____________________________________ to identify a chronological series of evolutionary and geological events ____________________ evidence Strata are laid down in succession For any given strata, the rock layer above is younger, the rock layer below is older. __________________________________- radioactive decay of elements in rock to determine age in years “_____________________________ dating” Earth Structure: 3 Major layers of Earth Crust- _____________________________ layer of earth o _____________________________Crust- 20-30 miles o Oceanic Crust- 7 miles o Rocky and brittle, and can fracture in earth quakes Mantle o Composed of iron, magnesium, aluminum, and silicates o Mostly solid, but the uppermost portion is more “______________________________” Core o _______________________ of the earth o Mosly iron Outer core = solid Inner core = liquid HOMEWORK: 1. What are strata in geology? 2. How are strata aged relatively? 3. What evidence can be obtained from rock layers? 4. What do we call the timeline of Earth’s history that has been constructed by scientists? 5. How have scientists organized this timeline? 6. What are the 4 major Eras? 7. What are eras categorized into? 8. How are eras and periods characterized? 9. What era do we currently live in? 10. What events characterize the Quaternary Period? 11. How old is earth? 12. What technique has science used to determine the absolute age of geological events? 13. What are the 3 layers of the Earth? 14. Which layer is thicker- oceanic crust or continental crust? 15. How does the mantle vary in property? Vocabulary- strata, stratification, Geologic Time Scale, era, period, radiometric dating, absolute age, relative age, crust, mantle, core