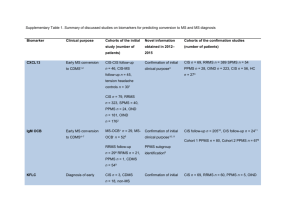
Supplementary Table 4: Summary of discussed studies on
advertisement

Supplementary Table 4: Summary of discussed studies on biomarkers for treatment response in the period 2012–2015 Blood biomarker Clinical purpose Cohorts of the Novel information Cohort initial studies obtained in 2012– confirmation (diagnosis and 2015 studies (number of number of patients) Anti-IFNβ Nab Response to IFNβ1 Numerous studies, Remarks patients) Numerous studies, RRMS n = 1642 2773 reviewed by Polman lack novelty to RRMS n = et al.1 previous published RRMS n = 1184 work IFNβ-Abs are early predictors Nab MxA miRNA correlated to disability progression in IFNβ treatment Antibody dissociation rates predict persistence of antiIFNβ-1b Nab Anti-natalizumab Response to (Nab) natalizumab5 IL-17F Response to IFNβ8 RRMS n = 6255 RRMS n = 268 Confirmation of initial RRMS n = 736 clinical purpose6,7 RRMS n = 1,3797 Initial findings RRMS n = 2399 confirmed only for very high levels9 miRNA Response to IFNβ Initial clinical RRMS n = 610 purpose10,11 RRMS n = 6011 Anti-JCV antibodies Predicting risk of PML n = 54 and non- Confirmation of initial PML n = 71 PML PML12 PML n = 5,89612 clinical purpose13 and non-PML n = 2,52213 L-selectin-expressing Predicting risk of PML n = 16 Initial clinical CD4+ T cells PML Non-PML n = 28914 purpose Lipid-specific IgM Predicting risk of PML n = 24 Initial clinical oligoclonal bands PML Non-PML n = 34315 purpose Abbreviations: IF-17F; interleukin 17F, IFNβ; interferon-beta, IgM, immunoglobulin M, JCV; John Cunnigham virus, miRNA; microRNA, Nab; neutralizing antibody, MxA; myxovirus-induced protein A, non-PML; patients without progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, PML; progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy RRMS; relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. 1. Polman, C. H. et al. Recommendations for clinical use of data on neutralising antibodies to interferon-beta therapy in multiple sclerosis. Lancet. Neurol. 9, 740–50 (2010). 2. Hegen, H. et al. Early detection of neutralizing antibodies to interferon-beta in multiple sclerosis patients: binding antibodies predict neutralizing antibody development. Mult. Scler. J. 20, 577–587 (2013). 3. Gibbs, E., Karim, M. E. & Oger, J. Antibody dissociation rates are predictive of neutralizing antibody (NAb) course: A comparison of interferon beta-1btreated patients with transient versus sustained NAbs. Clin. Immunol. 157, 91–101 (2014). 4. Serana, F. et al. MxA mRNA quantification and disability progression in interferon beta-treated multiple sclerosis patients. PLoS One 9, e94794 (2014). 5. Calabresi, P. a et al. The incidence and significance of anti-natalizumab antibodies. Neurology 69, 1391–1403 (2007). 6. Vennegoor, A. et al. Clinical relevance of serum natalizumab concentration and anti-natalizumab antibodies in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 19, 593– 600 (2013). 7. Lundkvist, M. et al. Characterization of anti-natalizumab antibodies in multiple sclerosis patients. Mult. Scler. 19, 757–64 (2013). 8. Axtell, R. C. et al. T helper type 1 and 17 cells determine efficacy of interferon-beta in multiple sclerosis and experimental encephalomyelitis. Nat. Med. 16, 406–12 (2010). 9. Hartung, H.-P. et al. Interleukin 17F level and interferon β response in patients with multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. 70, 1017–21 (2013). 10. Hecker, M. et al. MicroRNA expression changes during interferon-beta treatment in the peripheral blood of multiple sclerosis patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14, 16087–110 (2013). 11. De Felice, B. et al. Small non-coding RNA signature in multiple sclerosis patients after treatment with interferon-β. BMC Med. Genomics 7, 26 (2014). 12. Bloomgren, G. et al. Risk of natalizumab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 366, 1870–80 (2012). 13. Plavina, T. et al. Anti-JC virus antibody levels in serum or plasma further define risk of natalizumab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Ann. Neurol. 76, 802–12 (2014). 14. Schwab, N. et al. L-selectin is a possible biomarker for individual PML risk in natalizumab-treated MS patients. Neurology 81, 865–71 (2013). 15. Villar, L. M. et al. lipid-specific IgM bands in csf associated with a reduced risk of developing pml during treatment with natalizumab. Ann. Neurol. 77, 447–57 (2015).