Sc 8 Unit 1 Ch 1 - St John Brebeuf
advertisement

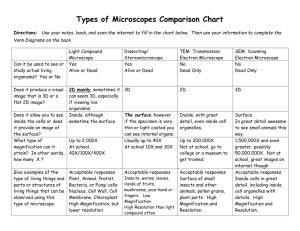
Science 8 Unit 1 Pack: Name__________________ Section 1.1: Observing Living Things Living things have characteristics that help them survive in their environment Small organisms can observed with the help of microscopes Words to Know ____ compound light microscope Definition A. produces realistic three-dimensional images using an electron beam B. this device uses two lenses to magnify an image ____ resolving power C. obtained by multiplying the magnifications of the objective and eyepiece lenses D. the ability to distinguish between dots or objects that are very close together ____ magnification power What are the characteristics of living things? Include examples for each. E. image produced by a scanning electron microscope 1. 4. 2. 5. 3. Explain how an animal might show each of the 5 characteristics of living things. Give an example for each. 1. 4. 2. Explain how a plant might show each of the 5 characteristics of living things. Give an example. 3. 5. 1. 4. 2. 3. 5. Name the parts of a compound light microscope. Give their function, too. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Using a math equation, show how you would calculate different magnifications of a compound light microscope. 1. Low= 2. Medium= 3. High= Name________________ _ Label the following parts of a compound light microscope. CALCULATING MAGNIFICATION A magnifying lens that magnifies the size of an image by 10 times has a magnification of 10. A compound microscope uses two lenses to create higher magnifications. To calculate the total magnification of a compound microscope, multiply the magnification of the eyepiece by the magnification of the objective lens. 1. What is the magnification of a microscope with two lenses that each enlarges an image by 10? ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. An eyepiece on a microscope has a magnification of 10. The objective lenses on the microscope have magnifications of 4 at low power, 10 at medium power, and 40 at high power. (a) Using the information how would you combine lenses on a microscope if you wanted to magnify an object 40? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ (b) How would you combine lenses if you wanted to magnify an object 100? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ (c) How would you combine lenses if you wanted to magnify an object 400? ___________________________________________________________________________ 3. If a compound microscope has an eyepiece of 15 magnification and you select an objective lens with a power of 40, what is the total magnification of the object? ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. Fill in the blanks within the brackets to express total magnification as a word equation. Total magnification = (___________) (___________) Section 1.2: Cells Pages ________ Cell theory states that the cell is the basic unit of life. Each cell structure and organelle carries out a specific task to help support the life functions of a cell. Cells are divided into two groups, prokaryotic and eukaryotic Cell Organelles Name vacuole organelle bacteria cell membrane nucleus cytoplasm mitochondria What are three differences between viruses and bacteria? Structure (Description/Location) Function (What it Does) What are the main differences between plant and animal cells? 1. 2. 3. What are the main parts of Cell Theory? Describe an example for each. 1. 2. 3. This is a(n) ___________ cell. This is a(n) ___________ cell. Section 1.3: Diffusion, Osmosis, and the Cell Membrane Pages ________ Diffusion is the movement of particles from high to low concentration Selectively permeable membranes control the movement of particles into and out of cells Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane Words to Know Definition ____ concentration A. movement of water particles through a selectively permeable membrane ____ selectively permeable membrane B. the amount of substance in a given space ____ osmosis C. particles move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration ____ diffusion D. allows some materials to pass but keeps other materials out Describe how particles move due to diffusion. 1. Describe how selectively permeable 1. membranes can control the movement of particles. Include a drawing. Give three examples of osmosis involving the movement of water into and out of cells. Use labeled diagrams to help you. 1. 2. Hint: 3.