Projectile Motion (AP)
advertisement
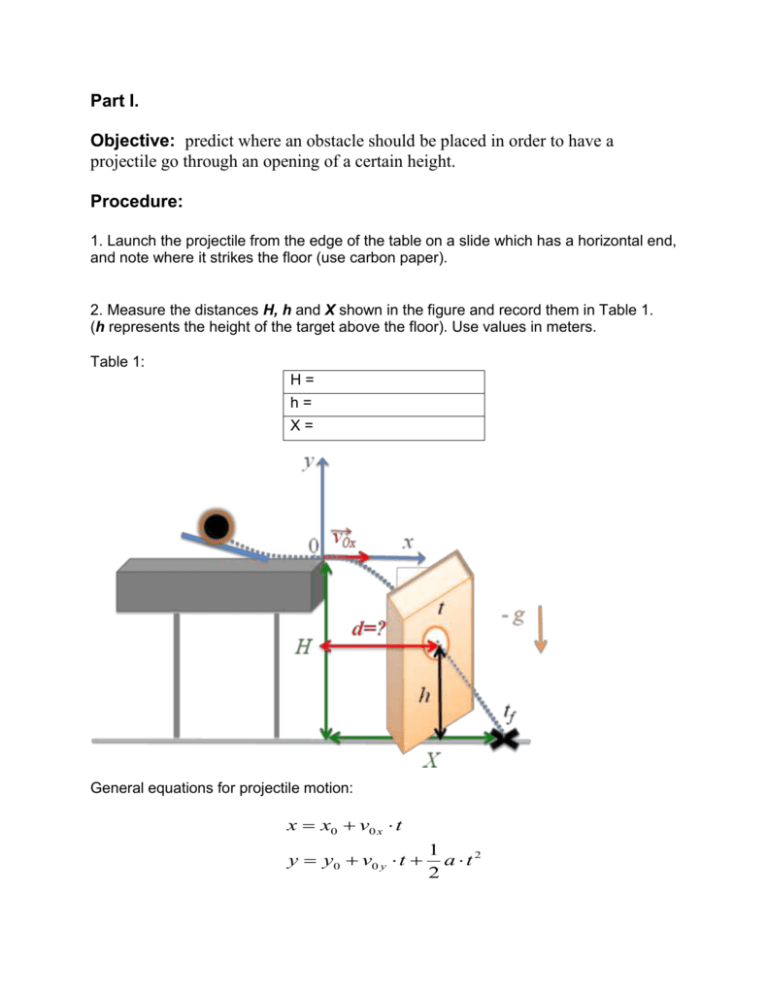
Part I. Objective: predict where an obstacle should be placed in order to have a projectile go through an opening of a certain height. Procedure: 1. Launch the projectile from the edge of the table on a slide which has a horizontal end, and note where it strikes the floor (use carbon paper). 2. Measure the distances H, h and X shown in the figure and record them in Table 1. (h represents the height of the target above the floor). Use values in meters. Table 1: H= h= X= General equations for projectile motion: x x0 v0 x t y y0 v0 y t 1 a t2 2 At time tf on projectile trajectory: 3. Using your measured values of X and H, calculate tf. 4. Using your calculated value of tf, and measured value of X, calculate vox. At time t on projectile trajectory: 5. Using your measured values of h and H, calculate time t. 6. Using your calculated values of t and vox, calculate the distance d where the target should be placed for the projectile to go through the opening. Part II. Objective: calculate where the projectile will strike the floor when slide is at an angle Procedure: 1. Launch the projectile from the edge of the table on a slide which has an end set at an angle. 2. Measure the angle of projection in degrees. 3. Measure the distances H, d shown in the figure and record them in Table 2. Use carbon paper on the small table and input values in meters. Table 2: H= d= = At time t on projectile trajectory: 5. Use your measured values of d and . Substitute t as a function of distance d, vo and angle from the x-direction equation into the y-direction equation and calculate vo. At time tf on projectile trajectory: 6. Using your measured value of H and the calculated value of vo, calculate time tf when the projectile will strike the floor. 7. Using your measured value of and the calculated values of vo and tf, calculate the distance X where the projectile strikes the floor. 8. Measure distance X where the projectile strikes the floor also experimentally by removing the small table (use carbon paper). Compute % difference between theoretical and experimental values of X.