The Properties: Commutative: a + b = b + a ab = ba Associative: (a +
advertisement

The Properties:
Commutative: a + b = b + a ab = ba
Distributive: a(b + c) = ab + bc
1
Multiplicative Inverse: a i
= 1
a
Multiplicative Identity: a i 1 = a
Associative: (a + b) + c = a + (b + c) (ab)c = a(bc)
Additive Inverse: a + – a = 0
Additive Identity: a + 0 = a
Coordinate Geometry and Functions
Linear – Line
Quadratic – U-shape
Exponential – One direction rising, other direction flattening out
Absolute Value – V-shape
-b
Equation of axis of symmetry: x =
2a
Vertex of a parabola is the turning point
In parabola y = ax2 + bx + c, as |a| gets larger the parabola gets narrower
The graph of a function passes the vertical line test.
A function has one y-value for each x value (for example (3, 4) and (3, 6) is not a function)
Equation of a line: y = mx + b (m = slope, b = y-intercept)
y -y
+ up - down
Slope Formula: 2 1
x2 - x1 + right - left
Horizontal Line: equation is y = a constant, slope = 0
Vertical Line: equation is x = a constant, slope is undefined
Parallel lines have equal slopes. Perpendicular lines have negative reciprocal slopes.
Roots: Solution(s) to a quadratic equation. Identified on a parabola as the x-intercepts
For graphing an inequality: Solid lines: £ ³ Dotted lines: < >
Label your graphs.
Draw arrows
Label your axes
Formulas:
Area of a circle: A = πr2
Remember to divide by 2 for half circles
Volume of a cylinder: V = πr2h
Circumference of a circle: C = πd
Area of a trapezoid: A = 12 (b1 + b2 )h
Rate Time = Distance
Exponent Rules:
3a2 i 5a 4 = 15a6
(2a2 )4 = 16a 8
12a 8
= 4a 6
2
3a
a0 = 1
a -2 =
1
a2
The Graphing Calculator
Use y = and TABLE to find the table for your parabola
To enter data go to STAT, EDIT
To graph a scatter plot or box and whisker plot go to STATPLOT then turn ON then select the
appropriate graph.
When graphing a STATPLOT use ZOOM 9 (clear any y = equation)
When graphing a y = equation use ZOOM 6 (turn your STATPLOT off)
For equation of the line of best fit go to STAT, CALC, 4, ENTER
Make sure the calculator is in DEGREE MODE (press MODE then DEGREE)
For absolute value go to MATH, NUM
The negative sign and the subtraction sign are different keys. You may get an error message if you
use the incorrect one.
A fraction is undefined when the denominator equals 0.
A set is closed under a particular operation when only the elements of the set can be obtained.
For example: {whole numbers} is closed under addition (2 + 5 = 7, 7 is a whole number) but
{whole numbers} is not closed under subtraction (2 – 5 = –3, –3 is not a whole number).
Relative Error:
measured - actual
actual
“At least”: ³ “At most”: £
Probability
Empirical probability – Based on Experimental Data. Theoretical Probability – Based calculation
Probability of independent events A and B = Probability of A multiplied by Probability of B
8P3 = 876
5! = 54321
Exponential Growth: (Initial Value)(1 + r)t
Exponential Decay: (Initial Value)(1 – r)t
r is percentage rate expressed as a decimal. t is the number o years.
Interval Notation [a, b): Includes all numbers between a and b. Includes a, does not include b
Sets
Union (A B): All elements of A and B combined.
Intersection (A B): All elements of A and B that they have in common (overlap).
Complement of a subset (A’ or Ac): All elements from the original set but not in the subset.
Statistics
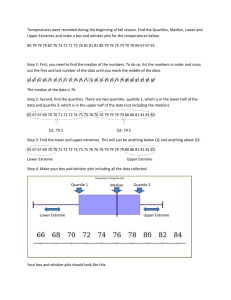
If there is an outlier, the median is the best measure of central tendency
Quantitative Data: Deals with numbers.
Qualitative Data: Non-numerical (favorite color, for example).
Univariate Data: One set of data.
Bivariate Data: Two sets of data being compared.
Box and Whisker:
lowest
1st quartile
25th %-tile
lower quartile
2nd quartile
50th %-tile
median
3rd quartile
75th %-tile
upper quartile
highest
Each interval represents 25% of the data.
Calculate the lower and upper quartiles by finding the median of the lower and
upper half of the data (not including the median). Also, you can identify these data
points using your graphing calculator using the TRACE function.
Stem and Leaf Plot: 4| 3 means 43.
Histograms: Bars must be adjacent. Intervals must be even.
Remember all titles and labels
Correlation: Positive – both go up or both go down. Negative – One goes up the other goes down.
Causal relationships: One variable changes because of the other.
Trigonometry:
Make sure the calculator is in DEGREE MODE (press MODE then DEGREE)
opposite
adjacent
opposite
Cos A =
Tan A =
hypotenuse
hypotenuse
adjacent
2
2
Sin A = ------ m < A = Sin-1 ( )
3
3
Sin A =
angle of elevation
Numbers
1 is neither prime nor composite
Natural Numbers: {1, 2, 3, 4, …}
Whole Numbers: {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, …}
Integers: {…–3, –2, –1, 0, 1, 2, 3, …}
Rational Numbers include all integers, fractions and repeating and terminating decimals.
Irrational Numbers { π, 3 , non-repeating, non-terminating decimals}
Foil/Factoring/Solving Quadratic Equations
Always remember to GCF factor first.
The difference of two perfect squares factor into conjugates: a2 – b2 = (a +b)(a – b)
Simplify algebraic fractions by factor and cancel.
(a + b)2 = (a + b)(a +b). Use FOIL.
Set a quadratic equation equal to zero before you factor.
General Tips:
You have plenty of time. 3 hours!! Don’t race through and make careless errors. Do each
question more than once.
Multiple Choice: Sometimes choices look similar. Choose carefully. The test makers anticipate
common errors and make them choices. Rework problems. Check your work constantly.
Parts II, III and IV: Show all work! Include units and follow instructions as to rounding.
Remember to label. Check your work. Read longer word problems several times. Underline.
Answer the question being asked. Check your work carefully.