Rayan Ghamri
advertisement

Rayan Ghamri
100837786
LSB based Steganography
Advanced security design CS 691
Semester Project
Dr.Edward Chow
Univsersity of Colorado at Colorado Springs.
Summer 2011
Overview
From time immemorial, people organized the need to pass the information from one
person to another while keeping that information unknown or as a secret to enemies.
Since then there was a need for the information to be secured and hidden. And that
what is securing all about.
Today there are computers and Internet, which means there is information and it needs
to be transmitted from one person to another but without getting stolen or reviled.
When we want to send some information to a person we use cryptography so the
message always encrypted and when it gets to the receiver it gets decrypted. It’s a
simple idea but too hard to implement. Also, sometimes when someone gets the
ciphertext they might get the plaintext after trying so hard to get it. But what if we had
used something no one can detect something we always send to each other’s.
Something will not attract any attention, such as an image, video or even a song by The
Beatles. This was the beginning of Steganography.
Definition
Steganography comes from the Greek words Steganós (Covered) and Graptos (Writing).
Steganography in these days refers to information or a file that has been concealed
inside a digital picture, video or audio file. If a person or persons view the object that
the information is hidden inside, he or she will have no idea that there is any hidden
information; therefore the person will not attempt to decrypt the information.
Steganographic Techniques
Physical Steganography
Physical Steganography is the first real use of Steganography and it has been widely
used in ancient times. For examples: people wrote message on wood and then covered
it with wax. Message was written on the back of postage stamps. Message was written
on paper by secret inks. Also shaved the head of his most trusted slave and tattooed a
message on it. After his hair had grown the message was hidden, this was used back on
440BC.
Printed Steganography
The letter size, spacing and other characteristics of a cover text can be manipulated to
carry the hidden message. A recipient who knows the technique used can recover the
message and then decrypt it. For example:
These messages were sent by the German embassy in World
War I. This is called a null cipher.
First litter
PRESIDENT'S EMBARGO RULING SHOULD HAVE IMMEDIATE NOTICE. GRAVE SITUATION AFFECTING
INTERNATIONAL LAW. STATEMENT FORESHADOWS RUIN OF MANY NEUTRALS. YELLOW JOURNALS
UNIFYING NATIONAL EXCITEMENT IMMENSELY.
The second letter
OF MANY NEUTRALS. YELLOW JOURNALS UNIFYING NATIONAL EXCITEMENT IMMENSELY. APPARENTLY
NEUTRAL'S PROTEST IS THOROUGHLY DISCOUNTED AND IGNORED. ISMAN HARD HIT. BLOCKADE ISSUE
AFFECTS PRETEXT FOR EMBARGO ON BYPRODUCTS, EJECTING SUETS AND VEGETABLE OILS.
¤ Taking the first letter in each word of message 1 or second letter in message 2 reveals
the hidden text. PERSHING SAILS FROM NY JUNE 1.
Digital Steganography
Digital Steganography is today’s Steganography and it can be wildly used because it uses
the concept of invisibly hiding data within data. It conceals the fact that message exists
by hiding the actual message. In this, secret data can be hidden inside the image, text,
sound clip that can be represented in binary.
Why steganography?
Steganography can provide a reliable, flexible and user friendly alternative to encryption
and can be used in countries where cryptography is prohibited.
Alternative to Cryptography
For sure there will be a malicious intervention as long as there are electrical
communication. Cryptography helped to fight this intervention and gives security and
confidentiality to the existing message and the outcome will be an encrypted message.
That message will have it’s own authentication code appended so that recipients must
prove their integrity and authenticity before unencryption occurs.
With steganography, the message, whether encrypted or not, is hidden in images and
invisible to unauthorised recipients, or at least hard to detect. It is a new science that
provides added security, privacy and confidentiality when used instead of or in
conjunction with cryptography.
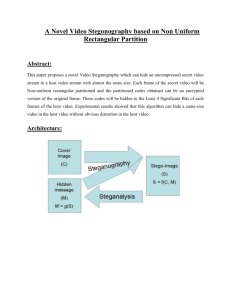
Steganography System
A steganographic system is composed of an encoder and a corresponding decoder, as
shown in Figure below. The encoder has three inputs. One is the payload we want to
embed, one is the stego key, the aim of which is to protect the carrier image so that
after encoding, unauthorized or malicious users cannot decode it, and the third is the
cover image in which payload will be embedded. The output of the encoder is the stego
image, which may be transmitted or recorded and will be the input to the decoder. The
encoder sends the stego key to the decoder to allow visibility of the payload.
Steganography Vs Cryptography
Cryptography is the science of scrambling a message by using algorithms to convert the
secret data into an incomprehensible form. Steganography hides the message, still in a
comprehensible form, so that it cannot be seen. The unauthorized recipient of an
encrypted message knows that secret information exists, while unlike a steganographic
message, whose very existence is unsuspected.
Steganography
Cryptography
Security in Steganography
Steganography is an efficient way to hiding data, protecting the data from unauthorized
access or viewing. Some steganographic approaches are too simple, however, such as
pure LSB hiding, as hidden data can be detected with ease Steganography Detection in
LSB
The commonest way to hide data is to embed it in an image by replacing the least
significant bits (LSB) of red, green and blue components in the pixels of a 24-bit image.
That anything has been embedded is difficult to detect visually as the human eye cannot
discriminate the difference in pixels. LSB methods cannot, however, resist extraction or
attacks like compression and cropping.
Least Significant Bit Technique (LSB)
In Least Significant Bit technique (LSB) steganography encoding occurs in spatial or
image domain not in frequency domain. Then in spatial domain various steps are
involved and are discussed in next section.
LSB Encoding Algorithm
LSB Encoding Algorithm
Input: secret message, stego key, original image
Procedure:
Step1. Convert original image to color bytes (no alpha byte)
Step2.
Step3. while complete message not embedded do
3.1 get next color byte
3.2.1 get next bit from message
3.2.2 replace color byte LSB with message bit
end{while}
Step4. Convert color bytes to stego image
End.
Output: stego image
LSB Encoding Process
This process consists of following steps
Step 1:
In step 1 first image is converted to pixels. Then these pixels split to R, G and B bytes.
These bytes are stored in array. These will be further processed in next steps.
Step 2:
In this step secret message is converted to bytes.
Step 3:
In this step actual data hiding occurs. Each bit of secret message is inserted to least
significant bit of color byte. So one byte of message is inserted in 8 color bytes. By using
this formula
N color bytes = N *1/8 message bytes
The process of inserting message bits to least significant bit of color byte repeats until all
messages are completed.
In order to understand how color bytes looks after modification we have to consider
example. Let we have message byte and we want that byte to insert it in color bytes,
message byte is
M = 0110 0010
M consists of 8 bits so it will require 8 bytes of color bytes. Let we have 9 color bytes
and before encoding process these bytes looks like
R
G
B
00101101
00011100
11011100
10100110
11000100
00001100
11010010
10101101
01100011
Before LSB Encoding
After LSB encoding we see from Table that least significant bit of color bytes are
changed indicated by bold letters. These bold bits are M message bits
R
G
B
00101100
00011101
11011101
10100110
11000100
00001100
11010011
10101100
01100011
After LSB Eencoding
This process repeats until the entire secret message bits are inserted in least significant
bit of color bytes.
Step 4:
In this step the modified color bytes are combined to pixels and are converted back to
image. Output of this process is stego image.
LSB Decoding Algorithm
LSB decoding algorithm
Input: stego image, stego key
Step1. Convert stego image to color bytes (no alpha byte)
Step2.
Step3. while complete message length do
3.1 get next color byte
3.2.1 concatenate color byte LSB to secret message
end{while}
Step4. Decode secret message and show output
End.
Output: secret message
LSB Decoding Process
Step 1:
In step 1 first image is converted to pixels. Then these pixels split to R, G and B bytes.
These bytes are stored in array. There will be further processed in next steps.
Step 2:
In this step actual extraction occurs. Here have color bytes, now in order to create
message least significant bit of these bytes are extracted and then they are
concatenated to create secret message. Concatenation occurs in length of 8 bits (1
byte). Eight bits are extracted and then they are concatenated to produce byte. This
process repeats until the entire secret message completes.
In order to understand how decoding works consider example. In this example we have
9 color bytes in the table we see bold letter these are message bytes that are inserted in
Encoding phase.
R
G
B
00101100
00011101
11011101
10100110
11000100
00001100
11010011
10101100
01100011
Encoded bytes
Least significant bit of each color byte is extracted and then concatenated to produce M
message byte M = 0110 0010. This process repeats until all the message bytes are
extracted.
Step 3:
In this step all extracted bytes are converted to secret message and presented to user.
LSB Decoding Algorithm
How invisibility achieved
After encoding step user cannot visually detect that something is hidden in stego image.
Since bytes values are changed if least significant bit changes. We see from Table byte
values are changed when LSB implemented but in color column we see that visually
before and after encoding colors are almost same. That’s why user cannot see any
difference in original and stego image.
Before Encoding
After Encoding
RGB value in bits
RGB value in bytes
00101101, 00011100, 11011100
45, 28, 220
10100110, 11000100, 00001100
166, 196, 12
11010010, 10101101, 01100011
210, 173, 99
00101100, 00011101, 11011101
44, 29, 221
10100110, 11000100, 00001100
166, 196, 12
11010011, 10101100, 01100011
211, 172, 99
Color
Compression of before and after encoding values
Experimental Results
From these two pictures we cannot find any difference visually but there is hidden
secret message.
Image before LSB Encoding
Image after LSB Encoding
Advantages
This algorithm provides high hiding capacity.
Simple algorithm and simple to understand.
It takes less time to encode secret message.
Disadvantages
By using steganalysis technique it will be easy to detect hidden message.
It is fragile technique.
References
[1] Wikipedia
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Steganography
[2] Ekta Walia, Payal jain, Naveep, “ An Analysis of LSB & DTC based Sreganography.” P.4 Global journal of
computer science and technology. April 2010.
[3] Alaa O. Khadidos “DISTRIBUTED STEGANOGRAPHY FILE SYSTEMS” University of Birmingham
[4] Michael T. Raggo, CISSP Principal Security Consultant VeriSign “Steganography, Steganalysis, &
Cryptanalysis”
[5] Brian Mearns, “Least-Significant Bit Steganography and Steganalysis”
[6] Java territorial in steganography
http://www.dreamincode.net/forums/topic/27950-steganography/