Lossless Compression and information hiding in
advertisement

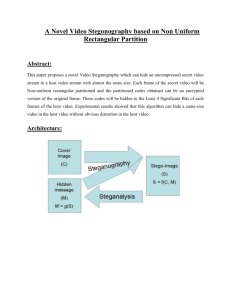
Lossless Compression and information hiding in images using Stegnography Abstract: In this paper a novel method is proposed to provide more security for the key information with the combination of image compression and data encryption method. This method requires less memory space and fast transmission rate because of image compression technique is applied. Steganography plays an important role in information security. It is the art of hiding the fact that communication is takes place, by hiding information in other information. Many different file formats can be used. For hiding secret information in images, there exist a large variety of stenographic techniques some are more complex than others and all of them have respective strong and weak points. Many applications have different requirements of the steganography technique used. Some applications may use absolute invisibility of the secret information, but others require a larger secret message to be hidden. This method has been implemented and tested on varies images and data. It provides better security for encrypted data and no distortion in the image quality. Existing System There are a large number of steganographic methods that most of us are familiar with, ranging from invisible ink and microdots to secreting a hidden message in the second letter of each word of a large body of text and spread spectrum radio communication. With computers and networks, there are many other ways of hiding information, such as: Covert channels (e.g., Loki and some distributed denial-of-service tools use the Internet Control Message Protocol, or ICMP, as the communications channel between the "bad guy" and a compromised system) Hidden text within Web pages Hiding files in "plain sight" (e.g., what better place to "hide" a file than with an important sounding name in the c:\winnt\system32 directory?) For Further details Contact A.Vinay,9030333433,08772261612 Null ciphers (e.g., using the first letter of each word to form a hidden message in an otherwise innocuous text) Steganography today, however, is significantly more sophisticated than the examples above suggest, allowing a user to hide large amounts of information within image and audio files. These forms of steganography often are used in conjunction with cryptography so that the information is doubly protected; first it is encrypted and then hidden so that an adversary has to first find the information (an often difficult task in and of itself) and then decrypt it. Disadvantages Normally must use the original program to hide and reveal data If the picture with the hidden information is converted to another format, then the hidden data may be lost. Proposed System To a computer, an image is a collection of numbers that constitute different light intensities in different areas of the image. The numeric value representation forms a grid and the individual points are referred to as pixels. Image is the most popular cover objects used for steganography. In the domain of digital images many different image file formats exist, most of them for specific applications. For these different image file formats, different stenographic algorithms exist. Image steganography techniques can be divided into two groups: those in the Image Domain and those in the Transform Domain. Image also known as spatial – domain techniques embed messages in the intensity of the pixels directly, while for Transform – also known as frequency – domain, images are first transformed and then the message is embedded in the image. Image domain techniques encompass bit-wise methods that apply bit insertion and noise manipulation and are sometimes characterized as “simple systems”. The image formats that are most suitable for image domain steganography are lossless and the techniques are typically dependent on the image format. Steganography in the transform domain involves the manipulation of algorithms and image transforms. These methods are used to hide messages in more significant areas of the image, making it more For Further details Contact A.Vinay,9030333433,08772261612 robust. Many transform domain methods are independent of the image format and the embedded message may survive conversion between loss and lossless compression. Advantages Main purpose of steganography is to provide secret communication Steganography has the advantage that even a talented code-cracker cannot decipher a message without knowing it is there. Steganography is beneficial for securely storing sensitive data, such as hiding system passwords or keys within other files. Software Requirements: Operating System : Windows XP Front End : Java Swing Programming tool : net beans Hardware Requirements: Processor : Intel Pentium IV Cache Memory : 1MB HDD : 40 GB RAM : 512 MB Processor Speed : 600 MHz Display Type : VGA For Further details Contact A.Vinay,9030333433,08772261612 Mouse : Logitech Monitor : 15” Samsung Color Monitor Data Flow Diagram: Embedded file: Master file output file Using Public keys Compressed Compressed file Data file Retrieve File: Compressed file Using Public keys Retrieve Data file View Data File Project Description: The simplest approach to hiding data within an image file is called Least Significant bit (LSB) insertion. In this method, we can take the binary representation of the hidden data and overwrite the LSB of each byte within the cover image. If we are using 24-bit color, For Further details Contact A.Vinay,9030333433,08772261612 the amount of change will be minimal and indiscernible to the human eye. As an example, suppose that we have three adjacent pixels (nine bytes) with the following RGB encoding: 10010101 00001101 11001001 10010110 00001111 11001010 10011111 00010000 11001011 Now suppose we want to "hide" the following 9 bits of data (the hidden data is usually compressed prior to being hidden): 101101101. If we overlay these 9 bits over the LSB of the 9 bytes above, we get the following (where bits in bold have been changed): 10010101 00001100 11001001 10010111 00001110 11001011 10011111 00010000 11001011 Note that we have successfully hidden 9 bits but at a cost of only changing 4, or roughly 50%, of the LSBs. The following formula provides a very generic description of the pieces of the steganographic process: Cover medium + hidden data + stego_key = stego_medium In this context, the cover medium is the file in which we will hide the hidden data, which may also be encrypted using the stego key. The resultant file is the stego medium (which will, of course. be the same type of file as the cover medium). The cover mediums (and, thus, the stego_medium) are typically image or audio files. In this article, I will focus on image files and will, therefore, refer to the cover image and stego image. For Further details Contact A.Vinay,9030333433,08772261612 For Further details Contact A.Vinay,9030333433,08772261612