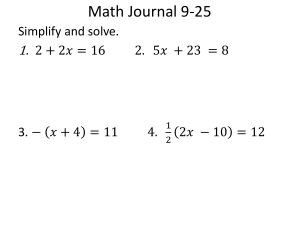Inverse Operations and One Step Equations
advertisement

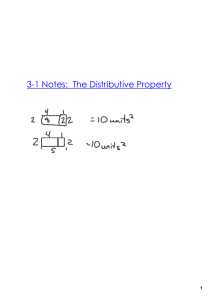
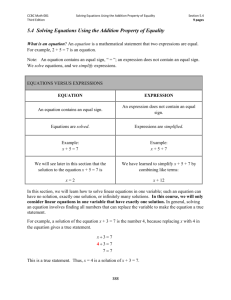
Inverse Operations and One Step Equations Equation: is a mathematical statement, in symbols, that two things are exactly the same (or equivalent). Equations are written with an equal sign. Equations can also be used to state the equality of two expressions containing one or more variables. Numerical equation: this type of equation consists of numbers and there are no variables (example: 20 +30=50) Algebraic equation: this type of equations contains at least one variable (example: 20 +x= 50) When solving equations the goal is to isolate the variable on one side of the equation in order to determine its value (the value that makes the equation true). In order to solve an equation containing a variable, you need to use inverse (opposite/undoing) operations on both sides of the equation. Inverses of each operation: Addition: Subtraction Multiplication: Division Squaring: Square root Cubing: Cube root There are four properties of equality that we will use to solve equations: Addition property: If a=b, the a +c= b +c for all real numbers a,b, and c. The same number can be added to each side of the equation without changing the solution of the equation Subtraction Property: If a=b, then a-c=b-c for all real numbers a,b, and c. The same number can be subtracted to each side of the equation without changing the solution of the equation Multiplication property: If a=b, then ac= bc for all real numbers a,b, and c. Each side of an equation can be multiplied by the same number without changing the solution of the equation Division Property: If a=b and c ≠ 0, then a ÷ c= b÷ c for all real numbers a,b, and c. Each side of an equation can be divided by the same number without changing the solution of the equation One step equations The purpose of solving an equation is to find a solution. A solution is a value that can replace the variable in order to make the equation true. To solve equations, you must work backwards through the order of operations to find the value of the variable. Remember to use inverse operations in order to isolate the variable on one side of the equation. Whatever you do to one side of an equation, you MUST do to the other side!