Cocaine Packer
advertisement

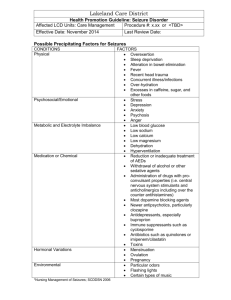
For Examiner Only Case Cocaine Body packer – seizure, chest pain Author: Larrisa Velez, MD Revewer: Karen Jubanyik, MD Approved 12/5/05 ORAL CASE SUMMARY CONTENT AREA NEUROLOGY Status Epilepticus from cocaine body-packing SYNOPSIS OF CASE This case involves a 27 y/o woman brought in by ambulance from the airport after she started acting strange and having seizures while at baggage claim at the airport. No one in the immediate vicinity claimed to know the patient. She has no past medical history, is not pregnant, and had no trauma, but this information is not readily available when patient arrives. The resident must suspect cocaine body packing, treat aggressively with benzodiazepines and barbiturates; consider whole bowel irrigation for decontamination; and call the surgeon for a laparotomy. The KUB will show multiple packets. SYNOPSIS OF HISTORY The patient is a healthy 27 y/o who is traveling back from Colombia into the States (this is not immediately volunteered – resident must ask paramedics to stay and will be able to get this information if they ask paramedics). The plane had been flying for about 6 hours. During the flight, she had complained of “not feeling well” according to flight attendants. Upon landing the patient has a seizure in baggage claim. She has received 2 mg IV Ativan by EMS. She is post-ictal on arrival to the ED. SYNOPSIS OF PHYSICAL The patient is post-ictal, with sonorous breathing, sweaty, tachycardic and hypertensive. The pupils are large. There are no signs of trauma. There are no stigmata of drug use. There is a bite mark on the tongue, but no incontinence. Sats are 87% at RA. CRITICAL ACTIONS 1. Secure the airway early (PM, PS) 2. Treat the seizures with benzodiazepines +/- barbiturates (PM) 3. Follow vital signs (PM) 4. Initiate gastrointestinal decontamination (PM) 5. Call surgery for emergent laparotomy (PM) SCORING GUIDELINES (Critical Action No.) 1. Score down if delays airway management. Have patient have additional seizures and lower the sats. 2. Dangerous action to treat with phenytoin only. Same as 1 (patient has more seizures and drops sats if patient not treated with benzodiazepines or barbiturates. For Examiner Only Case Case Summary - Page Two 4. Score down/dangerous action if initiates GI decontamination without managing the airway. PLAY OF CASE GUIDELINES (Critical Action No.) 1. Have patient have additional seizures and lower the sats if resident delays airway management. Patient codes if airway management is further delayed. 1. Ask resident how to perform a RSI. Ensure that only short acting paralytics are used. Dangerous to paralyze the patient since unable to monitor for seizure activity/seizure control. 2. Seizures continue and patient deteriorates if treated with phenytoin only. Same as 1 (patient has more seizures and drops sats if patient not treated with benzodiazepines or barbiturates). Patient eventually codes if status epilepticus is not identified and correctly treated. 2. If resident uses adequate doses of benzodiazepines, vital signs improve. 3. If resident uses beta blockers to control hypertension and tachycardia, blood pressure increases. 4. If resident initiates GI decontamination without managing the airway, the patient has a seizure, vomits, and aspirates. Nurse can warn once, saying “the patient started having another seizure as I was placing the nasogastric tube. Do you still want it, doctor?”. FOR EXAMINER ONLY For Examiner Only Critical Actions 1. Secure the airway early (PM, PS) This critical action is met by the candidate doing early airway management and describing the proper sequence for RSI. Cueing Guideline: 2. Treat the seizures early with benzodiazepines +/barbiturates (PM) This critical action is met by the candidate treating with proper drugs and doses and reassessing patient for resolution of the seizure activity and improvement of the vital signs. Cueing Guideline: 3. Follow vital signs (PM) This critical action is met by the candidate requesting repeat vital. Cueing Guideline: Nurse may tell resident that patient’s vitals are “worse”. 4. Initiate gastrointestinal decontamination (PM) This critical action is met by the candidate initiating GI decontamination after airway has been secured. Cueing Guideline: 5. Call surgery for emergent laparotomy (PM) This critical action is met by the candidate consulting general surgery before end of case. Cueing Guideline: If totally lost about reason for seizures, have airline representative call on phone to ED and want to speak to candidate about patient’s condition and mention that “patient frequently flies from Colombia to the USA”. For Examiner Only History Data Panel Onset of Symptoms: About 1 hour ago Description of Complaint: Seizures for about 30 minutes. Past Medical History Surgical: Unknown Medical: Unknown Injuries: Unknown Allergies: None. No Medic Alert bracelets noted (must ask) Last menstrual period: unknown Habits Smoking: Unknown Drugs: Unknown Alcohol: Unknown Family Medical History Father: Unknown Mother: Unknown Siblings: Unknown Social History Married: No Children: None Employed: Unknown Education: Unknown For Examiner Only Physical Data Panel Patient: 27 y/o woman Patient Name: Unidentified female General Appearance: Post-ictal, sonorous breathing. In ambulance stretcher. Vital Signs: BP : 214/121 P : 136 R : 23 T : 38.3 (tympanic) Sats (upon request only): 87% D stick (upon request only): 123 mg/dl Head: No trauma. No nystagmus or gaze. No perforated septum. Eyes: Dilated pupils, sluggish and symmetric, to 6 mm. Ears: Normal Mouth: Normal, except for tongue bite mark. Pooling of secretion in posterior throat. Neck: Normal Skin: Diaphoretic. No rashes, no needle tracks. Chest: No signs of trauma. Normal breasts. Hyperdynamic precordium. Heart: Tachycardic and regular. No murmurs, rubs, or gallops. Abdomen: Decreased bowel sounds. No trauma, not distended. No masses. Extremities: Diaphoresis noted. No signs of trauma. Symmetric pulses. Rectal: Heme negative stools. Decreased tone (if done after intubation) Pelvic: Normal Neurological: Normal cranial nerves except for mydriasis. Normal reflexes. Eyes closed. Withdraws to pain (if not seizing). Noisy breathing and non-verbal. Mental Status: Post-ictal. See above. For Examiner Only Lab Data Panel Stimulus #2 - Hematology Complete Blood Count WBC 23,000/mm3 Hgb 11.9 g/dL Hct 35 % Platelets 240,000/mm3 Differential Segs 90% Bands 1% Lymphs 5% Monos 2% Eos 2% Stimulus #5 - Arterial Blood Gases (right after intubation) pH 7.14 pCO2 pO2 O2 Sat 30 mm Hg 305 mm Hg 100% Stimulus #6 - CK 4,304 Stimulus #7 – see KUB Stimulus #8 – CRX, portable: adequately placed ETT, normal otherwise Stimulus #3 - Chem-7 Na+ K+ CO2 Cl- 140 mEq/L 4.1 mEq/L 12 mEq/L 109 mEq/L Glucose BUN Creatinine 135 mg/dL 24 mg/dL 1.4 mg/dL Stimulus #4 - Urinalysis Color yellow Sp gravity 1.035 Glucose negative Protein negative Ketone positive Leuk. Est. none Nitrite neg WBC 0-1/HPF RBC 2-4/HPF VERBAL REPORTS Monitor shows sinus tachycardia at 136/minute. 12 lead ECG shows sinus tachycardia at 140/minute. Intervals are normal. QRS is normal. There is no ectopy. Initial sats: 87% If applies oxygen: 92% After intubation: 100% D-stick: 123 mg/dl. Must ask for this. Can make hypoglycemic if resident does not ask for it. Pregnancy test: negative Note: hold all labs until seizures are managed. This case does not need labs in general. Mock Oral Feedback Form Date: Examiner: Examinee: Data acquisition Worst 1 NOTES 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Best Problem solving Worst 1 NOTES 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Best Patient management Worst 1 2 NOTES 3 4 5 6 7 8 Best Resource utilization Worst 1 2 NOTES 3 4 5 6 7 8 Best Health care provided Worst 1 2 NOTES 3 4 5 6 7 8 Best 4 5 6 7 8 Best Comprehension of path physiology Worst 1 2 3 4 NOTES 5 6 7 8 Best Clinical competence (overall) Worst 1 2 3 NOTES 5 6 7 8 Best Patient Interpersonal relations Worst 1 2 3 NOTES 4 Critical Actions Dangerous actions Secure the airway early (PM, PS) and omissions Treat the seizures with benzodiazepines +/- Follow vital signs (PM) Initiate gastrointestinal decontamination (PM) Call surgery for emergent laparotomy (PM) For Examiner Only Stimulus Inventory #1 Emergency Admitting Form #2 CBC #3 BMP #4 Urinalysis #5 ABG #6 Creatinine Kinase level #7 KUB showing multiple radio-opaque drug packets #8 Chest X ray #9 #10 FOR EXAMINER ONLY Stimulus #1 ABEM General Hospital Emergency Admitting Form Name : Unidentified Female Age : 27 Sex : F Method of Transportation : EMS Person giving information : EMS Presenting complaint : seizures Background: 27 y/o woman s/p seizure, which EMS treated with Ativan, 2 mg. Vital Signs BP : 214/121 P : 136 R : 23 T : 38.3 (tympanic) Stimulus #2 CBC Complete Blood Count WBC 23,000/mm3 Hgb 11.9 g/dL Hct 35 % Platelets 240,000/mm3 Differential Segs 90% Bands 1% Lymphs 5% Monos 2% Eos 2% Stimulus #3 Electrolytes Na+ K+ CO2 ClGlucose BUN Creatinine 140 mEq/L 4.1 mEq/L 12 mEq/L 109 mEq/L 135 mg/dL 24 mg/dL 1.4 mg/dL Stimulus #4 Urinalysis Color yellow Sp gravity 1.035 Glucose negative Protein negative Ketone positive Leuk. Est. none Nitrite neg WBC 0-1/HPF RBC 2-4/HPF Stimulus #5 Arterial Blood Gases (right after intubation) pH 7.14 pCO2 pO2 O2 Sat Stimulus #6 Creatine Kinase CK 4,304 30 mm Hg 305 mm Hg 100% Stimulus # 7 KUB film