Cells: The Basics
advertisement

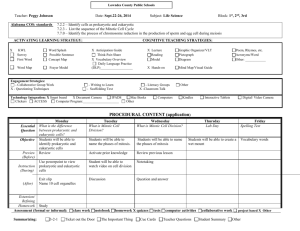
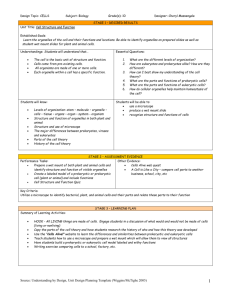
Cells: The Basics Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. The first cells to appear on Earth were prokaryotic cells. A prokaryote is an organism made of a single prokaryotic cell. The earliest prokaryotes may have arisen more than 2.5 billion years ago. Bacteria are prokaryotes. They are very small cells with a simple structure. Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus. This means that their DNA is not enclosed in a membrane inside the cell. Instead, prokaryotes have a single loop of DNA that floats in the cell’s cytoplasm. Protein-making bodies called ribosomes also form part of the cytoplasm. Like all cells, prokaryotes have a cell membrane. All prokaryotes also have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane. The cell wall helps provide support and protection for the cell. Some prokaryotes are enclosed by an additional layer. This layer is called the capsule. The capsule has a sticky surface area, so it allows prokaryotes to cling to surfaces, such as your skin and your teeth. Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells. They all have a cell membrane, ribosomes, and DNA as prokaryotic cells do. However, the DNA of eukaryotic cells does not float freely in the cytoplasm. Instead, it is found in the nucleus, an internal compartment bound by a cell membrane. The nucleus is one kind of organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Organelles are structures that perform specific functions. Most organelles are surrounded by a membrane. Some organelles have membranes that form channels which help transport substances from one part of the cell to another part of the cell. Eukaryotes are organisms made of one or more eukaryotic cells. The earliest eukaryotes, like the first prokaryotes, were single-celled organisms. They arose about 1 billion years later than the earliest prokaryotes. Later, multicellular eukaryotes arose. Every type of multicellular organism that exists is made up of eukaryotic cells. SKILL: READING EFFECTIVELY Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. 1.What is a prokaryote, and when did prokaryotes arise? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 2. Describe three main features inside a prokaryotic cell. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 3. Describe the structures that form the outside of a prokaryotic cell. Tell whether each structure is common to all prokaryotes. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 4. What is a eukaryote, and when did eukaryotes first arise? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ SKILL: ORGANIZING INFORMATION Fill in the Venn diagram to compare and contrast the structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. In the space provided, write the letter of the phrase that best answers the question. _____ 8. From which type of cells did multicellular organisms arise? a. prokaryotic cells b. prokaryotic cells with a capsule c. eukaryotic cells d. both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Reinforcement Worksheet – Cell Theory, Scientists, & Cell Types KEY CONCEPT Cells are the basic unit of life. The invention of the microscope in the late 1500s revealed to early scientists a whole new world of tiny cells. Most cells are so small that they cannot be seen without a microscope. The discoveries of scientists from the 1600s through the 1800s led to the cell theory, which is a unifying concept of biology. The cell theory has three major principles: • All organisms are made of cells. • All existing cells are produced by other living cells. • The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells can be divided into two major groups: prokaryotic cells or eukaryotic cells. The main differences between the two kinds of cells are in their structure: • Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus defined by a membrane, while prokaryotic cells have no nucleus. • In eukaryotic cells, the DNA, or genetic information, is found in the nucleus. In prokaryotic cells, the DNA is found in the cytoplasm, the jellylike substance that fills both types of cells. • Eukaryotic cells have organelles, structures that perform jobs for a cell. Most organelles are surrounded by membranes. Prokaryotic cells do not have organelles surrounded by membranes. Prokaryotic cells make up organisms called prokaryotes. All prokaryotes are tiny and consist of single cells. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells make up eukaryotes. You are a eukaryote, as are plants and some types of single-celled organisms. All multicellular organisms, or organisms that have many cells, are eukaryotes. 1. What is the smallest, most basic unit of life? __________________________________________ 2. Where is the DNA in a prokaryote? in a eukaryote? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Why would you need a microscope to see a prokaryotic organism? __________________________________________________________________________________ 4. A friend tells you he read somewhere that rotting garbage can turn into maggots, which are fly larvae, and the maggots then can grow into adult flies. What part of the cell theory could you use to refute his claim? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell theory. In a phrase, tell what each scientist did to help develop the cell theory. Scientist Contribution to Cell Theory 1. Hooke 2. Leeuwenhoek 3. Schleiden 4. Schwann 5. Virchow What are the three parts of the cell theory? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ MAIN IDEA: Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and most internal structures of eukaryotic cells. In the top left side of the Y shape below, write the characteristics of eukaryotic cells. In the top right side of the Y shape below, write the characteristics of prokaryotic cells. At the bottom of the Y shape below, write the characteristics that both kinds of cells have in common.