quiz_3_2013_06_20
advertisement

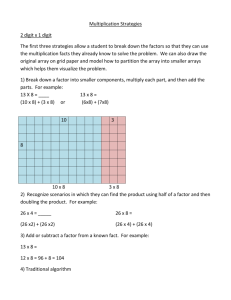
Student’s Name: Date: June 20, 2013 ESCI-61, Introduction to Photovoltaic Systems Quiz 3 Question 1 An Air Conditioning unit consumes on average 36 kWh of electricity per day; what is the average power of this AC unit? A – 36 kW B – 1500 W C – 35 kWh D – We cannot calculate the average power from these data Question 2 Short Circuit Current (Isc) of a Crystalline Silicon PV module varies: A – Significantly with irradiance and significantly with temperature B – Slightly with irradiance and significantly with temperature C – Significantly with irradiance and slightly with temperature D – Slightly with irradiance and slightly with temperature Question 3 Open Circuit Voltage (Voc) of a Crystalline Silicon PV module varies: A – Significantly with irradiance and significantly with temperature B – Slightly with irradiance and significantly with temperature C – Significantly with irradiance and slightly with temperature D – Slightly with irradiance and slightly with temperature Question 4 List 4 tools or accessories you wouldn’t forget to take with you for a residential PV site evaluation A– B– C– D– Question 5 We’re comparing 2 PV arrays, Array_A and Array_B ; Array_A has 36 modules connected as 4 parallel strings of 9 modules each and Array_B has 36 modules connected as 6 parallel strings of 6 modules each ; if both arrays are built using the same PV module (same brand and same model), what can you say about the overall rated power of these arrays? A – Array_A has a higher rated power than Array_B B – Array_A has a lower rated power than Array_B C – Both arrays have the same rated power D – One needs more information about these arrays in order to answer this question Question 6 We’re comparing 2 PV arrays, Array_A and Array_B ; Array_A has 36 modules connected as 4 parallel strings of 9 modules each and Array_B has 36 modules connected as 6 parallel strings of 6 modules each ; if both arrays are built using the same PV module (same brand and same model), what can you say about the overall Open Circuit Voltage (Voc) of these arrays? A – Array_A has a higher Voc than Array_B B – Array_A has a lower Voc than Array_B C – Both arrays have the same Voc D – One needs more information about these arrays in order to answer this question Question 7 We’re comparing 2 PV arrays, Array_A and Array_B ; Array_A has 36 modules connected as 4 parallel strings of 9 modules each and Array_B has 36 modules connected as 6 parallel strings of 6 modules each ; if both arrays are built using the same PV module (same brand and same model), what can you say about the Short Circuit Current (Isc) of the strings in each of these arrays? A – Each string in Array_A has a higher Isc than each string in Array_B B – Each string in Array_A has a lower Isc than each string in Array_B C – All strings in Array_A and Array_B have the same Isc D – One needs more information about these arrays in order to answer this question Question 8 Standard Test Conditions (STC) for PV modules are: A – 1,000 W/m2, AM1.5 solar spectral irradiance distribution, and 25°C cell or module temperature B – 1,000 W/m2, AM1.5 solar spectral irradiance distribution, 20°C ambient temperature, and 1m/s wind speed C – 1,000 W/m2, AM1.5 solar spectral irradiance distribution, and 25°C ambient or module temperature D – 1,000 W/m2, AM1.5 solar spectral irradiance distribution, 20°C cell temperature, and 1m/s wind speed Question 9 The Solmetric SunEye, the shading measurement tool that solar professionals use to determine the solar access of potential PV system sites: A – Can be used during the day or at night B - During the day only Explain briefly your answer Question 10 The Solmetric SunEye, the shading measurement tool that solar professionals use to determine the solar access of potential PV system sites: A – Can be used in sunny or cloudy days B – Can be used in sunny days only Explain briefly your answer Question 11 What is true about a PV system? A - A PV system converts solar energy into electricity, and heat is a byproduct of that process B – PV systems convert heat into electricity C – The higher the ambient temperature the better for the PV system’s electricity production D – Clouds do not affect PV system electricity production Question 12 Partial shading of PV modules and arrays can cause A – Proportional reductions in power output B – Disproportional reductions in power output C – No reduction in power output D – Total reduction in power output Question 13 The overall voltage of a PV array is A – Dependent on the number of modules in series per string B – Dependent on the number of strings in parallel in the array C – Dependent on the total number of modules in the array D – Independent of all these considerations Question 14 What information do you get from a sun path chart? A - Sun energy for every day of the year and every hour of the day B - Sun position for every day of the year and every hour of the day C - Sun color for every day of the year and every hour of the day D - Sun power for every day of the year and every hour of the day Question 15 The best place to install an inverter is A – In a sunny location so that more sunlight is converted into electricity B – in a cool and shaded location C – In the outside of the house so that utility staff can easily come and read the electricity production from the inverter D – in an accessible location so that you can turn it on in the morning and off in the evening Question 16 In a grid–tied PV system without a backup storage system, amongst other features, the inverter must A – Track the maximum voltage point of the PV array B – Track the maximum current point of the PV array C – Track the maximum power point of the PV array D – Track the maximum energy point of the PV array Question 17 Sun position in the sky relative to a given location on Earth is measured with the following angles (circle two answers) A – Sun Altitude B – Sun Longitude C – Sun Latitude D – Sun Azimuth Question 18 Sun Irradiance is a measure of A – Intensity of the solar power (W/m2) B – Total amount of solar energy accumulated on an area over time (Wh/m2) C – all of the above D – None of the above Question 19 The atmosphere absorbs extraterrestrial radiation A - At all wavelengths, except visible ones, resulting in no effect of the atmosphere on the terrestrial sun spectrum at visible wavelengths B - At visible wavelengths only, resulting in no effect of the atmosphere on the terrestrial sun spectrum at non visible wavelengths C - At certain wavelengths, resulting in an altered spectral distribution for terrestrial radiation D - At Ultra-Violet and Infra-Red wavelengths only, resulting in an unaltered spectral distribution for terrestrial radiation at visible wavelengths Question 20 What is the maximum STC rating of a PV array that can be installed on a roof space of approximately 600 ft2, assuming module efficiency is 15% (1 m2 = 10.8 ft2)? A – 3 kW B – 6 kW C – 8 kW D – 10 kW Bonus Question 1 Given the following STC Specs for 2 different PV modules, what can you say about the rated power of these PV modules? Module_1 Voc = 60 V Isc = 3.2 A Vmp = 48 V Imp = 3 A Module_2 Voc = 30 V Isc = 6.4 A Vmp = 24 V Imp = 6 A A – Module_1 has a higher rated power than Module_2 B – Module_1 has a lower rated power than Module_2 C – Both modules have the same rated power D – One cannot answer this question because other specs are missing Bonus Question 2 Calculate the total area of the roof described below 30 ft 19 ft 3 in 8 ft A – 770 sq. ft. B – 1015 sq. ft. C – 1210 sq. ft. C – 1540 sq. ft. 17 ft 6 in 17 ft 6 in 30 ft 26 ft 7 in 20 ft