Appendex2
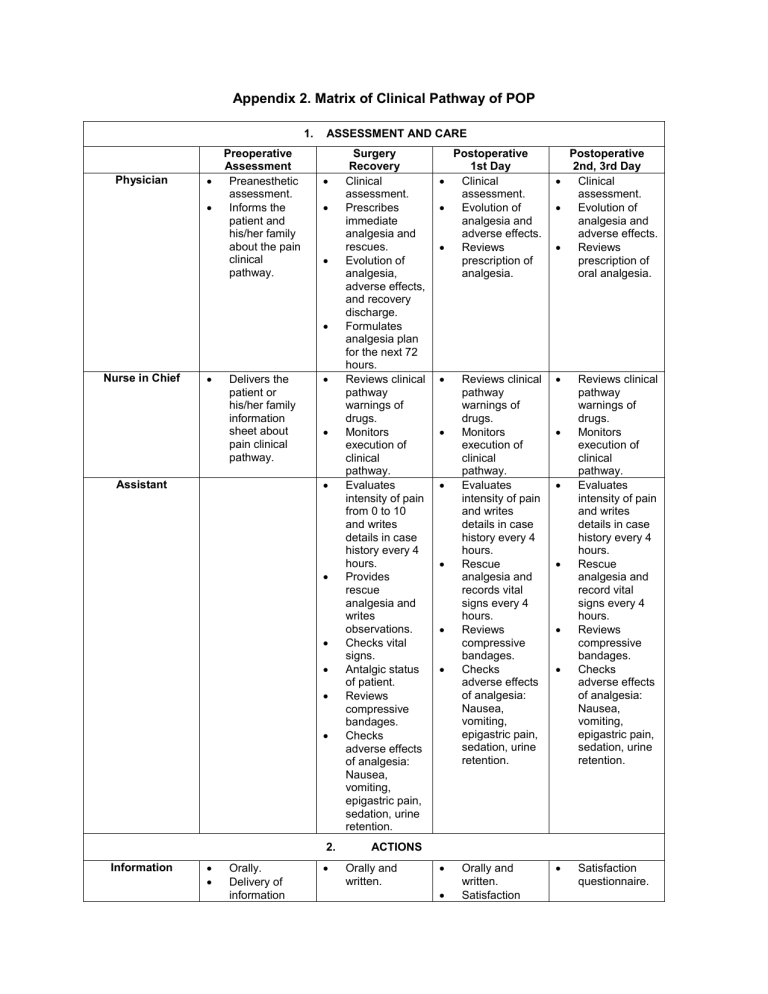
Appendix 2. Matrix of Clinical Pathway of POP
Physician
Nurse in Chief
Assistant
Information
Preoperative
Assessment
Preanesthetic assessment.
Informs the patient and his/her family about the pain clinical pathway.
Delivers the patient or his/her family information sheet about pain clinical pathway.
1. ASSESSMENT AND CARE
Surgery
Recovery
Clinical assessment.
Prescribes immediate analgesia and rescues.
Evolution of analgesia, adverse effects, and recovery discharge.
Formulates analgesia plan for the next 72 hours.
Reviews clinical pathway warnings of drugs.
Monitors execution of clinical pathway.
Evaluates intensity of pain from 0 to 10 and writes details in case history every 4 hours.
Provides rescue analgesia and writes observations.
Checks vital signs.
Antalgic status of patient.
Reviews compressive bandages.
Checks adverse effects of analgesia:
Nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, sedation, urine retention.
Postoperative
1st Day
Clinical assessment.
Evolution of analgesia and adverse effects.
Reviews prescription of analgesia.
Reviews clinical pathway warnings of drugs.
Monitors execution of clinical pathway.
Evaluates intensity of pain and writes details in case history every 4 hours.
Rescue analgesia and records vital signs every 4 hours.
Reviews compressive bandages.
Checks adverse effects of analgesia:
Nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, sedation, urine retention.
Orally.
Delivery of information
2. ACTIONS
Orally and written.
Orally and written.
Satisfaction
Postoperative
2nd, 3rd Day
Clinical assessment.
Evolution of analgesia and adverse effects.
Reviews prescription of oral analgesia.
Reviews clinical pathway warnings of drugs.
Monitors execution of clinical pathway.
Evaluates intensity of pain and writes details in case history every 4 hours.
Rescue analgesia and record vital signs every 4 hours.
Reviews compressive bandages.
Checks adverse effects of analgesia:
Nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, sedation, urine retention.
Satisfaction questionnaire.
Objectives
Performance
Criteria
Inclusion Criteria sheet to patient or his/her family.
To reduce anxiety caused for fear to pain.
Education about pain management.
To assure that patient or his/her family has received relevant information.
Preoperative patients.
To determine pain intensity.
To control pain.
To control adverse effects.
To inform treating physician immediately about the following signs of alarm:
1.
Intense pain which does not improve after 3 rescues.
2.
Deep sedation
(Grade 3).
3.
Respiratory rate lower than 10/min.
4.
Systolic blood pressure below 90 mm/Hg.
*In cases 2 , 3 and
4 , to apply oxygen through nasal cannula, 3 liters per minute.
-To request Narcan
1 ampule.
Adult patients with moderate to severe postoperative pain. questionnaire.
To manage pain control and other adverse effects.
To inform treating physician immediately about the following signs of alarm:
1.
Intense pain which does not improve after 3 rescues.
2.
Deep sedation
(Grade 3).
3.
Respiratory rate lower than 10/min.
4.
Systolic blood pressure below 90 mm/Hg.
*In cases 2 , 3 and
4 , to apply oxygen through nasal cannula, 3 liters per minute.
-To request Narcan
1 ampule.
Adult patients with moderate to severe postoperative pain.
To manage pain control and other adverse effects.
To inform treating physician immediately about the following signs of alarm:
1.
Intense pain which does not improve after 3 rescues.
2.
Deep sedation
(Grade 3).
3.
Respiratory rate lower than 10/min.
4.
Systolic blood pressure below 90 mm/Hg.
*In cases 2 , 3 and
4 , to apply oxygen through nasal cannula, 3 liters per minute.
-To request Narcan
1 ampule.
Controlled pain until third day after surgery.
Exclusion Criteria Major surgery requiring assistance at the Acute Pain
Service
3. PHARMACOLOGICAL RECOMMENDATIONS FOR ANALGESIA AND SIDE EFFECTS
RECOVERY:
ANESTHESIOLOGIST
Rescue analgesia:
Opioids:
Option 1:
Morphine 0.05 mg/Kg every 10 minutes until pain is relieved; or
Option 2:
Tramadol 2 mg/Kg. If severe pain persists, to change to morphine IV.
Adjuvant analgesia:
NSAID Option 1:
Diclofenac 75 mg IV,
POSTOPERATIVE 1ST TO
3RD DAY:
SURGEON
Analgesia by schedule:
Opioids:
Option 1:
Tramadol 1-2 mg/Kg every 6 hours, plus rescues with Tramadol
1 mg/Kg, between schedule dose, 4 rescues maximum in
24 hours; or
Option 2:
Morphine 0.05 – 0.1 mg/Kg every 4-6 hours, plus rescues with
Morphine 0.05 mg
PRECAUTIONS
NSAID’s contraindications:
History of ulcer.
Epigastric pain.
Coagulopathy.
Hypovolemia or mass transfusion.
Renal failure.
Heart failure.
Myocardial infarction.
Allergy to NSAID’s.
diluted in 100 mL SSN
0.9% (see contraindications).
NSAID Option 2:
Dipyrone 1 gr IV, diluted in 100 ml SSN
0.9% (see contraindications).
Adverse Effects
Prophylaxis:
Dexamethasone 8 mg
IV. Only dose.
Haloperidol 1 mg IV
In case of active vomiting, rescue with
Metoclopramide 10 mg and Ranitidine 50 mg
IV. every hour.
Adjuvant analgesia:
NSAID Option 1:
Diclofenac 75 mg IV, diluted in 100 mL SSN
0.9% (see contraindications).
NSAID Option 2:
Dipyrone 1 gr IV, diluted in 100 ml SSN
0.9%, every 6 hours
(see contraindications), through pharmacological monitoring.
Acetaminophen 1 gr., orally every 6 hours, if patient tolerates oral consumption of solid food.
Omeprazole 20 mg orally every 24 hours, when NSAID’s are prescribed.
Haloperidol 1 mg IV every 12 hours, if still with no oral consumption; or
Haloperidol 2 mg, if oral consumption has started (20 drops).
If vomiting persists, rescue with metoclopramide 10 mg
IV every 6 hours and to pass haloperidol 2 mg
IV every 12 hours.
Prescription for adverse effects of analgesia:
Vomiting:
Rescue with metoclopramide 10 mg
IV every 6 hours.
Haloperidol 2 mg IV every 12 hours.
Ranitidine 50 mg IV every 8 hours.
Epigastric Pain:
To stop NSAID’s.
Omeprazole 40 mg IV every 24 hours.