Vocabulary
advertisement
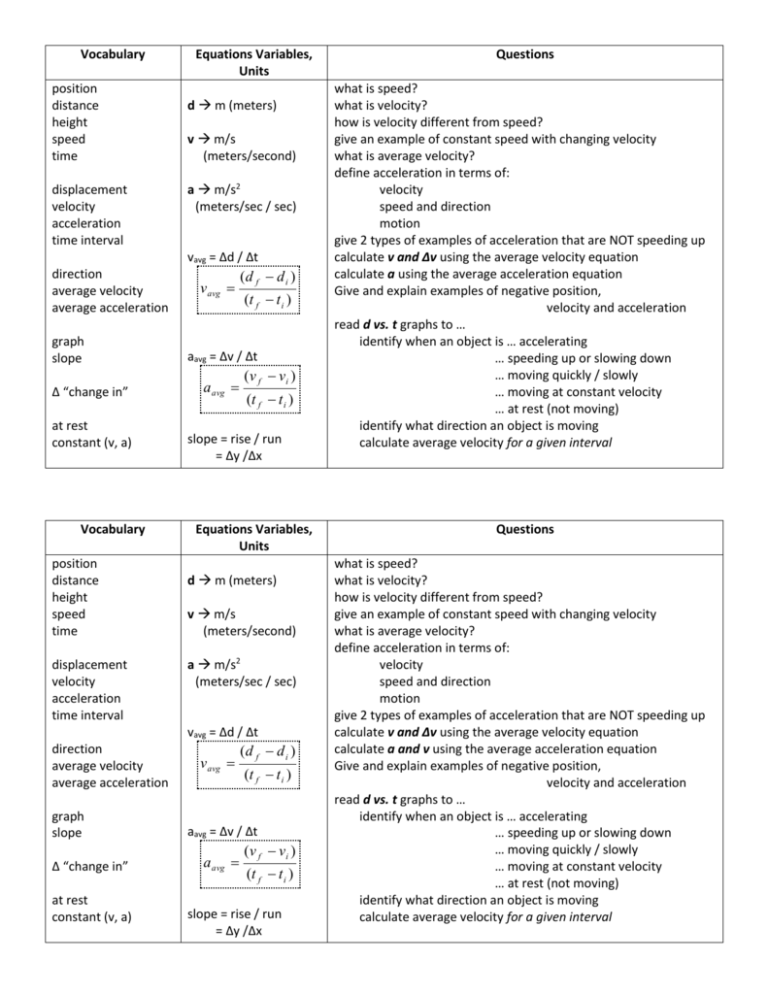
Vocabulary position distance height speed time displacement velocity acceleration time interval Equations Variables, Units d m (meters) v m/s (meters/second) a m/s2 (meters/sec / sec) vavg = ∆d / ∆t direction average velocity average acceleration graph slope ∆ “change in” at rest constant (v, a) Vocabulary position distance height speed time displacement velocity acceleration time interval v avg (d f d i ) (t f t i ) aavg = ∆v / ∆t a avg (v f v i ) (t f t i ) slope = rise / run = ∆y /∆x Equations Variables, Units d m (meters) v m/s (meters/second) a m/s2 (meters/sec / sec) vavg = ∆d / ∆t direction average velocity average acceleration graph slope ∆ “change in” at rest constant (v, a) v avg (d f d i ) (t f t i ) aavg = ∆v / ∆t a avg (v f v i ) (t f t i ) slope = rise / run = ∆y /∆x Questions what is speed? what is velocity? how is velocity different from speed? give an example of constant speed with changing velocity what is average velocity? define acceleration in terms of: velocity speed and direction motion give 2 types of examples of acceleration that are NOT speeding up calculate v and ∆v using the average velocity equation calculate a using the average acceleration equation Give and explain examples of negative position, velocity and acceleration read d vs. t graphs to … identify when an object is … accelerating … speeding up or slowing down … moving quickly / slowly … moving at constant velocity … at rest (not moving) identify what direction an object is moving calculate average velocity for a given interval Questions what is speed? what is velocity? how is velocity different from speed? give an example of constant speed with changing velocity what is average velocity? define acceleration in terms of: velocity speed and direction motion give 2 types of examples of acceleration that are NOT speeding up calculate v and ∆v using the average velocity equation calculate a and v using the average acceleration equation Give and explain examples of negative position, velocity and acceleration read d vs. t graphs to … identify when an object is … accelerating … speeding up or slowing down … moving quickly / slowly … moving at constant velocity … at rest (not moving) identify what direction an object is moving calculate average velocity for a given interval Coordinated Science: Motion Final Review Sheet 𝑣𝑎𝑣𝑔 = ∆𝑑 ∆𝑡 𝑎𝑎𝑣𝑔 = ∆𝑣 ∆𝑡 1. Explain how you can move with constant speed but changing velocity. 2. What does it mean if something has a negative velocity? (Is it possible to have a negative speed?) 3. A snowflake falls from 28 meters high to 4 meters high in 8 seconds. Calculate its average velocity. 4. How can you accelerate with constant speed? 5. Ian speeds up from 3 m/s to 15 m/s in 4 seconds. Calculate his average acceleration. 6. Sandra’s hydroplane accelerates from rest to a velocity of 103 m/s in 5.7 seconds. What is the hydroplane’s acceleration? Assume constant acceleration. 7. Draw a circle around any sections of dots that show uniform motion. 8. Draw a rectangle around any sections of dots that show the cart accelerating. 9. For the position vs. time graph shown, do all of the following: a. Describe the motion in words. Specify direction, whether the motion is uniform, and, if not, whether the object is speeding up or slowing down. b. Calculate the average velocity from 4 to 8 seconds. Coordinated Science: Motion Final Review Sheet 𝑣𝑎𝑣𝑔 = ∆𝑑 ∆𝑡 𝑎𝑎𝑣𝑔 = 1. Explain how you can move with constant speed but changing velocity. 2. What does it mean if something has a negative velocity? (Is it possible to have a negative speed?) 3. A snowflake falls from 28 meters high to 4 meters high in 8 seconds. Calculate its average velocity. 4. How can you accelerate with constant speed? 5. Ian speeds up from 3 m/s to 15 m/s in 4 seconds. Calculate his average acceleration. 6. Sandra’s hydroplane accelerates from rest to a velocity of 103 m/s in 5.7 seconds. What is the hydroplane’s acceleration? Assume constant acceleration. 7. Draw a circle around any sections of dots that show uniform motion. 8. Draw a rectangle around any sections of dots that show the cart accelerating. 9. For the position vs. time graph shown, do all of the following: a. Describe the motion in words. Specify direction, whether the motion is uniform, and, if not, whether the object is speeding up or slowing down. b. Calculate the average velocity from 4 to 8 seconds. ∆𝑣 ∆𝑡








