File
advertisement

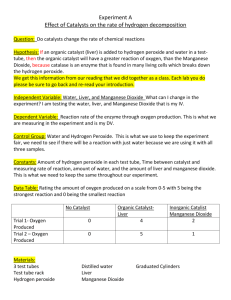
Identifying Mystery Gases Part 1:Hydrogen Peroxide and manganese dioxide You will learn how to use chemical tests to detect oxygen, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide gases. In this experiment, you will observe some chemical reations that produce gases and use the tests to infer which gas is produced Materials: Hydrogen peroxide Manganese Dioxide Glowing splint Add manganese dioxide to the 4ml of hydrogen peroxide. Wait 10s Warning: Hydrochloric acid is corrosive. Any spills on the skin, in the eyes, or on clothing should be washed immediately with Put a glowing splint half way into the test tube cold water. Report any spills to your teacher. Hydrogen peroxide is poisonous and a strong irritant. Manganese dioxide is also toxic. Report any spills to your teacher Question: Record observations in table Each of the following reactions produces a colourless, odourless gas. Which gas is produced in each reaction? Procedure : Materials: Safety goggles Apron 4 test tubes Test-tube rack Hydrogen peroxide Manganese dioxide Toothpick 3wooden splints Candle Lighter Hydrochloric acid Magnesium ribbon (3cm) Tongs Limewater solution Sodium bicarbonate Test –tube stopper Hypothesis: predict what gas will be produced. Pre-lab: Read the following handout and produce a flow chart that describes the steps for each test. Part 1 is done for you. 1. 2. 3. 4. Put on safety goggles. Examine the flow chart and chart for each test. Fill out a hypothesis for each test. Collect 4 test tubes and place into a test tube rack. PART 1: Hydrogen Peroxide and Manganese Dioxide 5. Put a clean, dry test tube in the test-tube rack. 6. Pour in 4ml of hydrogen peroxide solution into the test tube 7. Obtain a tiny amount of manganese dioxide powder on the blunt end of toothpick. 8. Add the manganese dioxide powder to the hydrogen peroxide. Allow the reaction to proceed for 10s, noting any changes. 9. Bring a flaming splint to the mouth of the tube. If nothing happens then put a glowing splint halfway into the test tube. 10. Observe the 2 reactants upon mixing and fill out your observation table. PART 2: Hydrochloric Acid and Magnesium 11. In another test tube, carefully pour about 25ml of Hydrochloric Acid into the test tube. 12. Obtain a 3cm long piece of magnesium ribbon 13. Roll the magnesium into a ball and then using tongs carefully add the magnesium ball to the acid. Wait 10s. 14. Bring a burning splint close to the mouth of the test tube. If no reaction occurs, blow out the flame, insert the glowing splint halfway into the test tube. 15. Record your observations. PART 3: Hydrochloric Acid and Sodium Bicarbonate. 16. Take the last two remaining test tubes and add 4mL of limewater into ONE test tube. 17. In the other tube pour 4mL of hydrochloric acid. 18. Obtain a penny sized amount of sodium bicarbonate. 19. Slowly add the sodium bicarbonate to the test tube containing the Hydrochloric acid. 20. After 5s, put a burning splint near the mputh of the tube, If there is no reaction, blow out the splint and insert a glowing splint. 21. If the splint goes out, carefully pour the gas into the test tube containing limewater and STOPPER. 22. Mix the contents by turning the test tube upside down several times. CLEAN-UP Dispose of all the mixtures in the test tubes as directed by your teacher. Clean all glassware with soap and water. Wipe down your work station. Wash your hands. MYSTERY GASES: THE TESTS A common chemical reaction is combustion (burning). OXYGEN must be present for combustion to take place. 1. Glowing splint ignites(combusts) its oxygen HYDROGEN is very explosive when ignited. 1. A flaming splint will produce a popping sound if hydrogen is present CARBON DIOXIDE does not burn and does not allow other materials to burn. 1. A burning splint will be extinguished in the presence of carbon dioxide. 2. Carbon dioxide will change lime water cloudy. Discussion Questions: 1. For each test you conducted, state what gas was produced and explain HOW you knew. a. Hydrogen peroxide and manganese dioxide b. Hydrochloric acid and Magnesium c. Hydrochloric acid and sodium bicarbonate 2. When the different chemicals were mixed in each test tube, was a chemical or physical change produced and why? 3. What chemical properties distinguish the reactivity between the three mystery gases (Combustion, not combustible or explosive)? 4. Give reasons for the following; a. One of the gases you found is used in fire extinguishers. Which one and Why? b. Another gas was used for many years to float transportation balloons. Which one and why is this gas not used today? c. Another gas is used in hospitals by many patients with breathing. Which one and why? 5. Research and state the chemical reactions that occurred during each reaction. Marking Scheme- Informal Mystery Gases Flow charts /2 T Purpose /1 T Hypothesis /3 T Observations /17 A Discussion /18 C Conclusion /5 C References /1 A