Author template for journal articles
Electronic Supporting Materials for
Preparation of Zirconium Carbonate as Water-Tolerant Solid Base Catalyst for Glucose Isomerization and
One-pot Synthesis of Levulinic Acid with Solid Acid Catalyst
1.
Thermodynamic data for glucose-to-fructose transformation
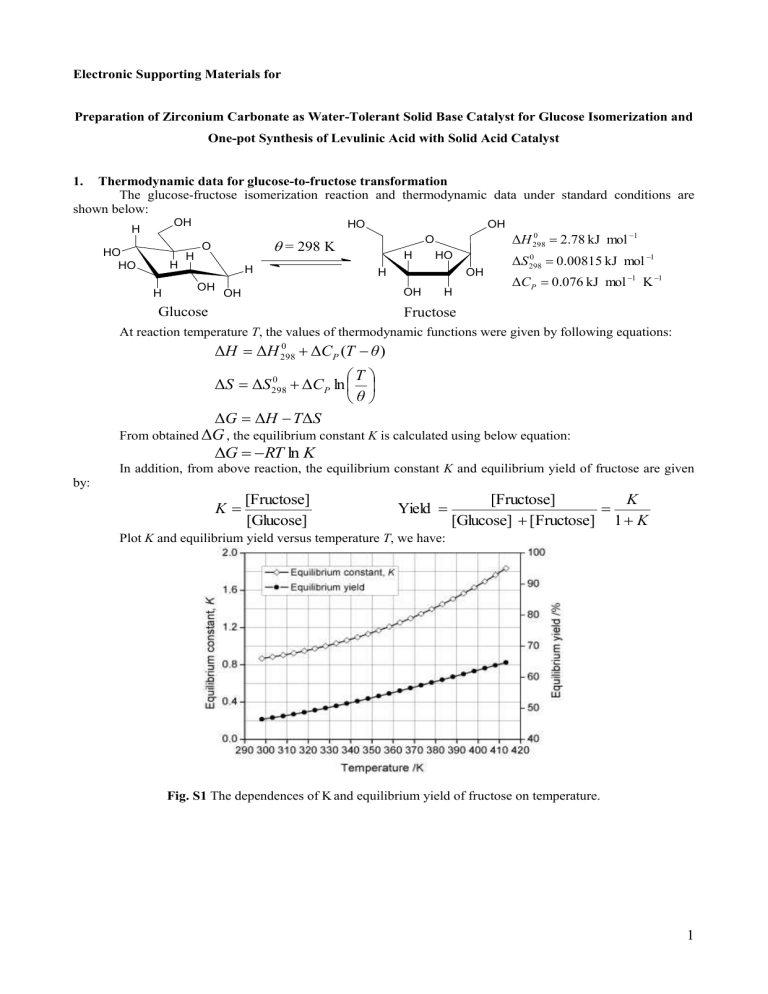
The glucose-fructose isomerization reaction and thermodynamic data under standard conditions are shown below:
H
OH H O OH
H O
H O
H
H
H
O
OH
OH
H
= 298 K
H
H
OH
O
H O
H
OH
Δ
Δ
Δ
H
S
C
0
0
298
298
P
2 .
78 kJ mol
1
0 .
00815 kJ mol
1
0 .
076 kJ mol
1
K
1
Glucose Fructose
At reaction temperature T , the values of thermodynamic functions were given by following equations:
Δ
H
Δ
H
0
298
Δ
C
P
( T
θ
)
Δ
S
Δ
S
0
298
Δ
C
P ln
T
θ
From obtained
Δ
Δ
G
Δ
G
G
Δ
H
T
Δ
S
, the equilibrium constant
RT ln K
K is calculated using below equation:
In addition, from above reaction, the equilibrium constant K and equilibrium yield of fructose are given by:
K
[Fructose]
Yield
[Glucose]
[Fructose]
[Glucose]
[ Fructose]
Plot K and equilibrium yield versus temperature T , we have:
K
1
K
Fig. S1 The dependences of K and equilibrium yield of fructose on temperature.
1
2.
XRD patterns of catalysts
Fig. S2 XRD patterns of catalyst based on zirconium
Fig. S3 XRD patterns of zirconium carbonate dried at different temperatures
2
3.
Possible composition and structure of zirconium carbonate
Prepared ZrC compound have chemical composition Zr(OH)
2
CO
3
ZrO
2 and possible structure below [41]:
O O
H O
Zr
O O
Zr
O OH
4.
Basic site content of ZrC catalysts dried at different temperatures
Table S1 Amount of basic site of ZrC dried at different temperatures determined by titration method with benzoic acid
Entry
Drying temperature
/ o C
Amount of basic site
/mmol g -1
1 80 0.15
2
3
120
150
0.20
0.19
4 200 0.07
Entry
1
Water
/mL
3.0
Solvent
5
Toluene
/mL
0.0
Glu
Conv.
/%
23
250 0.01
5.
Glucose to levulinic transformation in biphasic solvent systems
Table S2 Transformation of glucose to levulinic acid in biphasic solvent system of water/toluene with different volume ratios
Fruc
Yield
/%
Sel.
/%
0 0
HMF
Yield
/%
Sel.
/%
0.3 2
Yield
/%
LA
Sel.
/%
4 17
Yield
/%
FA
Sel.
/%
3 13
2 2.5 0.5 16 0 0 0.4 3 7 44 6 35
3 2.0 1.0 18 0 0 0.4 3 8 44 6 32
4 1.5 1.5 26 0 0 0.4 2 11 43 7 26
Reaction conditions : glucose (0.3 g, 1.67 mmol), ZrC (0.3 g), Amberlyst-15 (0.3 g), reaction temperature (120 o C), 500 rpm, time (24 h).
3