Hydrology Unit- Study Guide Part 1 2015
advertisement

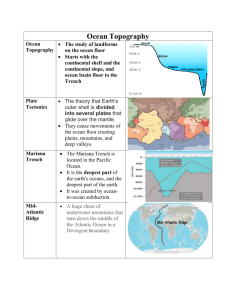
Name:_________________________________________________________________Date:_______Pd:____ Standard S6E3 a. b. and c. 1. What percent of Earth's water is fresh water (rivers, lakes, underground, ice-caps, and glaciers) 3% 2. The percent of the Earth Water that is frozen (ice caps and glaciers) 3. The percent of the Earth’s surface that is covered by water 4. The percent of Earth’s water that is in usable liquid form 5. The percent of the Earth’s water that is salt water 6. Water that collects below Earth’s surface in aquifers Water from rain and melted snow that flows over the land and collects in bodies of water 7. A layer of permeable rock underground that collects and stores water 8. What is source of energy drives the water cycle? 2% 9. What are the three main processes that are involved in the water cycle? 10. Where can water be stored or accumulated? Evaporation, Condensation, Precipitation 11. Define the water cycle. Movement of water from the surface of the Earth to the Earth’s atmosphere back to the surface of the Earth again 12. What is evaporation? Changing from a liquid to water vapor- Sun’s energy 71% 1% 97% Groundwater Runoff Aquifer Sun Aquifer- below the surface and in Rivers, streams, lakes, etc. at the surface 13. What is condensation? Changing from water to a liquid- clouds form 14. What makes water evaporate? 15. What is precipitation? 16. What are some types of precipitation? 17. What does it mean to conserve water? 18. Water that is found underground is called… 19. Water that ends up in our rivers and lakes is called… Sun’s energy Rain, hail, sleet, or snow that falls to the Earth’s surface from clouds Rain, hail, sleet, and snow To save water Groundwater Surface water 20. Where is most of our water on earth found? 21. Draw and label a diagram of the water cycle. oceans 22. The deepest part of the Ocean that is under the most pressure 23. What factors affect the salinity of ocean water (increase or decrease)? 24. What is the name of the area Deep ocean Trench between the shoreline and continental slope (gradually sloping end of a continent that extends out under water)? 25. What is the name of the area between the continental shelf and the continental rise (this ocean floor feature is very steep)? 26. What is the name of the base of the continental slope (made of large piles of sediments) - area located between the continental slope and the deep ocean basin (abyssal plain)? 27. What is the name of the broad flat part of the deep- ocean basin (covered by mud and the remains of marine organisms)? 28. What is the name of the volcanic chain of mountains on the ocean floor - (forms where oceanic crust pulls apart - new oceanic forms here)? 29. What is a submerged (underwater) volcanic mountain on the ocean floor called? 30. A huge crack or depression/ canyon in the ocean floor is also called? Evaporation, water freezing, rainfall, melting of ice/glacier/snow, current Continental shelf Continental Slope Continental Rise Abyssal Plain Mid-Ocean Ridge Seamounts Deep ocean trench form at convergent boundaries 31. What are seamounts that extend up out of the ocean called? 32. Most of the salt in ocean water is…… 33. Create a diagram of the ocean floor and label the following feature: continental shelf, continental slope, abyssal plain, seamounts, mid-ocean ridge, Volcanic island, trench and rift valley Volcanic Islands Sodium chloride