The effects of force and mass on motion printable pages
advertisement

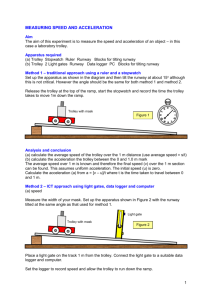
The effects of force and mass on motion Class practical Students can quickly see that force and mass have opposite effects on acceleration. Apparatus and materials For each student group Dynamics trolleys, up to 3 Rods for stacking trolleys Elastic cords, 3 Runway Stopwatch or stopclock String Health & Safety and Technical notes Long runways or heavy shorter ones should be handled by two persons. In operation ensure that a string is tied across the bottom of the runway, to prevent the trolley falling onto the floor (or someone's foot). It might not be possible for every group to have three trolleys at all times, and so groups may need to share. Procedure a Set up the runway and compensate for friction, as in the experiment Compensating for friction [2]. b Accelerate a single trolley using a single strand of elastic cord. c Measure the time taken to travel a marked distance along the runway. d Predict how this time will change if you double the force by using two elastic cords in parallel, stretched by the same amount as before. Try it out to test your prediction. e Predict how the time will change if you double the mass (approximately) by stacking another trolley on top of the first one. Test your prediction. f Predict how the time will change, compared with your first measurement, if you double both the force and the mass. Test your prediction. g Predict how the time will change if you treble both the force and the mass. h If a ticker-timer is used then the acceleration can be measured. See the experiment Finding average acceleration with a ticker-timer [3]. Teaching notes 1 The degree of necessary compensation varies with the number of trolleys. Students will obtain the best results if they readjust the slope of the runway when they increase the number of trolleys, so that it is still compensated for friction. 2 Make sure that students understand that the time is a reliable indication of acceleration. The shorter the time, the greater the acceleration. 3 When the mass of a moving object is changed, students are apt to find the interpretation more difficult. For them, mass is more artificial and less familiar than force. The reciprocal relationship between F and m for a constant acceleration is itself a barrier. 4 The ratio of force/mass is constant if the acceleration is kept constant. This experiment was safety-checked in March 2005 Source URL: http://www.nuffieldfoundation.org/practical-physics/effects-force-and-massmotion