The Ultimate Take
advertisement

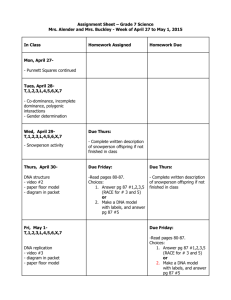
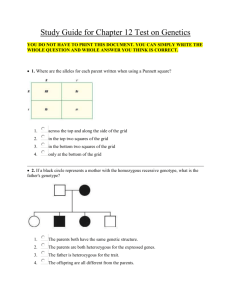
The Ultimate Take-Home Test! Instructions: Unlike every other assignment, you MUST PRINT this out and bring it to class on Friday! Please put your name on the back of the last page. This is NOT open notes. But! I’ll grant you ONE “get out of jail pass”: If you get to a section that you have no idea about, you can pause the test, and go study up on the topic. Then close your notes again, and proceed. I trust you to do what’s right. DNAmazing! 1. DNA stands for ________________________________________________________________. 2. DNA is both a physical molecule and __________________________________. 3. DNA is made up of 4 bases called ____________________________, _______________________________, _______________________________, and __________________________________. 4. __________ The bases fit together by both __________ and __________. (a) size and shape (b) shape and charge (c) molecular weight and charge (d) color and shape 5. ___________ This kind of bond is what keeps the bases together: (a) Covalent (b) hydrogen (c) strong (d) weak 6. ___________ This is the way that DNA communicates its intricate message: (a) Magnetism (b) molecular weight (c) bonds (d) sequence of bases 7. ___________ If the DNA coding strand is ACAGTCGAT, the complementary (non-coding) strand will be which? (a) ACAGTCGAT (b) TGTCAGCTA (c) UGUCAGCUA (d) none of these RNA RNA stands for _____________________________________________________________________. 1. ___________ Which of the following are differences between DNA and RNA? (a) RNA is single stranded (b) DNA has nucleotides (c) RNA uses Uracil (d) RNA’s shape matters to its function 2. ______________ The "Central Dogma" of protein synthesis can be summed up as follows: (a) DNA --> transcription --> mRNA --> translation (b) DNA --> translation --> mRNA --> transcription (c) DNA --> mRNA --> transcription --> translation (d) DNA --> mRNA --> translation --> transcription 3. __________ In transcription, which of the following “unzips” the DNA? (a) RNA polymerase (b) DNA polymerase (c) helicase (d) mRNA 1 4. __________ In transcription, which of the following “assembles” the mRNA by “reading” the DNA? (a) RNA polymerase (b) DNA polymerase (c) helicase (d) mRNA 5. __________ In transcription, where does the mRNA go after it has been created? (a) Out of the nucleus (b) into the cytoplasm (c) into a ribosome (d) out into oblivion 6. __________ A DNA gene strand with the base sequence CCA - TAT - TCG will be transcribed into RNA with the base sequence: (a) CCA - TAT – TCG (b) GGU - AUA – AGC (c) CCA - UAU – UCG (d) GGT - ATA – AGC 7. Describe the process of translation below: GENETICS! _____________________1. A gene that masks or overshadows the expression of another gene. _____________________2. An organism possessing two different alleles for a trait, such as Tt. _____________________3. The Austrian monk who established the first laws and principles of heredity. _____________________4. A small segment of DNA that controls the expression of a hereditary trait. _____________________5. The offspring of parents with different traits are referred to as? _____________________6. Term that refers to sex cells – the egg and sperm cells. _____________________7. A diagram that is used to show all the allele combinations that might result from a genetic cross between two parents. In a genetic cross, how does one represent a dominant allele? _____________________8. _____________________9. How many alleles must be present in order for a trait to show up in the offspring? ____________________10. The different forms of a gene are called? ____________________11. What types of plants did Mendel use in his experiments? 2 _______12. Mendel considered those traits that were hidden in the first generation to be: (1) heterozygous (2) recessive (3) incompletely dominant (4) incapable of breeding true (5) incapable of being inherited. _______13. Brown eye color is dominant; blue eye color is recessive. If a brown-eyed man marries a blueeyed woman and they have a brown-eyed son and a blue-eyed daughter, we can safely conclude that: (1) the man is not the true father (2) the man is heterozygous (3) eye color is sexlinked (4) the man has the genotype for blue eyes but the phenotype for brown eyes. _______14. If pure-breeding tall peas are crossed with dwarf peas, the resulting offspring will always be tall. This illustrates Mendel's law of (1) segregation (2) unit characters (3) dominance and recessiveness (4) independent assortment. _______15. Which of the following would be a homozygous recessive individual? (1) Tt (2) tt (3) TT (4) both tt and TT. _______16. Mendel's principle of segregation states that factors separate during: (1) fertilization (2) gamete formation (3) cross-pollination (4) seed dispersal. _______17. The appearance of an organism, such as smooth versus wrinkled seeds, is referred to as a: (1) genotype (2) variety (3) phenotype (4) factor (5) allele. _______18. The genetic makeup of an organism is called: (1) a gene pool (2) its phenotype (3) a trait (4) an allele (5) its genotype. _______19. An organism with two identical alleles for a given trait is: (1) homozygous (2) dominant (3) independently assorting (4) self-pollinating (5) heterozygous. __2 _20. A cross between a plant with red flowers and one with white flowers produces an F 1 generation that is all pink. The simplest explanation for this is: (1) crossing over (2) nondominance or incomplete dominance (3) mutations (4) sex-linked inheritance (5) multiple alleles. _______21. In a dihybrid cross between an individual that has the genotype “AABB” and an individual with the genotype of “aabb”, all of the resulting offspring will have a genotype of: (1) AABB (2) AaBB (3) AaBb (4) AABb (5) aabb _______24. Which of the following would represent the sex chromosomes of a normal female? (1) XX (2) XY (3) XXY (4) XhXh (5) XYY. _______25. Chromosomes that are the same in both males and females are called: (1) sex chromosomes (2) autosomes (3) homologous (4) codominant (5) recombinant. _______27. Genes that have more than 2 alleles for the trait are referred to as: (1) multiple alleles (2) incomplete dominance (3) polygenic inheritance (4) codominant. 3 In humans, dimples (D) are dominant over no dimples (d). Curly hair (A) is dominant over straight hair (a). Paul, who is heterozygous for dimples and curly hair, marries Jane, who has curly hair but does not have dimples. Jane's mother had straight hair, but her father had curly hair. Paul and Jane had a child named Peter, who had curly hair but did not have dimples. Create the dihybrid cross for Jane and Paul’s potential offspring. This seems tricky, but it is doable! Write down the possible genotypes and phenotypes in the columns below. ________1. What is Jane's genotype? ________2. What is Paul’s genotype? ________3. Where did Jane get her gene for curly hair? From her mother or father? ________4. True or False: Jane's mother was heterozygous for curly hair? ________5. What percent of Paul and Jane's children should have curly hair and dimples? ________6. What percent of their children would have straight hair and no dimples? ________7. What percent should have dimples but not curly hair? ________8. What is the probability of getting any offspring with dimples? 4 You guys haven’t learned this, but you can try it! In the case of incomplete dominance, it’s not about the dominant “winning” and the recessive “losing”. When they are heterozygous, the blend traits together. In the cross below, when BB mixes with WW, you get a blue BW. This isn’t for credit, so don’t be scared! Feather color in chickens is due to incomplete dominance. BB = Black chicken, WW = White chicken, and BW = Blue chicken. Cross a white chicken with a blue chicken. Fill in the cross below, and put the possible genotypes and phenotypes in the columns. ________1. What fraction of the offspring will be blue? ________2. What fraction of the offspring will be black? ________3. What fraction of the offspring will be white? EXTRA CREDIT: Use the information above to complete the next part. Double comb (R) in chickens is dominant over single comb (r). Cross a white heterozygous double comb chicken to a black single comb chicken. Write out the possible genotypes and phenotypes in the columns. 5 ________4. What is the genotype of the white heterozygous double comb chicken? ________5. What is the genotype of the black, single combed chicken? ________6. What fraction of the offspring will be blue double comb? ________7. What fraction of the offspring will be blue? ________8. What fraction of the offspring will be single comb? ________9. What fraction of the offspring will be white double comb? Ok, great!! Thank you for your concentration and effort on this thang! Give yourself a pat on the back: You’ve learned something important, and this is us telling your brain not to forget it! 6