No45-HandlingStoringandTransportingHazardousSubstances
advertisement

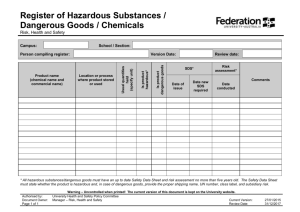
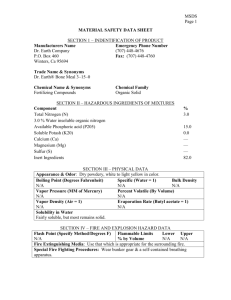
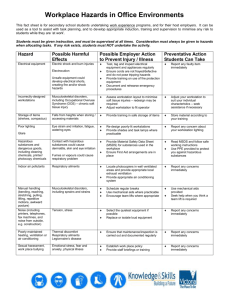
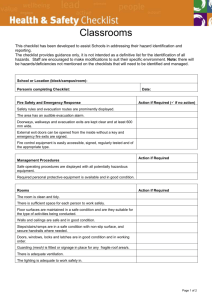
Code of Practice COP 45 Issued July 2010 No 45 – HANDLING, STORING AND TRANSPORTING HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCES 1. BACKGROUND TO COP Reason for COP: To prevent injury and protect the health and safety of employees by taking necessary precautions when handling, using, storing and transporting hazardous substances. Relevant Regulations: Employee Training/Skills Reqd: All employees with potential to be exposed to hazardous substances and those supervising others using hazardous substances shall be trained in: Purchasing Policy Tools/Plant : Hazardous Substances and New Organisms Act 1996 Health and Safety In Employment Act 1992 Land Transport Rule: Dangerous Goods 2005 Safe chemical handling techniques, spill response. Procedures, appropriate use of PPE and Material Safety. Data Sheets (MSDS) and use of fire extinguishers. First Aid training. Council will ensure staff have ready access Material Safety Data Sheets and will provide and maintain adequate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) to protect staff who work with hazardous substances. 2. COP WORK PROCEDURE ETY Handling Storing and Disposing Hazardous Materials: 1. Ensure that Hazardous substances are stored and handled in accordance with the HSNO Act 1996, which is listed within the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS). 2. Staff involved with handling and using hazardous substances should at all times comply with the manufactures instructions as listed on the label. In the absence of a label the MSDS requirements must be followed. 3. Wear personal protective equipment (safety glasses, apron, gloves as required) in the manner in which you have been trained and have ready access to MSDS. 4. Ensure that the disposal of dangerous goods/hazardous substances is carried out in accordance with all local bylaws and that the disposal does not contravene any provisions of the Resource Management Act 1991 and any additions or amendments. If in doubt ask Hawke’s Bay Regional Council’s Hazardous Waste Advisor. Inappropriate disposal is a dismissible offence. Spills: 1. Promptly access the Materials Safety Data Sheet to determine the actions to be taken to clean up and dispose of the spill. Document1 Page 1of 3 2. Locate the spill kit in the storage room and use appropriate Personal Protective Equipment as detailed on the MSDS. If you are by yourself, if the spill is large or if you are unsure on how to clean it up, contact the pollution team at HBRC Dalton Street Office. 3. Report any accident/incident involving hazardous materials immediately via HBRC Accident/Incident Reporting system. Transporting Hazardous Substances: 1. Ensure that the quantity of hazardous substances being transported is within the limit defined in the regulations. This limit can also be found in HBRC Hazardous Substances Management Procedure. 2. Ensure that the hazardous substance is labeled so that the contents of the container can be quickly identified and load the vehicle safely to ensure the container does not get damaged. Purchasing Hazardous Substances: 1. Purchase the most appropriate and least hazardous material in the minimum quantity and under no circumstances purchase Formalin without Managers approval. 2. Ensure that a Materials Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) is obtained from the manufacturer when ordering hazardous materials and update old MSDS with new MSDS. 3. Update the hazardous substances inventory and ensure that the MSDS are placed in easy access to where the hazardous substance will be used. Document1 Page 2of 3 Hazard Identification & Analysis Worksheet – HBRC Work Task, Activity or Item of Equipment What can cause harm? How could potential harm situation arise? Significant Hazard Yes/No* Controls that Reduce Harm 045 – Handling, Storing and Transporting Hazardous Sustances Using Hazardous Chemicals Storing Hazardous Chemicals Transporting Hazardous Chemicals Document1 Working in Laboratory – Generic Hazards Skin and eye Incorrect or no PPE irritations, Inexperience with hazardous ingestion or substance chemical No MSDS available burns Personal Hygiene Date: JULY 2010 Y Y Y Y Incorrect or no PPE No ventilation in working area Y Y Toxic fumes igniting Y Incompatible substances stored together. Hazardous chemicals not labelled. No MSDS Sheets available. Y Chemicals stored gradually spilling/ leaking Chemicals spilling while transported leading to unprotected exposure and possible fire Containers of hazardous substance unbunded Y Carrying more than the limit allowed in the regulations in inappropriate containers. Chemical container unsecured while driving. Y Only carry chemicals in approved containers and within the Y approved limits for full licence holders (this can be found in HBRC Hazardous Substances Management Procedure). Secure the container so that it does not get knocked around and damaged while driving. Wear PPE when handling chemicals Staff training on safe handling techniques and ready access MSDS. There is a purchasing procedure in place to ensure MSDS are obtained when chemicals are purchased. Eating and drinking in laboratory prohibited. Wash hands before eating and remove protective equipment before entering eating areas. Using Chemicalssplashes and inhalation of fumes Toxic fumes and fire Incorrect storage leading to corrosion, fire explosion etc Status Y Y Wear PPE when handling chemicals and work in a well ventilated area (open doors) /fume cupboard. Follow manufactures instructions located on MSDS Sheets Work in a ventilated area and always use MSDS. Allow no naked flames in lab. Refer to MSDS when Storing Hazardous Substances, and only store compatible classes together i.e. Acids with acids, and flammable with flammable. All chemicals are to be labelled and a purchasing procedure is in place to ensure MSDS are obtained. Bund all hazardous chemicals and check regularly for leaks and spills in storage cabinet. Page 3 of 3