File - NCEA Level 2 Biology
advertisement

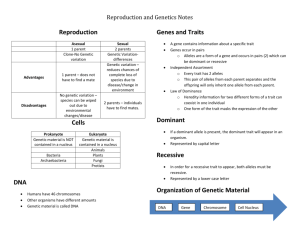
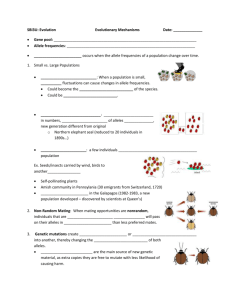
Timaru Girls’ High School Level 2 Biology External 4 Credits Keywords for Unit: 2.5 - Demonstrate Understanding of Genetic Variation and Change 1 Allele One of the alternative forms of a gene. Amino acids Any of a group of water-soluble organic compounds that possess both a carboxyl(-COOH) and an amine (-NH2) group attached to the same carbon atom. Anticodon A sequence of three nucleotides on a tRNA molecule that matches with a specific codon on a strand of mRNA during translation. Centromere The part of a chromosome that attaches to the spindle during cell division. Chromatid A threadlike strand formed from a chromosome during the stages of cell division. 2 3 4 5 6 Chromosome 7 8 Cloning A threadlike structure made of DNA and (in eukaryotes) associated histone proteins on which the genetic information of an individual is stored. artificial production of genetically identical individuals Co-dominance The condition that arises when both alleles in a heterozygous organism are dominant and fully expressed - eg. the human blood group AB. Codon A triplet of nucleotides within a molecule of messenger RNA that specifies a particular amino acid during the synthesis of proteins in a cell. Diploid Describing a cell or organism with twice the haploid number of chromosomes. 11 DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid. The genetic material of most living organisms. It plays a central role in the determination of hereditary characteristics by controlling protein synthesis in cells. 12 Dominant allele Double Helix The allele that is expressed when two different alleles of a gene are present in the cells of an organism. It is denoted by a capital letter. ladder-like molecule twisted into a helix Eukaryotic cells Cells that have a distinct nucleus where the cell’s genetic information is stored. F1 generation The first generation of offspring resulting from an arranged cross between selected parents in breeding experiments. 9 10 13 14 15 16 F2 generation 17 Fertilization The second generation of offspring in breeding experiments, obtained by crosses between individuals of the F1 generation. fusing of an egg and sperm 18 Gametes 19 Gene 20 A reproductive cell that fuses with another to form a zygote - eg. eggs (ova) and sperm (spermatozoa). A section of DNA that codes for a particular protein and cannot be broken by recombination. Genetic code The genetic information in DNA which controls the manufacture of specific proteins by the cell. It takes the form of a series of triplets of bases in DNA. 21 Genome All the genes contained in a single (haploid) set of chromosomes. 22 Genotype The genetic composition of an organism, i.e. the combination of alleles it possesses. 23 Haploid Describing a cell or organism with a single set of unpaired chromosomes. 24 Heterozygous Describes an organism that has two different alleles controlling a particular feature. Histone Water-soluble proteins found in association with the DNA of eukaryotic chromosomes. They serve as a scaffold around which the DNA coils. 25 27 28 Homozygous Matching pairs of chromosomes, i.e. Chromosomes that have the same structural features. In diploid cells, one chromosome comes from the female parent, the other from the male parent. Describes an organism that has two of the same alleles for a trait. Incomplete dominance The condition where neither allele controlling a characteristic is dominant and the resulting phenotype is partially influenced by both alleles. 29 Independent assortment The separation of the alleles of one gene into gametes independently of the way in which the alleles of other genes have segregated. 30 Inheritance The transfer of genetic traits from one generation to the next. Lethal genes A mutant form of a gene that eventually results in the death of an organism if expressed in the phenotype. Most of these genes are recessive, eg. Sickle-cell anaemia. 26 Homologous Chromosomes 31 32 Meiosis 33 Mitosis 34 A type of cell division that gives rise to four gametes each with half the chromosome number of the parent cell. A type of cell division that results in two daughter cells, each having a nucleus containing the same number and kind of chromosomes as the mother cell. Monohybrid The offspring of a cross between parents that differ in the alleles they possess for one particular gene, one parent having two dominant alleles, the other two recessives. mRNA RNA that carry’s the genetic code transcribed from DNA to the ribosomes. Multiple alleles Three or more alleles that produce different versions of the same protein. Eg. The human ABO blood group system has three alleles IA, IB and i. IA and IB are co-dominant alleles. 37 Nucleotide An organic compound consisting of a nitrogen-containing purine or pyrimidine base linked to a sugar and a phosphate group. 38 39 Pedigree Chart Phenotype a chart used to identify genotypes in families The observable characteristics of an organism. 35 36 Prokaryotic cells Cells where the genetic material is not enclosed in a cell nucleus. Protein synthesis The process by which living cells assemble amino acids into proteins based on the genetic information carried in the DNA of the chromosomes. Punnett Square A grid used to calculate the expected offspring phenotype ratios resulting from a cross between two parents of known genotypes. Pure-breeding A lineage where characteristics are passed on unchanged from generation to generation. Purines The chemical family to which the organic nitrogenous bases adenine and guanine belong. Pyrimidines The chemical family to which the organic nitrogenous bases uracil, thymine and cytosine belong. 46 Recessive allele An allele whose effects are masked by those of a dominant allele. It is denoted by a lower case letter. 47 rRNA A type of RNA that is present in the ribosomes. 48 SelfReplication ability of DNA molecules to make identical copies of themselves 49 Somatic cells All cells in the body other than the reproductive cells. Test-cross An organism with a dominant phenotype may possess two dominant alleles, or one dominant and one recessive. This can be determined by crossing it with an organism showing the recessive characteristic (ie. homozygous recessive). Trait feature whose appearance is determined by genes (inherited) Transcription The process in living cells in which the genetic information of DNA is transferred to a molecule of mRNA as the first step in protein synthesis. Translation The process in living cells in which a sequence of mRNA triplets (codons) is used to build a polypeptide chain during protein synthesis. Triplet A sequence of three nucleotides coding for a specific amino acid during protein synthesis. tRNA RNA that is responsible for bringing specific amino acids to the site of translation on the ribosome. Variation Differences between organisms created by their different genetic make-up. It can either be discrete, where a trait is controlled by a single gene; or continuous, where a trait is influenced by several genes. 40 41 42 43 44 45 50 51 52 53 54 55 56