launch
advertisement

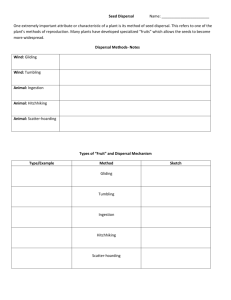
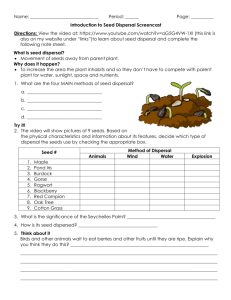
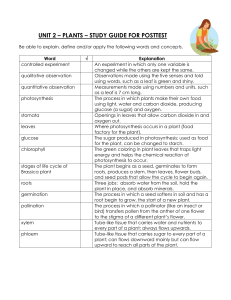
LESSON PLANS-MS.CHANDLER-WEEK __JAN. 2-6,2014 MONDAY – INTRODUCE- PLANTS Unlike animals, plants can make their own food through the process of photosynthesis and are incapable of moving about. In this conc 6.L.1.2 - Explain the significance of the processes of photosynthesis, respiration, and transpiration to the survival of green plants and other organisms. Lesson Overview Lesson Objectives: ept, you will learn more about plants. Curriculum Standards By the end of this lesson, students should be able to: Describe the structure of a flowering plant. Explain plant reproductive strategies and how they allow plants to thrive. Describe photosynthesis Identify and describe the parts of a plant Overarching Questions: How do organisms live, grow, respond to their environment, and reproduce? Focus Questions: How do organisms grow and develop? How do organisms obtain and use the matter and energy they need to live and grow? How do food and fuel provide energy? If energy is conserved, why do people say it is produced or used? Lesson Questions: How do plants obtain and store energy from the environment? How does plant structure aid in photosynthesis? Why are plant reproductive structures ideal for plant reproduction? Background for the Teacher Photosynthetic plants use energy from the sun, water, and carbon dioxide from the environment to store energy in the form of carbohydrates. Oxygen is released when a plant makes carbohydrates in this way. Photosynthetic organisms are primary producers, and are located at the bottom of nearly every food chain on Earth. Plants are made of cells which are organized into specialized tissues. Some of these tissues include root tissue, leaf tissue, xylem, phloem, bark, and reproductive tissues. Plants have roots to pull water into themselves. The water travels through xylem to the leaves, stems, or needles. Cells in the leaves, stems, or needles make carbohydrates by using the energy of sunlight to combine carbon dioxide and water. These cells then release excess oxygen, wastes, and water into the air. The carbohydrates are transported to other parts of the plant by phloem. Water is pulled through the whole system, from roots to leaves, through the process of transpiration. Transpiration occurs when water evaporates out of little holes on each leaf, called stomata. As water leaves the stomata, the natural cohesion of water molecules pulls water like a chain through the plant. Xylem is made of hydrophilic materials, which helps water climb up very tall plants through the process of adhesion. PUT WORDS ON BOARD –INTRODUCE KEY TERMS AND DEFINE THEM Key Vocabulary: plant, photosynthesis, root, leaf, stem, cone, needle, xylem, phloem, producer, flower, pollen, pollinator, sexual reproduction, carbon dioxide, oxygen, fruit, seed, seed dispersal, stomata, pollination TUESDAY-EXPLORE-DISCOVERY EDUCATION EXPLORE (Guided Inquiry 55 minutes or Directed Inquiry 50 minutes) Exploration Student Resources for Guided Inquiry Reading Passages Plant Planet Could Plants Grow on the Moon? (Spanish Version) Video Segments Plants: Essential Contributors of the Carbon Cycle Animal Respiration and Plant Photosynthesis Chloroplasts and Photosynthesis Four Groups of Plants All Living Things Need and Use Energy WEDNESDAY-THURSDAY Essential Question(s): Why are plant reproductive structures ideal for plant reproduction? Guided Inquiry Have students respond to the essential questions by exploring the Discovery Education resources listed in the Explore section. Ideally, each student will use more than one resource for information, but no student is expected to use all of the resources within the time allotted. Encourage students to take notes as they explore. If needed, you may want to further guide students by asking more specific questions: What function does the flower of a plant fulfill? Why is it important for seeds to be small and tough? How do plants overcome their inability to move? Circulate among the students as they are exploring and challenge them to summarize for you what they have learned. Encourage students to use reading, viewing, and note-taking strategies to get the most out of each resource. Directed Inquiry Have students use the video segments Seed Dispersal, Fruits and Seed Dispersal, and the reading Pollination to Bee or Not to Bee to define the terms: fruit, seed, flower, dispersal. Review student definitions as a class, clarifying and explaining where necessary. When students have defined these terms, have them work together in groups of three to create an illustrated concept map that shows the relationships between each term. For example, flowers develop seeds, which can be encased in fruits, which allow for dispersal. When student groups are finished, encourage members to share their concept maps with the class. Finally, have students draft a response to the third essential question in their groups. Then, review student responses before moving on to the Explain section. EXPLAIN (15 minutes) Have students review plant reproduction by doing the reading An Apple...a Year. When students are done, have them return to their concept map groups to create a parallel concept map for apple trees, based on their reading and the terms from the explore section. Review these parallel maps with the class View Video Segment (5:24) All Living Things Need and Use Energy Plants use energy to grow and make new parts. Phloem tubes carry glucose throughout the plants.... LAUNCH Video Segment (1:04) Animal Respiration and Plant Photosynthesis Clip provides an explanation of animal respiration as a process that uses oxygen and gives off ... LAUNCH Video Segment (0:50) Chloroplasts and Photosynthesis Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts. Plants convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water ... LAUNCH Full Video (17:46) Development of Plants: Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Analyzes the internal and external structures that separate these complex plants from simpler o... LAUNCH Video Segment (7:49) Four Groups of Plants Plant species can be divided into four types: bryophytes, ferns and fern allies, gymnosperms, a... LAUNCH Video Segment (3:24) Fruits and Seed Dispersal Once pollination has occurred, a seed develops inside a protective fruit. Eventually the seeds ... LAUNCH Video Segment (4:10) Leaves and Photosynthesis Leaves are essential to plants, since they perform photosynthesis, the process by which plants ... LAUNCH Video Segment (4:15) Seed Dispersal Seeds travel away from their parent plant by air, on the water, by exploding, and on animals' f... LAUNCH FRIDAY-WRITING AND ASSESSMENT BRAINPOP