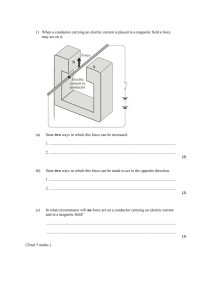
class xii
advertisement

Difficulty level –L1-1 Class XII Physics SAMPLE PAPER XII - PHYSICS Time : Three Hours Max. Marks : 70 General Instructions (a) All questions are compulsory. (b) There are 30 questions in total. Questions 1 to 8 carry one mark each, questions 9 to 18 carry two marks each,questions 19 to 27 carry three marks each and questions 28 to 30 carry five marks each. (c) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one question of two marks, one (d) question of three marks and all three questions of five marks each. You have to attempt only one of the given choices in such questions. (e) Use of calculators is not permitted. (f) You may use the following physical constants wherever necessary : c = 3 x 108ms-1 h = 6.6 x 10-34Js e = 1.6 x 10-19 C Boltzmann constant k = 1.38 x 1023 JK-1 Avogadro’s number NA = 6.023 x 1023/mole Mass of neutron mn = 1.6 x 10-27 kg ________________________________________________________ 1. The radius of innermost electron orbit of a hydrogen atom is 5.3X10-11m.What is the radius of orbit in the third excited state? 2. What is the range of frequencies used for TV transmission? 3. In which orientation, a dipole placed in a uniform electric field is in i)unstable ii) stable equilibrium 4. Calculate the speed of light in a medium whose critical angle is 30 0 Name a physical quantity whose S.I unit is N /C. Is it scalar or vector quantity? 5. 6. Define self inductance of a coil. Write its SI units 6. A 10 ohm thick wire is stretched so that its length gets doubled. Assuming that there is no change in its density on Stretching. Calculate the new resistance of the wire. 7. 8. What is the work done by magnetic field on a moving charge? Give the nature of V-I graph for i) ohmic ii) non ohmic circuit elements. Give one example of each type. 9. Name the phenomenon associated with the production of back emf in a coil due to change of electric current through the coil itself. 10. Name and define the S.I unit used for measuring this characteristic of the coil. 11. Name the device that converts changes in intensity of illumination into changes in electric current. Give any three applications of this device. 12. Use the mirror equation to deduce that a convex mirror always produces a virtual image independent of the location of the object. 13. What happens to band width i) in forward bias ii) in reverse bias? 14. Derive relationship between real depth and apparent depth. 15. Calculate the ratio of de Broglie wavelength associated with a deuteron moving with velocity 2v and an alpha particle accelerated with potential difference V. 16. Explain with suitable diagram the working of Zener diode as voltage regulator. 17. Define the term i) disintegration constant ii) average life of a radio active element 18. Prove that average power across a capacitor is zero 19. An electric dipole of dipole moment P is placed in a uniform electric field of intensity E. Write the expression for the torque experienced by the dipole. Identify two pairs of perpendicular vectors in the expression. 20. Derive an expression for between current density, conductivity and electric field. 21. Write the conditions for minimum deviation for a prism. Also derive an for refractive index of the material of prism in terms of angle of prism (A) angle of minimum deviation (Dm). 22. Obtain an expression for the magnetic moment of an electron in a circular orbit of radius r and moving with a speed v. State the rule to find its direction. 23. What are EMW? Write their properties. 24. Write postulates of Bohr’s atom model. Prove that the radius of an electron in a stationary orbit is α n2 .Where n is the number of orbit. 25. Explain the working of junction diode as i) half wave rectifier ii) full wave rectifier. 26. What are the elements of communication system? Explain them separately 27. State Ampere’s circuital law. Use this law to obtain an expression for magnetic field due to a toroide solenoid. OR What is Biot-Savart Law? Use this law to obtain an expression for magnetic field at the center of a circular coil 28. State the principle, construction and working of Vande Graaff generator with labeled diagram. OR Derive the expression for the capacitance of parallel plate capacitor. Discuss the effect of dielectric on capacitance. 29. What is interference of light? Write any two conditions for interference of light. Using young’s double slit experiment derive expression for the fringe width in interference pattern OR Derive the relation between the focal length of convex lens in terms of radius of curvature of two surfaces and refractive index of material of lens. Write the sign convention used in the derivation of this relation. Calculate the focal length of a convex length of refractive 1.5 and each of radius 20cm. 30. Write the principle, construction, and working of transformer. Write the various losses in transformer. Is it possible to construct 100% efficient Transformer ? Explain. OR Write the principle, construction and working of A.C generator. Why does long distance power transmission preferred on high voltage MARKING SCHEME(L1-1) 1. r α n2 : r = 47.7X10-11m (1) 2. 54 M Hz to 890 M Hz. (1) 3. i) 1800 ii) 00 ( 1/2+1/2) 4. c/v=1/Sin 30. v=c/2 = 1.5X108 m/s ( 1/2+ ½) 5. Electric field, Vector Quantity ( ½+1/2) 6.It is the property of the coil to oppose the change of electric current or flux within it. henry 7.R=ρl/A (1/2+1/2) resistance will be 4 times 8.ZERO 9. straight line, i.e 40 ohm ( ½ +1/2 ) (1) curved line metallic conductor vacuum diode (½+1/2+1/2+1/2) 10.self induction.s.i unit;henry. One henry is defined as the magnetic flux developed in the coil per unit electric current through it. (1/2+1/2 +1) 11.photo diode . it is used i.)in detection of optical signals ii)in light operatedswitches iii)in electronic counters. (1/2+1/2+1/2+1/2) 12.The mirror equation is 1/u +1/v =1/f. so 1/v =1/f -1/u As f is taken as positive for convex mirror and u is generally taken negative so 1/v as well as v will be always positive and image will be virtual. (1+1) 13.i)in forward bias band width decreases where as in reverse bias it increases. (1+1) 14. μ= Real depth/ apparent depth 2 15. for deuteron λ= h/mv,for alpha particle λ= 12.27/V1/2 16 Circuit diagram ½ Explanation 1+1/2 17.Define disintegration constant and average life (1 +1 ) 18. Pav = Erms X Irms X Cos θ ½ 1+1 For capacitor θ = 900 cos900 =0 Pav = 0 1 ½ 19.diagram ½ Derivation 2 Pair of perpendicular vectors 20.j= I/A= neAVd /A = neVd ½ 1 Vd = eEt/ml so, j=ne2Et/ml J= E (et/ml) = σE 1 1 21. Angle of incidence i = Angle of emergent e d = (i1+i2 )+(r1+r2 ) 1 1 R1+r2 = A but r1=r2 = r so r = A/2 I1=i2=I so I = A+Dm/2 ½ ½ From Snell’s law μ= Sin i/Sin r or μ= Sin(A+Dm)/2 1 SinA/2 22. I= e/t m =IA= eA/t T= 2Лr/v so M= evr/2 Direction 23.Definition 1 1 1 1 Properties : i) They are transverse in nature 1/2 ii) They transfer the energy 1/2 iii) They travel with the speed of light in vacuum 1/2 iv) They can superimpose on each other 1/ 2 24. I postulates : Electrons revolves around the nucleus in certain permitted orbits. 1/2 II postulate : The angular momentum of an electron should be an integral multiple of h/2Л. 1/2 III postulate : When an electron jumps from an higher energy level to a lower energy level than it radiates energy equal to the energy difference between these two levels. i.e E = E2 – E1 1/2 From I postulate mv2/r = ke2/r2 1/2 From II postulate mvr = nh/2Л 1/2 From the above equations r = n2h2/4Л2kme2 or r α n2 1 25. diagram of half wave rectifier 1/2 For the positive half cycle of ac applied diode D is forward bias and for negative half cycle diode is reverse bias.In this way half cycle is rectified 1 diagram of full wave rectifier ½ For the positive half cycle of applied ac diode D1 is forward bias and D2 is reverse bias. So output obtained through D1. For the negative half cycle of ac applied D1 is reverse bias and D2 is forward bias. In this way the output is obtained through D2. In this way full cycle of ac is rectified. 1 26.Elements of communication i)sender ii)channel iii)receiver 1 Sender: There is a sender who sends the message after sorting and coding the message received. Medium: Some thing through which the signal passes called medium or chnnel Receiver: There is a receiver at the other end which receive the signal after the decoding or demodulation. 2 27.State ampere’s circuital law ; According to this law for a closed surface the line integral of B.dl is equal to μ0 times the total current 1 Derivation of magnetic field for toroid 2 Or State Biot - savart’s law; According to this law the magnetic field due to a current element is dB = μ0 Idlsinθ/4Л r2 1 Derive of magnetic field at the centre of circular coil carrying current 2 28. Principle: It works on the principle of sharp point action Construction: 1 1+1/2 Working: 2+1/2 Or Expression for capacitance: Electric field between the plates pf capacitor is E0 = q/A€0 the potential difference between the plates is V = E0d = qd/€0A Capacity C = q/v = €0A/d so 2 Effect of dielectric on capacitance: The capacity of a parallel plate capacitor with dielectric constant of dielectric constant k is C = k€0A/d. So as the dielectric constant of the medium increase the capacity of the capacitor also increase. It is due to the polarization polarization of dielectric which decreases the electric field and hence the potential difference. As the potential difference decrease the capacity of the capacitor increase 3 29. Interference of light: The unequal redistribution of light energy when the two rays of light coming from two coherent sources of light superimpose on each other is called interference of light Conditions of Interference: i) The two sources should be coherent. ii) the light should be monochromatic 1 Derivation of fringe width using young’s double slit experiment Β = λD/d 3 Or Derivation ; The relation is 1/f = (μ-1)(1/R1-1/R2) 3 Sign convention: i) Light travel from object to lens. ii) In the direction of light all the distances are taken as positive. iii) All the distances measured opposite to the direction of light are taken as negative. iv)All the distances measured above the principal axis are taken as positive and vice versa Numerical: 1/f = (1.5-1)(1/20+1/20) or f = 20 cm 1 1 30. Principle: It works on the principle of mutual induction. 1 Construction: It consists a laminated iron core. There are two coils of insulated copper wire on this laminated core called primary coil and secondary coil. Input is applied at the primary coil and output is taken from secondary coil. 1 Working: When the a.c voltage is applied to the primary ,emf is induced in the secondary. 2 It is not possible to prepare a 100% efficient transformer. ½ There are various kinds of losses which can not be eliminated completely. 1/2 or principle 1 construction 1 working 2 long distance power transmission is done in high voltages as in that case current decreases so i2rt term reduces and heat loss decreases. 1 --------0----------- Difficulty level –L1-2 Blue Print(L1-2) Class XII Subject – Physics Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks: 70 General Instructions : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) (viii) All questions are compulsory. There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided inone question of three marks and in all three questions of five marks. You have to attempt only one of the choice in such questions. Question numbers 1 to 8 are very short answer type questions, carrying one mark each. Question numbers 9 to 18 are short answer type questions, carrying two marks each. Question numbers 19 to 27 are also short answer type questions, carrying three marks each. Questions numbers 28 to 30 are long answer type questions, carrying five marks each. Use of calculators is not permitted. However, you may use log tables, if necessary. You may use the following values of physical constants wherever necessary: Questions : 1. Write the relationship between amplitudes of electric and magnetic fields in free space for an electromagnetic wave ? 2. The vertical component of earth’s magnetic field at a place is √ 3 times the horizontal component . what is angle of dip at that place. ? 3. What is power dissipated by an ideal capacitor ? 4. Write value of impedance of LCR circuit at resonance ? 5. The refractive index of a material is √ 3 what is angle of refraction if unpolarised light is incident on it at polarising angle of medium ? 6. What is function of control rods in nuclear reactor ? 7. What is net charge on n-type semiconductor ? 8. Which logic gate is represented by Boolean expression Y= ? 9. A charge of 10 μC is given to a hollow metallic sphere of radius 0.1 m . find the potential at outersurface of sphere ? 10. A voltage of 30 Volt is applied across a carbon resistor with first second and third rings of blue, black and yellow colours respectively . calculate value of current through resistor ? 11. A closely wound solenoid 80 cm long has 5 layers of winding of 400 turns each . The diameter of solenoid is 1.8 cm .if the current carried is 8.0 A , estimate the magnitude of inside the solenoid near its centre ? 12. Name the following constituent radiations of electromagnetic spectrum which is used for 1) studying crystal structure 2) taking photographs of sky during night and foggy conditions ? 13. What are optical fibers ? Mention their one practical application ? 14. An α particle and a proton are accelerated from the state of rest through some ratio of de-Broglie wavelength associated with them ? potential difference V . Find 15. The work function of certain metal is 4.2 eV . will this metal give photo electric emission for wavelength 330 nm ? incident radiation of 16. Find series limit of Lyman series ? 17. Write the truth table for NAND gate ? 18. Derive condition of balance of Wheatstone’s bridge ? 19. Find capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor ? 20. A 4 μF capacitor is charged by 200V supply . It is then disconnected from the supply and is connected to another 2 μF capacitor . How much electrostatic energy of the first capacitor is lost in form of heat and electromagnetic radiations 21. Using Kirchhoff’s law to determine the currents I1 , I2 and I3 for the network shown below ? 22. Explain with the help of labelled diagram , the principle and working of cyclotron ? 23. A sinusoidal voltage V = 100 Sin314t is applied to a resistor of 5 resistance .calculate 1) rms value of voltage ? 2) rms value of current ? 3) power dissipated ? 24. Find ratio of intensities at two points on a screen in young’s double slit experiment when waves from the two slits have a phase difference of 00 and 900 ? 25. State Huygen’s Principle . Verify Snell’s law of refraction using Huygen’s wave theory ? 26. Boron has two isotopes 5B10 and 5B11 .their respective masses are 10.01294u and 11.00931u and the atomic weight of Boron is 10.811u . Find abundances of 5B10 and 5B11 ? and two advantages for satellite transmission ? 27. Write principle 28. Derive Lens Maker’s formula for a double convex lens . A double concave lens of glass of refractive index 1.6 has radii of curvature 40 cm and 60 cm . Calculate its focal length ? Or Derive an expression for fringe width in a two slit interference experiment ? In young’s experiment the width of fringes obtained with light of wavelength 6000 A0 is 2.0 mm . What will be the fringe width if the entire apparatus is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.33 ? 29. Two circular coils X and Y having radii R and R/2 respectively are placed in horizontal plane with their centers coinciding with each other . coil X has current I flowing through in clock wise sense . what must be current in coil Y to make total magnetic field at the common center of two coils to zero ? with the same currents flowing in two coils , if the coil Y is now lifted vertically upwards through a distance R , what would be net magnetic field at Centre of coil Y ? Or With the help of a neat and labelled diagram , explain underlying Principle and working of moving coil galvanometer ? A galvanometer coil has resistance of 12 and the meter shows full deflection of 3 mA . How will you convert the meter into a voltmeter of range 0 – 18 volt ? 30. Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a common emitter amplifier using a p- n –p transistor . Define the term voltage gain and write expression for it. Explain how the input and output voltages are out of phase by 1800 for a common emitter transistor amplifier ? Or With the help of a suitable circuit diagram explain working of transistor as an oscillator ? Find the voltage gain and power gain in a CE transistor amplifier when β =66 and the input and output resistances are 0.5 K and 50 K ? Solutions 1. E o = C Bo (1) 2. θ = 600 (1) 3. 0 (1) 4. Impedance = R 5. 300 (1) 6. control rods absorbs neutrons and provided limited no. of neutrons for fission (1) 7. zero (1) 8. NOR (1) 9. V = q/4πε0R -5 = 9X10 volt (1) 10 .R = 6X105 5 X 10-5 A (1) (1) 11. B = μο nI = 8π X 10-3 T (1) 12 . 1) X rays(1) 2) infrared radiation (1) 13. 1)Use to carry optical signal to large distance without energy loss (1) 2) Brilliance of Diamond (1) 14 . λ = h/√2mev (1/2) λα / λp = 1/ 2√2 (11/2) 15. E = hc/ λ (1/2) = 6.03 x 10-19 joule (1) = 3.77 eV (1/2) Not possible (1/2) 1/ λ = R (1/12-1/n22) (1/2) 16 . For series limit n2 For correct λ = ∞ (1/2) (1) 17. (1/2) 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 a wheatstone’s bridge consists of 4 resistances connected as shown. Between A & B a cell is connected and between C & D a galvanometer is connected. 18. (ii) Applying Kirchoff’s 2nd law for the branch ACDA, -I2R-IgG+I1P=0 --------------equation 1 For the branch BDCB, (I1+Ig)Q+IgG – (I2-Ig)S = 0 ---------------- equation 2 when Ig = 0; from Equation 1; I1P = I2R -------------- equation 3 from Equation 2; I1Q = I2S ------------- equation 4 Dividing equation 3 by 4 P/Q = R/s (1+1) Ans. Consider a parallel plate capacitor of plates area A and separation d. If + and - be surface charge densities of the plates respectively, then the electric field intensity between the plates, E = /0 19 Pot.difference V = Ed = d/0 A0/ d = 0A/d 20. U1=1/2c1v12 = 8 X 10 -2 J (1) V = q1 + q2/(c1+c2) = 400/3 volt U2=1/2(c1+c2)v2 (3) =5.33 x 10-2 j dU = U1 - U2 = 2.67 x 10 -2 Or 21 . 2I1 + 6 I2 = -3 (1) 4 I1 - 10 I2 = 27 I1 = I 2 + I (1) 3 I1 = 3 A , I2 = -1.5 A , I3 = 4.5 A 22 Principle , (1) construction and working of a cyclotron: A cyclotron is used to accelerate the positive charged particles. Principle: A positive charged particle can be made highly energetic by allowing it to move again and again in a high frequency electric field under effect of strong magnetic field. Working of cyclotron is based on motion of charged particle perpendicular to magnetic field Mv2/r = qvB r = mv/ qB time for semi circular path t = π m/qB cyclotron frequency = qB/2πm 23. Vo = 100 V (1/2) W = 314 rad s-1 (1/2) For Vrms (1/2) For Irms (1/2) For Power dissipated (1) 24. I = a12 + a22 + 2 a1a2 cos Ф I1 = I2 = I1 / I2 25. 4 a2 (1) (1/2) 2 a2 (1/2) = 2/1 (1) Huygen’s Principle: Each point on a primary wave front is a source of new disturbance that sends out disturbances in all the directions as the original light source does. The envelope of secondary wave lets in forward direction will give the exact position of secondary wave front at later time Verification of Snell’s law : From diagram, ABC = AA’B’ and AB’ is common. Sin i = BB’/AB’ and sin r = AA’/AB’ Sin i /Sin r = BB’/AA’ = ct/vt = c/v = µ 26. Formula (1) abundance of = 19.9% abundance of = 80.1% 27. (1) (1) Principle : centripetal force required in circular motion is balanced by gravitational force (1) Application: i) Weather forecasting ii) Remote sensing (1) 28 . Lens maker formula is relation between focal length of lens, refractive index and radii of curvature of its two surfaces 1/F = (µ - 1) (1/R1 - 1/R2) . Refraction through First surface : -µ1/ u + µ2/ v1 = (µ2 - µ1) / R1 --------------------------------------(1) Refraction through second surface: -µ1/ v + µ2/ v1 = (µ2 - µ1) / R2---------------------------------------(2) Equation (1) - (2) µ1/ v - µ1/ u = = (µ2 - µ1) (1/R1 - 1/R2) Divide by µ1, 1/F = (µ - 1) (1/R1 - 1/R2) 29. Proved Diagram (1/2) B1 –B2 = 0 For calculation of B1 ,B2 and B (1 mark for each) Principle , construction and working of Moving coil galvanometer: Definition: A moving coil galvanometer is an instrument used for detection and measurement of small electric currents. Principle: A current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field experiences a torque. Construction It consists of N turns of coil PQRS wound over a non-magnetic metallic frame usually rectangular or circular. The coil is suspended from a torsion head H by means of phosphor bronze strip in a magnetic pole by pieces N and S. A mirror M is attached to the phosphor bronze strip. The other end of the coil is connected to a hairspring, which in turn is connected to an external terminal. The concave or cylindrical pole pieces ensure that the plane of coil is parallel to B thus (cosӨ = 1 and sinӨ = 1) in the expression Ʈ = NIBA cosӨ and Ʈ= NIBA sinӨ. The whole arrangement is enclosed in non-magnetic case, which is provided with leveling screws. The torsion head is connected to terminal T1. The galvanometer can be connected to the circuit through terminals T1 and T2. Working: When a current is passed through the coil in the direction PQRS, then the coil experiences a torque Ʈ = NIBA sinӨ Since the magnified field is radial the plane of the coil is parallel to the magnetic field such that a = 90o and hence Ʈ = NIBA. The coil rotates and the phosphor bronze strip gets twisted. As a result a restoring torque comes into play trying to restore the coil back to original position. If f be the twist produced in the strip and C be the restoring torque per unit twist then the restoring torque = Cf. In equilibrium, Where G is the galvanometer constant. This shows that galvanometer has a linear scale and detects the presence of current 30. The output voltage Vo = Vcc - IcRL ------------------------(1) Ie = Ib +Ic -------------------------(2) For (+) half cycle of i/p a.c. signal, It supports Fwd bias of EB circuit So, Ie increase, so Ic increase so Vo decrease (less positive or more negative) For (-) half cycle of i/p a.c. signal, It opposes Fwd bias of EB circuit So, Ie decrease, so Ic decrease so Vo increase ( more positive) This shows that we get the o/p voltage 180 out of phase than i/p. SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER L1-3 FOR CLASS XII - PHYSICS BLUE PRINT SL. No UNIT VSA (1 Mark) SA I (2 Marks) SA ( Ma 1(1) 4(2) 3 - 2(1) 1 Electrostatics 2 Current Electricity 3 Magnetic Effect of Current and Magnetism 1(1) 2(1) 4 E$lectromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents 1(1) 4(2) 5 Electromagnetic Waves 1(1) 2(1) 6 Optics 1(1) 2(1) 6 7 Dual Nature of Matter 1(1) - 3 8 Atoms and Nuclei. 1(1) 2(1) 3 9 Electronic Devices 1(1) - 6 10 Communication Systems - 2(1) 3 8(8) 20(10) 27 TOTAL SAMPLE PAPER-L1-3 PHYSICS FOR CLASS XII 3 General Instructions: (a) All questions are compulsory (b) There are 30 questions in total. Qns. 1 to 8 carry 1 mark each. Qns. 9 to 18 carry 2 marks each, Qns. 19 to 27 carry 3 mark each and Qns. 28 to 30 carry 5 marks each. (c) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one question of 2 marks, one question of 3 marks and all three questions of 5 marks each. You have to attempt only one of the given choices in such questions. (d) Use of calculators is not permitted. (e) You may use the following physical constants wherever necessary. c = 3 x 108 ms-1 h = 6.6 x 10-34 Js e = 1.6 x 10-19C µo = 4π x 10-7 TmA-1 1/4πεo = 9 x 109 N m2C-2 Avogadro number NA = 6.023 x 1023 mol-1 Mass of the neutron = 1.675 x 10-27 kg Boltzmann constant, k = 1.38 x 1023 J K-1 1. An electric dipole is placed in a uniform electric field what is the net force acting on it ? 2. There are two identical galvanometers. One is converted into an ammeter and the other into milliammeter. Which of the shunts will be of larger resistance? 3. Two identical loops, one of copper and another of constantan are removed from a magnetic field within the same time interval. In which loop will the induced current be greater? 4. Which E M wave is used for haze or night photography? Write its frequency. 5. In Young’s double slit experiment, one slit is covered. What will be the effect? 6. On what factor does the energy carried by a photon of light depend? 7. Two nuclei have mass numbers in the ratio 1:27. What is the ratio of their nuclear radii? 8. In the following diagrams, which of the diodes are forward biased and which are reverse biased? 9. The figure shows tracks of three charged particles crossing a uniform electrostatic field with same velocities along the horizontal. Give the signs of the three charges. Which particle has the highest charge to mass ratio? 10. X and Y are two parallel plate capacitors having the same area of plates and same separation between the plates. X has air between the plates and y contains a dielectric medium of K =5. Calculate the potential difference between the plates of X and Y. 11. In a metre bridge, the null point is found at a distance of 33.7 cm from A. If now a resistance of 12is connected in parallel with S, the null point occurs at 51.9 cm. Determine the values of R and S. 12. A ray of light passes through an equilateral prism (such that angle of incidence is equal to angle of emergence and the latter is equal to 3/4th of angle of prism. Calculate the angle deviation. 13. A circular coil of wire consisting of 100 turns, each of radius 8.0 cm carries a current of 0.40 A. centre What is the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the of the coil? 14.When the primary of a transformer is connected to the a.c. mains the current in it (a) is very small if the secondary circuit is open but (b) increases when the secondary circuit is closed. Explain. 15. A circular copper disc 10cm in radius rotates at 20radian/sec about an axis through its centre and perpendicular to the disc. A uniform magnetic field of 0.2T acts perpendicular to the disc. (i) Calculate the potential difference developed between the axis of the disc and the rim. (ii) what is the induced current if the resistance the disc is 2 16. State any four properties of electromagnetic waves. 17. A radioactive isotope has a half-life of T years. How long will it take the activity to reduce to a) 3.125%, b) 1% of its original value? 18. A modulating signal is a square wave, as shown in Figure .The carrier wave is given by c(t)2sin(8t) volts. (i) Sketch the amplitude modulated waveform (ii) What is the modulation index? 19. Define Electric flux . What is its S.I. Unit? A student is asked to calculate the ratio of electric flux through the surfaces of spheres S1 and S2 with charges placed inside, as shown in the figure. He gets the answer as 4 : 1. Check the correctness of the answer by actually calculating the electric flux ratio through the two surfaces and state whether his answer is correct or incorrect. 20. A series LCR circuit connected to a variable frequency 230 V source. L = 5.0 H, C = 80F, R = 40 . (a) Determine the source frequency which drives the circuit in Resonance. (b) Obtain the impedance of the circuit (c) and the amplitude of current at the resonating frequency. 21. Calculate the de-brogrlie wavelength of (i) an electron moving with a speed of 1/100 of speed of light in vacuum (ii) a ball of radius of 5mm and mass 0.03 kg moving with a speed of 100m/s . Hence show that the wave nature of matter is important at the atomic level but is not really relevant at the macroscopic level. 22. Derive an expression for the total energy of electron in the nth orbit. 23. With the help of circuit diagram explain the working of a transistor as a switch. 24. Distinguish between metals, insulators and semiconductors on the basis of energy band diagrams. OR With the help of circuit diagram explain the working of a p-n junction diode as a full wave rectifier . Show the input and output wave forms. 25. Deduce an expression for the distance up to which the TV signals can directly be received from a TV tower of height h . 26. Which of the following can be polarized : (i) X-rays and (ii) Sound waves. Give reasons. Two polaroids are used to study polarization , one of them is kept fixed and other is initially kept with its axis parallel to the polarizer axis . The analyzer is then rotated through angles of 45,90 and 180 degrees in turn. How would the intensity of light coming out of the analyzer be affected for these angles of rotation, as compared to the initial intensity and why? 27. Show graphically the intensity distribution of a single slit diffraction pattern. State with reason how would the linear width of central maximum change if (i) monochromatic yellow light is replaced with red light (ii) distance between the slit and screen is increased. 28. With the help of circuit diagram explain in brief the use of potentiometer for comparison of emf of two cells. A 10 m long wire of uniform cross-section of 20 resistance is fitted on the board. The wire is connected in series with a battery of 5V along with an external resistance of 480. If an unknown e.m.f. E is balanced at 600 cm of this wire, calculate (i) the potential gradient of wire, (ii) value of unknown e.m.f. OR State two kirchoff’s laws. In the circuit shown in Fig. calculate the current in 4.5resistor. Assume the internal resistances of the cells are negligible. 29. How will a dia ,para , and a ferro magnetic material behave when kept in a non-uniform external magnetic field . Give two examples of each of these materials . Name two main charactrestics of a ferro magnetic material which help us to decide its suitability for making (i) a permanent magnet (ii) an electro magnet. Which of these two characteristics should have high or low values for each of these two types of magnets. OR With the help of labeled diagram explain the priniciple and construction of moving coil galvanometer . Explain (i) importance of radial magnetic field. (ii) role of phosphor bronze strip. 30.Write two conditions necessary for total internal reflection to take place. A small bulb is placed at the bottom of a tank containing water to a depth of 80cm. What is the area of the surface of water through which light from the bulb can emerge out. Refractive index of water is 1.33 OR Draw a labeled diagram to show the image formation in an astronomical telescope for normal adjustment position. Two convex lenses of same focal length but aperture 5cm and 10cm are used as objective lenses in two astronomical telescopes. (i) What will be the ratio of their resolving power . (ii) Compare the intensity of images formed in two cases. *************************************** SAMPLE PAPER-L-1-3 PHYSICS FOR CLASS XII MARKING SCHEME Q.No Value points Marks Total Marks 1 Zero 1 1 2 Milliammeter 1 1 3 Copper 1 1 4 Infrared wave, 1011Hz -5× 1014 Hz ½.½ 1 5 Diffraction 1 1 6 Frequency 1 1 7 1:3 1 1 8 (i)forward (ii) reverse ½,1/2 1 9 1,2 –ve, and 3 +ve , particle 3 has more e/m ratio 1 +1 2 10 X = 10V ,Y = 2V , Ux : Uy=5 :1 1+1 2 11 Formula used, correct &S=13.5ohms)with units 12 answer (R=6.86ohms 1 + 1 2 i+e=A+d , d=30 1+1 2 13 B = 0NI/ 2r , 2.5 X 10-3T 1+1 2 14 When the secondary is open power output is zero, 1 + 1 less current flows in primary , when the secondary is closed power out put is there , more current flows 2 15 Emf developed 0.0618V,I=0.0309A 16 Br2/2 ,emf= 1 + 1 2 Any four properties 4x½ 2 17 (a)A/A0=( ½)n n =5 (b)t=5T, N=N0e-t t=6.65T 1+1 2 18 Sketch, mod. Index = 0.5 1 +1 2 19 = q/0 1 : 2 = 1 : 1 ; his answer is incorrect 1+1+1 3 20 (a) = 1/2LC = 7.95Hz ,(b)Z = 1+2 R=40,I0=V0/Z I0=8.13A 21 =h/mve= 2.43 Ao ; ball =2.2 X 10-34m; 1+1+1 3 22 Derivation of En= - me4/802n2h2 3 3 23 Circuit diagram; working of transistor as switch 1+2 3 24 Energy band diagram of metals,semiconductors 1+1+1 3 and insulators E = 3 Circuit diagram, working of full wave rectifier ,wave 1+1+1 3 forms 25 A radio wave that can travel directly from one point 1 + 2 3 to another point on the surface of the earth is called ground wave propagation. Ground waves are relatively changing atmospheric conditions. Ground waves require transmission power. 26 a unaffected by relatively high X-rays, em waves are transverse hence can be 1+1+1 3 polarized, based on malus law I = I0 cos2 The intensity is ¼ , 0, ½ of initial intensity 27 Graph, width of central max= D/d, red has more 1+1+1 3 wave length compared to yellow, (i)width increases (ii)increases 28 Circuit diagram, explanation, I = V/R ,I=0.01A, V/l= 1+1+3 5 0.02V/m ,E=0.12V Kirchoff ‘s laws , correct answer 29 30 2+3 5 Dia ,para ,ferro magnetic properties , More 3+2 coercivity and more retentitivity for permanent magnet and less coercivity and less retentivity for temporary magnet 5 Diagram, principle, working, to have linear scale , 3+2 to increase the current sensitivity k should be more 5 Two conditions ; sin = 3/4tan=3/7 and 2+3 r=3h/7 A=2.58sq.m 5 Labeled diagram, R.P=D/1.22 R.P1: R.P2= 1:2 5 Intensity is proportional to diameter I1:I2=1 : 2 2+3 CBSE SAMPLE PAPER Level I-4 PHYSICS FOR CLASS XII General Instructions: (a) All questions are compulsory (b) There are 30 questions in total. Qns. 1 to 8 carry 1 mark each. Qns. 9 to 18 carry 2 marks each, Qns. 19 to 27 carry 3 mark each and Qns. 28 to 30 carry 5 marks each. (c) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one question of 2 marks, one question of 3 marks and all three questions of 5 marks each. You have to attempt only one of the given choices in such questions. (d) Use of calculators is not permitted. (e) You may use the following physical constants wherever necessary. c = 3 x 108 ms-1 h = 6.6 x 10-34 Js e = 1.6 x 10-19C µo = 4π x 10-7 TmA-1 1/4πεo = 9 x 109 N m2C-2 Avogadro number NA = 6.023 x 1023 mol-1 Mass of the neutron = 1.675 x 10-27 kg Boltzmann constant, k = 1.38 x 1023 J K-1 1 State Gauss law and write mathematical expression for Gauss law. 2 Write the definition of 1 ampere in terms of force between two parallel spaced current carrying wires. 3 Define wattles current and write the value of phase angle between V & I ? 4 Write one use of each (i) microwave (ii) infrared radiation. 5 Define Brewster’s law. Value of Brewster angle for a medium is 600, find refractive index of the medium. 6 Work function of a material is 1.1 eV, calculate the value of threshold frequency for the material. 7 Write the name of one doping element for n-type semiconductor and name the mobile charge carriers in case of n-type semiconductors. 8 Identify the forward biased and reversed biased p-n junction diode configuration +5 V +3 V +3 V (a) 9 +5 V (b) Define equipotential surface. Draw an equipotential surface for point charge. OR Two point charges 4µC and -4 µC are separated by a distance of 1 m in air. Calculate electrostatic potential at a point on equatorial line. 10 The balance points in a potentiometer experiment for two combinations of cells are found to be at 980 cm and 800 cm respectively. Calculate the ratio of the emf of the two cells. 11 Colour of strips on a carbon resister is in the order of red, black, white and silver. Find the value of resistance of this carbon resister. 12 Define current sensitivity of a moving coil galvanometer. A moving coil galvanometer gives full scale deflection when 10 mA current flows through it. Calculate the value of shunt resister to increase it`s range to 600 mA. 13 State Lenz law. Show that Lenz law is in accordance with law of conservation of energy. 14 Define resonance in case of LCR series circuit. Write condition of resonance in LCR series circuit. 15 A ray is used to sterilize medicine containers and can travel in vacuum. Identify the ray and write its wave length. 16 Red colour monochromatic ray is replaced by a green colour monochromatic ray in Young`s double slit experiment. Show the effect on fringe width thus obtained. 17 Draw circuit diagram of a diode as half wave rectifier. Give Input and output wave form of a sine wave for a half wave rectifier. 18 What does the term LOS means in communication system? Name the type of wave used for LOS communication. 19 Define Ohm`s law. Draw a circuit diagram for Ohm`s law. Write two examples of circuit elements which do not follow Ohms law. 20 Using phasor diagram calculate impedance of LCR series circuit. 21 Identify that in which of the following (i) n1>n2 (ii) n1=n2 (iii) n1<n2, here n1 is refractive index of external medium and n2 is refractive index of material of lens. (a) (b) (c) OR Derive a formula for combined focal length of combination of two thin lenses. 22 State Huygen’s principle of wave theory of light. Prove Laws of refraction of light using Huygen’s principle. 23 State postulates of Bohr`s atomic theory. Establish Bohr`s quantization of angular momentum of the electron using de-Broglie hypothesis. 24 Define the term demodulation. Draw a simple circuit diagram for amplitude demodulation and show input intermediate and output wave form for demodulation. 25 Draw a schematic experimental arrangement used by Davisson and Germer to establish wave nature of electrons. Describe briefly how the de-Broglie relation was experimentally verified in the case of electrons. 26 Plot the distribution of kinetic energy of β-particles and State why the energy spectrum is continuous. 27 Explain the working of transistor as a switch. 28 Draw a neat labelled diagram of Van de Graaf generator .Write its principle and explain its working. Mention its two uses. OR What is an electric dipole? Deduce an expression for the torque acting on an electric dipole placed in a uniform magnetic field. Hence define dipole moment.An electric dipole of length 2 cm is placed with its axis making an angle of 60o to a uniform electric field of 105 NC-1. If it experiences a torque of 8√3 Nm, calculate the; (i) magnitude of charge on the dipole. (ii) potential energy of the dipole. 29 Explain the principle and working of a cyclotron, with the help of a labelled diagram. A cyclotron’s oscillator frequency is 10 MHz. What should be the operating magnetic field for accelerating protons? If the radius of its dees is 60 cm, what is the kinetic energy of the proton beam produced by the accelerator? Express your answer in MeV. (Charge of proton = 1.6 x 10-19 C, mass of proton = 1.67x10-27 kg, 1 MeV = 1.6 x 10-13 J) OR With the help of a neat labelled diagram, explain the principle and construction of a moving coil galvanometer. Define the terms current sensitivity and voltage sensitivity of a galvanometer. In a galvanometer there is a deflection of 10 div per mA. The coil resistance of the galvanometer is 78 Ω. If a shunt of 2Ω is connected to the galvanometer and there are 75 divisions in all on the scale of the galvanometer, calculate the maximum current which the galvanometer can read. 30 Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of a point object placed in a medium of refractive index n1 on the principal axis of a convex spherical surface of radius of curvature R and refractive index n2. Using the diagram derive the relation; n2 n1 v n2 - n1 u R A converging lens of focal length 50 cm is placed co axially in contact with another lens of unknown focal length. If the combination behaves like a diverging lens of focal length 50 cm, find the power and nature of the second lens. OR Derive the lens maker’s formula in case of a double convex lens. State the assumptions made and conventions of signs used. A converging lens has a focal length of 20 cm in air. It is made of a material of refractive index 1.6. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.3, what will be its new focal length? L1 -5 XII - PHYSICS Time: Three Hours Max. Marks: 70 General Instructions (a) All questions are compulsory. (b) There are 30 questions in total. Questions 1 to 8 carry one mark each, questions 9 to 18 carry two marks each, Questions 19 to 27 carry three marks each and questions 28 to 30 carry five marks each. (c) There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one question of two marks, one Question of three marks and all three questions of five marks each. You have to attempt only one of the given Choices in such questions. (d) Use of calculators is not permitted. (e) You may use the following physical constants wherever necessary : c = 3 x 108ms-1 h = 6.6 x 10-34Js e = 1.6 x 10-19 C o = 1 7 A m T 10 x 4 Boltzmann constant k = 1.38 x 1023 JK-1 Avogadro’s number NA = 6.023 x 1023/mole Mass of neutron mn = 1.6 x 10-27 kg 1. What is angle between the directions of the electric field at any (i) axial point (ii) equatorial point due to an electric dipole? 1 2. What is the direction of force acting on a charged particle q, moving with a velocity v in the uniform magnetic field? 1 3. Define the magnetic flux and its SI units. 1 4. Name the electromagnetic radiation used for viewing objects through haze and fog.1 5. What are coherent source of light? 1 6. An atom of mass no. “A’ has mass defect Δm, give the formula for the binding energy per nucleon, of the nucleus.1 7. Draw voltage current characteristics of a zener diode.1 8. What is the stopping potential applied to a photocell if the maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron is 5ev? 9. Distinguish between isotopes and isobars. Give one example for each of the species.2 10. S1 and S2 are two hollow concentric sphere enclosing charge Q and 2Q respectively as shown in figure. 2Q S2 . Q O S1 (i) What is the ratio of electric flux through S1 and S2? (ii) How will the electric flux through the sphere S1 change if a medium of dielectric constant 5 is introduced in space inside S1 in place of air? 2 11. State Kirchhoff’s rule of current distribution in an electrical network. 2 12. The instantaneous current and voltage of an ac circuit are given by I=10 Sin314t A, V=50 Sin314t V. what is the power dissipation in the circuit? 2 13. Write the faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. 2 14. Find the wavelength of electromagnetic wave of frequency 4x109Hz in free space. Give its two applications.2 15. How will you convert a galvanometer and a voltmeter? What will be the resistance of voltmeter formed? 2 16. Give two differences between interference and diffraction of light.2 17. What is the amplitude modulation? Represent the process graphical. Write its two limitations.2 18. Find the total energy stored in the capacitor in the given network; 2 2 µf 6 V 2µf 1µ f 1 µf 2 µf 19. Derive the lens equation for convex lens. 20. Show that the energy stored in a parallel plate capacitor is 1/2CV2. 3 21. What is meant by impedance? Using the phasor diagram derive an expression for the impedance of an electrical circuit containing L, C and R in series.3 22. Define the term activity of a radioactive substance. State its SI units Two different radioactive elements with half lives T1 and T2 have N1 and N2 atoms respectively present at given instant, determine the ratio of their activities at this instant.3 23. What does the term LOS communication mean? Name the types of wave that are used for this communication, give typical examples with the help of suitable diagram of communication system that used space wave mode propagation.3 24. Explain the refraction on the basis of theory of wave front.3 25. Write Einstein’s photoelectric equation in terms of stopping potential and the threshold frequency for a photosensitive material. Draw a plot showing the variation of stopping potential versus frequency of incident radiation.3 26. Explain the full wave rectifier with necessary diagram.3 27. Find the truth table of the following gate; 3 A Y B A Y B 28. State the principal of potentiometer. Draw a circuit diagram to compare the emf of two primary cells. Write the formula used. How can the sensitivity of a potentiometer be increased? 5 29. Write the principal of cyclotron with the help of labeled diagram and explain its construction and working. 5 Or Derive the expression for the force per unit length between two long straight parallel current carrying conductors, and hence define one ampere. 30. Draw the labeled diagram for the formation of image by compound microscope. Derive an expression for its total magnification (or magnifying power) Or Derive lens maker formula. In the accompanying diagram the direct image formed by the lens (f=10cm) of an object placed of o and that formed at the same point o. what is the radius of curvature of the mirror. ……………………………….********……………………………………………… Marking Scheme L1-5 Ans.1 (i) Zero (ii) 1800 Ans. 2 Perpendicular to the plane of V and B as force F=q(vxB) Ans.3 Number of field lines passing any surface is called magnetic flux. Unit is waber (Wb) Ans.4 Infrared rays Ans . 5 Two sources of light having same frequency and constant initial phase difference are called coherent sources Ans 6 Bn= Δm.c2/A Ans7. I mA V µA Ans8. Ek=eV0 =5eV ( negative) Ans9. Isotopes. Same atomic no But different atomic mass 1 2 3 1H , 1H , 1H Isobars same atomic mass no but different atomic no 40 40 20Ca , 18Ca Ans. 10. (i) ӨS1=Q/€0 Өs2=Q+2Q €0 Өs1= Q/€0 =1 Өs2 3Q/€0 3 (ii) Ө’s1= Q/5€0 Ө’s1= 1/5 Өs1 Ans.11 Kirchhoff’s rule; (i) Junction rule: The algebraic sum of current meeting at a junction is equal to zero; i.e. ∑I=0 (ii) The algebraic sum of potential difference across circuit element of a closed circuit is zero. i.e. ∑V=0 Ans12: Pav= Vrms Irms cos Ө =250watt. Ans13 . faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction; (i) Whenever there is change in the magnetic flux linked with the circuit on induced emf is set up in it and last as long as magnetic flux is changing. The magnitude of the induced emf is directly proportional to rate of change of flux; e=-d Ө/dt Ans14. Wavelength λ=c/υ, range microwave, uses in microwave oven and radar system. Ans.15 A galvanometer can be converted into voltmeter by connecting high resistance (R) in series with the coil of the galvanometer. G R V= IgG+ IgR R=V/Ig-G Ans.16 Interference Diffraction It is due to superposition of two it is due to superposition of secondary waves waves coming from two coherent coming from different part of the same wave sources. The width of the interference Front. The width of the diffraction bands is not same Band is equal. The intensity of all maxima is same The intensity of central maxima is maximum And goes on decreasing rapidly with inc. order Ans17. Changing the amplitude of carrier waves in accordance modulating signal. Is called AM waves. Limitations: noisy, it can’t be used for high frequency carrier waves. Ans18. The equivalent capacitance is 2µf Energy stored= 36x10-6j Ans 19. 1/f=1/v-1/u Ans 20 w=∫vdq=(1/2)cv2 Ans.21 Impedance: it is the ratio of rms voltage applied and rms current produced in circuit Z=V/I, unit ohm ‘Ω’. Expression. VR VC VL V= V0Sinwt VL V VL-Vc Ө VR i Vc V2=VR2+(VL-Vc)2=i2(R2+(XL-Xc)2; z=√R2+(wL -1/wc)2 Ans 22 Activity- The decay rate of a sample is called activity R=dN/dT Unit – Becquerel (Bq) We know that N=N0 e-λt R=-N0e- λt R1 /R2 = N1/N2 Ans 23=LOS= line of sight Waves used= space waves It is both - the height of transmitting antenna as well as the height of the receiving antenna that affects the range of the mode of communication. Dm Ht Dt dT=(2ReHt)1/2 dR=(2ReHr)1/2, maximum distance= dT+dR Ans 24 Hr Earth Dr B 90 X Y A 90 B’ A’ In triangle ABB’ Sin i=BB’/AB’=v1t/AB’ , in triangle AA’B sin r= v2t/AB’ Sin i/sinr=v1/v2=contant Ans 25Eisteins photoelectric equation in terms of stoping potential Vs is eVs=hυ-Ф0 Vs Frequency-υ υ0 D1 Ans 26 Circuit Diagaram ac Vo D2 Suppose during first half cycle of input ac signal the terminal S1 is +ve related to s and S2 is negative related to S then diode is reverse bised The current flows in diodeI and not diodeII and vice-verse. Ans 27 -Truth Table (I) Input Output A B Y=A+AB 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 (II) Truth Table Input A Output B 0 A’ 0 0 A’+B 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 Ans.28 Principal of potentiometer. When a constant current flows through a wire of uniform cross-section then the potential difference across any length of the wire is directly proportional to the length. εᾳ l ε=kl Comparing of emf;s of the cells. Battery Key Rh J1 J2 ε1 G RB ε2 Ε1 =kl1 =l1 E2= k l2 l2 Ans 29. Cyclotron: A device which accelerate charge particle or ions up high energies. Construction and working. The particles, injected near the center of the magnetic field, accelerate only when passing through the gap between the electrodes. The perpendicular magnetic field (passing vertically through the "D" electrodes), combined with the increasing energy of the particles forces the particles to travel in a spiral path. (The particles move in a spiral, because a current of electrons or ions, flowing perpendicular to a magnetic field, experiences a force perpendicular to its direction of motion. The charged particles move freely in a vacuum, so the particles follow a spiral path.) The radius will increase until the particles hit a target at the perimeter of the vacuum chamber. Application. used to treat cancer. Ion beams from cyclotrons can be used, as in proton therapy, to penetrate the body and kill tumors by radiation damage, while minimizing damage to healthy tissue along their path. the best source of high-energy beams for nuclear physics experiments; several cyclotrons are still in use for this type of research. Or P R ΔL F I1 I2 Q S suppose two long wire PQ and RS are placed parallel to each other in air or vacuum carrying currents I1 and I2. the magnetic field produced by current carrying conductor PQ at the location of other wire RS. B1=µ0I1/2Πr Magnetic force on element ΔL ΔF=B1 I2 ΔL sin 900 = µ0I1 I2 ΔL 2Πr Force acting on per unit length of the conductor= ΔF= µ0I1 I2 ΔL 2Πr According to Fleming’s right hand rule; the force will be attractive when current flow in same direction and repulsive when current in opposite direction. If I1=I2=1A, r=1m Then f=2x10-7N/m Thus 1 ampere is the current which when flowing in each parallel conductors placed at seperation1m in vacuum exert a force of 2x10-7 on 1 meter of length of the wire. Ans30.(ii) f=10 U=-x V=15 Using 1/f=1/v-1/u 50-x=R R=20cm For the first part see NCERT text book. (i) 1/f=( µ2/ µ1 -1)(1/R1-1/R2)