Eye About 4/5 of the eye is enclosed within the bony orbit I. Basic
advertisement

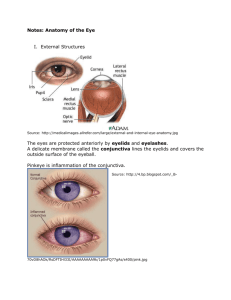
Eye About 4/5 of the eye is enclosed within the bony orbit I. Basic Layers A. Sclera – white of the eye Outer fibrous protective layer; avascular; helps give shape to the eye; permits light to come in 1. Cornea (anterior portion of the sclera) – colored portion of the eye; most of the focusing power; avascular B. Choroid (middle layer) – highly vascular and supplies blood for the entire eye; opaque layer (light cannot pass through) darkish brown in color 1. ciliary body – attaches by ligaments to the lens 2. lens – clear, flexible capsule behind the iris and pupil 3. Iris – pigmented muscle that surrounds the pupil; regulates the diameter of the pupil; controls the amount of light coming into the eye 4. Pupil – circular opening in the center of the iris C. Retina – nervous tissue of the eye that receives images; forms image 1. rods- reacts to light; black/white vision 2. cones – reacts to color and fine detail; color vision II. Chambers of the eye A. Aqueous (middle) – Tear layer Contains the 3rd eyelid (nictitating membrane) for protection; helps maintain the shape of the eye and supplies nutrients to the cornea and lens; waste removal B. Vitreous chamber – soft, clean, jellylike mass III. Vocabulary 1. Ophthalm , ocul,opt = eye a. ophthalmoscope b. ophthalmic c. optic d. intraocular 2. Lacrim, dacryl – tear 3. is – equal a. aniso(unequal) coria – unequal pupil diameter 4. mi – small a. miotic – pupil contraction 5. mydri – wide a. mydriatic – pupil dilation 6. tropia – to turn a. esotropia – crossed eye b. Entropion – turning in of the eyelid c. Ectropion – turning out of the eyelid 7. epiphora – excessive tearing IV. Pathological Conditions 1. Glau coma – increased intraocular pressure; blue appearance to the eye 2. Cataract – opacity of the lens; caused by age, diabetes, scratch on the eye 3. Cherry eye – collapse of the 3rd eyelid; treatment usually is to tack the membrane under the lid. 4. Enucleation – removal of the eye 5. Conjunctivitis - pinkeye 6. Distichiasis – 2 rows of eyelashes on one eyelid that rubs on the cornea 7. Progressive retinal atrophy –retina slowly degenerates and causes blindness 9. Keratoconjunctivitis (dry eye) – decrease production of the aqueous portion