SOP - STANBIO UREA NITROGEN
advertisement

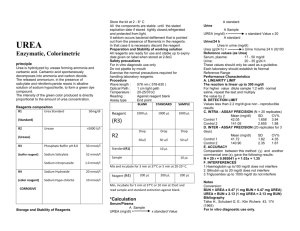
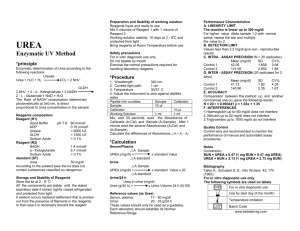
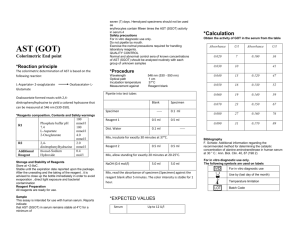
CLS Laboratory San Francisco State U niversity 1600 Holloway Avenue San Francisco, CA 94132 CLS Laboratory Procedure #STANBIO-BUN-0580 Section: Chemistry Date of Implementation: 11/29/2010 Page 1 of 6 STANBIO UREA NITROGEN (BUN) Quantitative Determination of Urea Nitrogen in Serum, Plasma, or Urine Policy The laboratory operates in strict accordance with CLSI GP2-A5 guidelines by identifying laboratory procedures using work processes in the laboratory’s operational path of workflow and writes procedures for preanalytical, analytical, and post-analytical laboratory practices. Purpose The STANBIO BUN method employs the diacetylmonoxime (DAM) methodology. In this condensation reaction, urea directly reacts with DAM under acid conditions. In the presence of thiosemicarbazide, a red-purple chromogen forms and is measured spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 520nm. Reaction Sequence: Thiosemicarbazide + Urea Responsibility Red-Purple Chromogen Diacetylmonoxime The CLS Internship Program Director shall review and approve procedural documents, appoint personnel for document implementation, control, and record. Interns, faculty, and any other individuals operating within the San Francisco State University CLS Laboratory must refer to this SOP and operate within its limits when performing the STANBIO BUN procedure. Clinical Utility The major pathway of nitrogen excretion is in the form of urea that is synthesized in the liver, released into the blood, and cleared by the kidneys. A high serum urea nitrogen occurs in glomerulonephritis, shock, urinary obstruction, pyelonephritis, and other causes of acute and chronic renal failure. Severe congestive heart failure, protein hyperalimentation, diabetic ketoacidosis, dehydration, and bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract elevate BUN. Low BUN often occurs in normal pregnancy, decreased protein intake, in acute liver failure, and with intravenous fluid administration.1 CPT Code 12345-0580 Specimen Requirements Specimens recommended for testing are serum, plasma, or, urine. Page 1 of 6 CLS Laboratory San Francisco State U niversity 1600 Holloway Avenue San Francisco, CA 94132 CLS Laboratory Procedure #STANBIO-BUN-0580 Section: Chemistry Date of Implementation: 11/29/2010 Page 2 of 6 Serum and plasma urea nitrogren is stable for 1 day at room temperature (15-25°C); several days refrigerated (2-8°C); and 6 months when frozen at -20°C. Serum: Hemolysis can alter results; therefore, serum specimens should be analyzed as soon as possible. Plasma: Plasma specimens may be used as long as anticoagulant used does not contain ammonium salts. Urine: Urine Specimens should be preserved with Fluoride-Thymol. Add 19.0 mL of water to 1.0 mL of diluted urine for analysis and multiply the observed value by a factor of 20 to obtain the mg/dL of BUN in the urine specimen. For 24 hour urine specimen: gram ) 24hours BUN ( Materials = (BUN ( mg ) x (Urine dL Equipment Pipettes o To accurately deliver: 20uL 2.0mL 1.0mL Test tubes Vortex Mixer Heat block or water bath, 100°C Cold Water Bath Spectrophotometer with 520nm absorbance reading capability Timer Volume (mL)))/100,000 Reagents BUN Color Reagent, Catalog No. 0584 o Diacetylmonoxime 1.7g/L o Thiosemicarbazide 0.3g/L BUN Acid Reagent, Catalog No. 0585 o Ferric Chloride Hexahydrate 33.4mg/L o Sulfuric Acid o Phosphoric Acid Urea Nitrogen Standard, (25mg/dL) Catalog No. 0581 o Contains Urea equivalent to 25 mg of BUN/dL in a weak sulfuric acid solution Urea Nitrogen Standard, (50mg/dL) Catalog No. 0582 o Contains Urea equivalent to 50 mg of BUN/dL in a weak sulfuric acid solution Urea Nitrogen Standard, (75mg/dL) Catalog No. 0583 o Contains Urea equivalent to 75 mg of BUN/dL in a weak sulfuric acid solution Page 2 of 6 CLS Laboratory San Francisco State U niversity 1600 Holloway Avenue San Francisco, CA 94132 Procedure CLS Laboratory Procedure #STANBIO-BUN-0580 Section: Chemistry Date of Implementation: 11/29/2010 Page 3 of 6 Step Action 1 Pipette the following volumes (in milliliters) to the corresponding test tube: Reagent Standard Sample (U) Blank (B) (S) Sample 0.02 Standard 0.02 Water 0.02 BUN Color Reagent 1.0 1.0 1.0 BUN Acid Reagent 2.0 2.0 2.0 *Mix well with each addition. *There will be three standard tubes – one for each standard: 25mg/dL, 50mg/dL, and 75 mg/dL. 2 Mix the test tubes and incubate for exactly 10 minutes in a boiling water bath. If a heat block is used, incubate for 12 minutes at 100°C. Remove the tubes from water bath/heat block simultaneously and immerse in cold water for 3-5 minutes. Remove from cold water bath, mix well and read absorbance (A) of unknown and standard against Reagent Blank at 520nm. 3 4 *Notes: Color is stable for 30 minutes. A reagent blank and 3 BUN standards must be run with every test. The readings obtained with the 3 standards are used to prepare a standard curve for each run. The reaction departs from linearity at levels below about 3 mg/dL, suggesting that it does not strictly follow the Beer-Lambert Law. Pipetting proper volumes of reagents and specimens is crucial. Use of micropipettes is recommended. Mixing of all reaction tubes with each addition of reagent/specimen as well as before and after heating is Page 3 of 6 CLS Laboratory San Francisco State U niversity 1600 Holloway Avenue San Francisco, CA 94132 CLS Laboratory Procedure #STANBIO-BUN-0580 Section: Chemistry Date of Implementation: 11/29/2010 Page 4 of 6 essential. “Vortexing” is recommended. During heating, ensure that water levels remain above reaction mixtures and that heating time is adequate according to method employed. If a heat block is used, heating time may be slightly extended. Interpretation of Results Calculations A reagent blank and 3 BUN standards must be run with every test. The readings obtained with the 3 standards are used to prepare a standard curve for each run. Derive BUN concentration of specimens using obtained absorbance. If using urine specimen, refer to “Specimen Requirements” section for calculation of BUN as well as urine specimen calculation. Expected Results The provided ranges should be used as a guideline. Serum/Plasma Urine Clinical Significance 5-25 mg/dL 6-17 grams/24 hrs BUN determination is useful in the evaluation of cardiac and renal function and may also yield information for other health conditions. Plasma BUN levels of 37 mg/dL or above are considered significantly high. See also section “Clinical Utility.” Interference Substances similiar to urea and which react with diacetylmonoxime in an analogous manner are the amino acids citrulline and allantoin. The presence of these materials are very low and do not lead to significant interference. The effects of drugs and their metabolites should be considered. Method Performance Specification Specific for BUN given the absence of citrulline and allantoin. Between Run Precision: +/- 5% Recoveries: 92-99% Reporting Report results after confirmation that controls are valid and no errors were detected. Page 4 of 6 CLS Laboratory San Francisco State U niversity 1600 Holloway Avenue San Francisco, CA 94132 CLS Laboratory Procedure #STANBIO-BUN-0580 Section: Chemistry Date of Implementation: 11/29/2010 Page 5 of 6 Supporting Documents Related Procedures Pointe 180 Analyzer – Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Reagent Set References 1. Tietz NW (ed). Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry. Ed. 3, Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 967; 1987. 2. Stanbio Laboratory. Stanbio Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Procedure No. 0580. Boerne, Texas: 2005. MSDS: DAM: doc#146078 Ferric Chloride Hexahydrate: doc# 1982833 Phosphoric Acid: doc#1855291 Sulfuric Acid: doc#2360643 Thiosemicarbazide: doc#1778034 Urea: doc#2801379 Author:_________________ Date:__________________ Approved by:______________ Date:____________________ Page 5 of 6 CLS Laboratory San Francisco State U niversity 1600 Holloway Avenue San Francisco, CA 94132 CLS Laboratory Procedure #STANBIO-BUN-0580 Section: Chemistry Date of Implementation: 11/29/2010 Page 6 of 6 Procedural Flow Chart: Stanbio Urea Nitrogen (BUN) I. PREANALYTICAL Specimen is urine, serum, or plasma? Yes - Was the stored properly handled: storage, temperature, no hemolysis, proper anticoagulant/additive used, etc? II. ANALYTICAL (To be done with each specimen) Reagent Blank (B): In a test tube, add 0.02 mL of water, 1.0 mL BUN Color Reagent, and 2.0 mL BUN Acid Reagent. Mix. In a test tube, add 0.02 mL of specimen, 1.0 mL BUN Color Reagent, and 2.0 mL BUN Acid Reagent. Mix. III. POSTANALYTICAL STANDARD: In a test tube add, 0.02 mL of standard, 1.0 mL BUN Color Reagent, and 2.0 mL BUN Acid Reagent. Mix. Use standard absorbances to construct a standard curve . X-axis: Concentration (mg/dL) (Repeat for remaining standards). Y-axis: Absorbance(A) at 520 nm Incubate for exactly 10 minutes in a boiling water bath. If a heat block is used, incubate for 12 minutes at 100°C. Incubate for exactly 10 minutes in a boiling water bath. If a heat block is used, incubate for 12 minutes at 100°C. Incubate for exactly 10 minutes in a boiling water bath. If a heat block is used, incubate for 12 minutes at 100°C. From the standard curve, derive the value(s) of specimen(s). Yes: Proceed to Analytical Phase Remove the tubes from water bath/heat block simultaneously and immerse in cold water for 35 minutes. Remove the tubes from water bath/heat block simultaneously and immerse in cold water for 35 minutes. Remove the tubes from water bath/heat block simultaneously and immerse in cold water for 35 minutes. Confirm that controls/standards are valid and no errors are detected. No: Request new aliquot or specimen collection Remove from cold water bath, mix well and read absorbance (A) of Reagent Blank at 520nm. Remove from cold water bath, mix well and read absorbance (A) of specimen against Reagent Blank at 520nm. Remove from cold water bath, mix well and read absorbance (A) of standard against Reagent Blank at 520nm. Yes: Report results. Record Reagent Blank (B) absorbance. Record specimen absorbance. Record specimen absorbance. No: Troubleshoot errors. No - Request proper specimen type. Proceed to Postanalytical Phase. Proceed to Postanalytical Phase. Proceed to Postanalytical Phase. Page 6 of 6