SGO FAQs for posting 08
advertisement
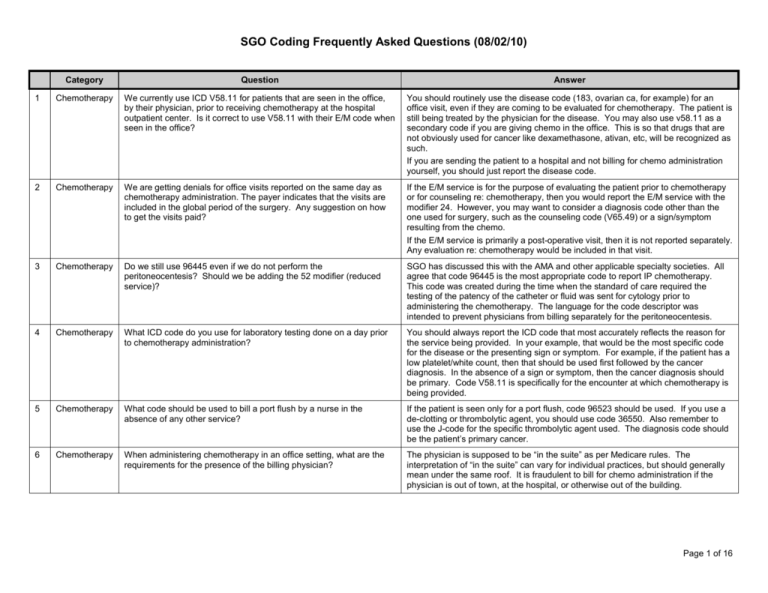
SGO Coding Frequently Asked Questions (08/02/10) Category Question Answer 1 Chemotherapy We currently use ICD V58.11 for patients that are seen in the office, by their physician, prior to receiving chemotherapy at the hospital outpatient center. Is it correct to use V58.11 with their E/M code when seen in the office? You should routinely use the disease code (183, ovarian ca, for example) for an office visit, even if they are coming to be evaluated for chemotherapy. The patient is still being treated by the physician for the disease. You may also use v58.11 as a secondary code if you are giving chemo in the office. This is so that drugs that are not obviously used for cancer like dexamethasone, ativan, etc, will be recognized as such. If you are sending the patient to a hospital and not billing for chemo administration yourself, you should just report the disease code. 2 Chemotherapy We are getting denials for office visits reported on the same day as chemotherapy administration. The payer indicates that the visits are included in the global period of the surgery. Any suggestion on how to get the visits paid? If the E/M service is for the purpose of evaluating the patient prior to chemotherapy or for counseling re: chemotherapy, then you would report the E/M service with the modifier 24. However, you may want to consider a diagnosis code other than the one used for surgery, such as the counseling code (V65.49) or a sign/symptom resulting from the chemo. If the E/M service is primarily a post-operative visit, then it is not reported separately. Any evaluation re: chemotherapy would be included in that visit. 3 Chemotherapy Do we still use 96445 even if we do not perform the peritoneocentesis? Should we be adding the 52 modifier (reduced service)? SGO has discussed this with the AMA and other applicable specialty societies. All agree that code 96445 is the most appropriate code to report IP chemotherapy. This code was created during the time when the standard of care required the testing of the patency of the catheter or fluid was sent for cytology prior to administering the chemotherapy. The language for the code descriptor was intended to prevent physicians from billing separately for the peritoneocentesis. 4 Chemotherapy What ICD code do you use for laboratory testing done on a day prior to chemotherapy administration? You should always report the ICD code that most accurately reflects the reason for the service being provided. In your example, that would be the most specific code for the disease or the presenting sign or symptom. For example, if the patient has a low platelet/white count, then that should be used first followed by the cancer diagnosis. In the absence of a sign or symptom, then the cancer diagnosis should be primary. Code V58.11 is specifically for the encounter at which chemotherapy is being provided. 5 Chemotherapy What code should be used to bill a port flush by a nurse in the absence of any other service? If the patient is seen only for a port flush, code 96523 should be used. If you use a de-clotting or thrombolytic agent, you should use code 36550. Also remember to use the J-code for the specific thrombolytic agent used. The diagnosis code should be the patient’s primary cancer. 6 Chemotherapy When administering chemotherapy in an office setting, what are the requirements for the presence of the billing physician? The physician is supposed to be “in the suite” as per Medicare rules. The interpretation of “in the suite” can vary for individual practices, but should generally mean under the same roof. It is fraudulent to bill for chemo administration if the physician is out of town, at the hospital, or otherwise out of the building. Page 1 of 16 SGO Coding Frequently Asked Questions (08/02/10) Category Question Answer 7 Chemotherapy Is it sufficient for a Physician Assistant-Certified to be onsite in a clinic during a chemo infusion, or must a physician be physically onsite? Generally speaking, NPs, PAs and non-oncology physicians can provide supervision for chemotherapy administration. You may want to clarify this with your individual Medicare carrier and other payers to make certain there are no local policies that contradict with this information. 8 Chemotherapy Can a gyn oncologist bill for chemotherapy counseling if that counseling falls within the global period following a surgical procedure? Yes. Use the relevant E/M code with the 24 modifier for distinct E/M service during the global period. Also, you must use an ICD-9 code for counseling, such as V65.49 (other specific counseling). 9 Brachytherapy How do you code for insertion of a Smitt sleeve? The SGO coding committee suggests that the insertion of the Smitt sleeve be reported either using code 57800-22 (dilation of cervix) or 58120-52 (Dilatation and curettage). The 22 modifier indicates increased procedural service and the 52 denotes a reduced service. The 22 modifier will require a copy or the procedure note in order to obtain additional reimbursement for the increased work. Not all payers utilized modifier 52 when determining reimbursement so you may receive full payment even with the modifier. 10 Brachytherapy How do you code for placement of Heyman’s capsules? Report code 58346 (Insertion of Heyman capsules for clinical brachytherapy). 11 Brachytherapy How do you code for placement of tandem/ovoids for brachytherapy? Gyn oncologists should use code 57155 (insertion of uterine tandems and/or vaginal ovoids for clinical brachytherapy). Modifier 76 (repeat procedure by the same physician) may be necessary for subsequent treatments. Radiation oncologists will bill for insertion of radioactive elements using separate codes 12 Brachytherapy How do you bill for insertion of vaginal applicator device in High Dose Rate (HDR) brachytherapy? The surgeon should use code 57155 (insertion of uterine tandems and/or vaginal ovoids for clinical brachytherapy) for insertion of tandem and ovoid. If a tandem is not placed, use a reduced service modifier 52. Page 2 of 16 SGO Coding Frequently Asked Questions (08/02/10) Category Question Answer 13 E/M Can you bill for inpatient and outpatient E/M services provided after surgery if the patient is seen for a post-operative complication such as a wound infection? Is a modifier required? The CPT global surgical package includes all routine postoperative visits normally provided in conjunction with the surgery. Medicare includes in this, the treatment of complications managed outside the operating/procedure room. Medicare has set the global period as either 0, 10,or 90 days depending on the specific procedure. Most other payers follow Medicare's post-operative periods. Most major gyn/onc procedures have a 90-day global period. Therefore, visits in the hospital immediately following surgery and routine outpatient visits are included in the payment for the applicable surgery and should not be separately reported. E/M services for post-operative complications such as wound infections and dehiscence cannot be reported to Medicare until the patient is taken to the OR for a surgical procedure. Any procedure performed in the operating room associated with these conditions can be reported by appending modifier 78 (Unplanned procedure). For non-Medicare payers, you can report any additional E/M services above routine care for services related to the surgery, such as wound infections. If visits for conditions unrelated to surgery are provided in the global period, these can be reported by appending modifier 24. Modifier 24 is used for E/M services provided in the global period that are "unrelated" to the surgery. No modifier is required for visits associated with complications or other related conditions. 14 E/M I heard that SGO suggests that all follow-up visits for cancer surveillance be reported using code 99214 for up to 5 years? SGO does not make blanket suggestions about the level of service selection for specific types of E/M encounters. The level of service should be based on the CPT guidelines for selecting E/M codes and the work necessary to appropriately evaluate and manage the patient. The CMS Documentation Guidelines describe the documentation components for the various types of history, examination, and medical decision-making. Medicare and most private payers use these guidelines when reviewing medical records for levels of service. Note that CMS states, “Medical Necessity is the overarching criterion for payment in addition to the individual requirements of a CPT code. It would not be medically necessary or appropriate to bill a higher level of evaluation and management (E/M) service when a lower level service is warranted.“ Page 3 of 16 SGO Coding Frequently Asked Questions (08/02/10) Category Question Answer 15 E/M How do you differentiate between a new patient and a consultation from another physician especially if I perform surgery and follow with chemotherapy? According to CPT, a consultation is a type of evaluation and management service provided by a physician at the request of another physician (or appropriate source) to either recommend care for a specific condition or problem or to determine whether to accept responsibility for ongoing management of the patient's entire care or for the care of a specific condition or problem. CPT further states you can initiate diagnostic or therapeutic services at that encounter or subsequent encounters and still report a consultation code. It is expected that the requesting provider will use the consultant's information in the care of the patient. This does not mean the referring physician has to provide all the f/up care for the condition but that the information was valuable to them as they continued to care for the patient. If a provider is sending the patient to have a specific service provided and is not seeking input on a specific problem, then consultation codes are not used. For example, a patient is sent by an internist for a routine pap and pelvic exam. This is not a consult because there is no opinion being requested. A patient with a gynecologic cancer sent to you by a physician, may very well be reported using a consultation code. At that visit, you are likely making an independent evaluation of the best plan of care which may include surgery. Based on your evaluation, you will provide your written recommendations back (required to bill consult code) to the requesting physician. Once you have provided the initial consultation, subsequent services will be reported using the appropriate established patient codes or appropriate inpatient services. Beginning January 1, 2010, Medicare no longer recognizes consultation codes. In the office or other outpatient area, you should report the appropriate new or established outpatient code. In the inpatient setting, Medicare instructs the consultant to report the appropriate initial inpatient code (99221-99223) for the first encounter and then subsequent inpatient services (99231-99233) for any additional inpatient care. 16 E/M Can consultation codes be reported to Medicare? Beginning January 1, 2010, Medicare no longer recognizes consultation codes. In the office or other outpatient area, you should report the appropriate new or established outpatient code. In the inpatient setting, Medicare instructs the consultant to report the appropriate initial inpatient code (99221-99223) for the first encounter and then subsequent inpatient services (99231-99233) for any additional inpatient care. If the evaluation does not support the requirements for initial inpatient care, a subsequent care code can be reported for the initial encounter with the patient. Page 4 of 16 SGO Coding Frequently Asked Questions (08/02/10) Category Question Answer 17 E/M Can the nurse or office staff document the History of Present Illness (HPI)? We were told the physician must document the HPI. The Documentation Guidelines for Evaluation and Management Services state that the Review of Systems (ROS) and the Past, Family, Social History (PFSH) can be recorded by ancillary staff or on a form completed by the patient. It does not specifically indicate that the History of Present Illness (HPI) can be recorded by staff. It is generally felt that the content of the HPI requires the expertise of a physician or mid-level provider to appropriately address the patient's presenting problem. If the physician is noting changes, additions, or agreement with the HPI then this may be seen as adequate in the event of a payer audit. The physician should be encouraged to make the necessary additions or changes as he/she interviews the patient. 18 E/M Can the stage of the malignancy be used to indicate the severity or progression of the disease and counted towards the severity in the History of Present Illness component of an E&M service when the patient presents with no symptoms (ie. for a follow-up visit)? Among the 8 possible elements of the HPI, the one referred to as "Severity", when applied to a patient whose chief complaint is a cancer, usually relates to the extent of disease (i.e. Stage). It is correct to use the stage of the malignancy as an HPI element. 19 E/M How long can you use the cancer diagnosis (183.0) for a patient once they have completed treatment? There are 2 options that can be used, either the primary malignancy code or the personal history of malignancy code. SGO and other oncology societies have taken the position that patients receiving surveillance for a treated malignancy should have the ICD-9 code for that malignancy as their diagnostic code. For example, a patient who is followed for ovarian cancer would have 183.0 as the diagnostic code to justify the clinic visit. Patients who are under surveillance for cancer recurrence are not cured by definition, since there would be no reason to do surveillance if they were cured. The length of time a primary cancer code should be used is up to the individual physician to decide. More recently, some institutions have taken the position that you should not use the cancer codes unless the patient has documented evidence for a primary cancer or a recurrent cancer. Patients who have completed treatment for the malignancy, are now considered to have a personal history of cancer (for example, V10.43-ovarian cancer, personal history). Either choice is acceptable and both codes appear to be covered by the majority of payors. 20 Endometrial How do you code for a laparoscopic hysterectomy/BSO and pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy done for endometrial cancer? You should code separately for the laparoscopic hysterectomy and the laparoscopic node dissection depending on exactly what was done. You CANNOT do this for an open TAH/BSO, and nodes, because there are specific codes for this (58200 or 58210), and coding separately for the hysterectomy and nodes is unbundling. Page 5 of 16 SGO Coding Frequently Asked Questions (08/02/10) Category Question Answer 21 Endometrial How do you code for a laparotomy with pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy and omentectomy for endometrial cancer when a TAH/BSO was done by the Ob/Gyn? In this instance, the OB/Gyn reports code 58150 for the TAH. The Gyn/Oncologist reports either code 38780 (Retroperitoneal transabdominal lymphadenectomy, extensive, including pelvic, aortic, and renal nodes (separate procedure)) for the retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy or 38770 (Pelvic lymphadenectomy, including external iliac, hypogastric, and obturator nodes (separate procedure)). Code 38780 includes renal nodes, so by CPT guidelines you should append the 52 modifier (reduced services). Code 38770 does not include the paraaortic nodes. However, of note, 38770 can be reported with the bilateral modifier (50) but 38780 cannot. Reimbursement using the 50 modifier typically results in 150% of the allowable amount. The 2010 RVUs for 38770 are 22.19 and 38780 are 28.23. Therefore, you would actually get better reimbursement reporting 38770-50 and certainly less reimbursement risk than if you used a 52 modifier. If there is cancer in the omentum (ICD-9 235.4), then you can bill separately for the omentectomy, and you would then append a 59 modifier to 49255. If the omentectomy is done for staging, and the final path report shows no cancer, then it will be difficult to get paid for the omentectomy. 22 Endometrial What is the correct way to code a TAH/BSO with omentectomy and full staging for a diagnosis of papillary serous endometrial carcinoma? The typical CPT code for surgical treatment of endometrial cancer is 58200 or 58210 depending upon the extent of the lymphadenectomy. These codes include a TAH/BSO and sampling or removal of pelvic lymph nodes and paraaortic nodes. If a lymphadenectomy is performed instead of lymph node sampling, then code 58210 is used. An omentectomy is considered to be a "separate procedure" under the Correct Coding Initiative (CCI), which means that it should not be reimbursed if billed separately in usual situations. Therefore, obtaining reimbursement for an omentectomy during an endometrial cancer surgery will be problematic, especially if performed for staging purposes (i.e., no gross metastatic disease). One situation that may be reimbursable is when the omentectomy is performed for metastatic disease. Under this scenario, use the omentectomy code 49255 with the 59 modifier, plus the ICD-9 code that justifies the procedure (i.e., 197.6, secondary malignancy of the omentum). Medicare will never reimburse for an omentectomy done at the time of a hysterectomy but other payors might under this circumstance. 23 General Is it appropriate to append the 22 modifier to code 58210 when a total omentectomy is performed? Our practice has been unsuccessful in getting additional reimbursement from either Medicare or the commercial payers. One of the problems lies in the fact that Medicare's CCI bundles an omentectomy into code 58210 and will not allow it to be paid even with a modifier. Therefore, they may not be willing to pay additionally for the omentectomy even though the code does not include a total omentectomy. A number of other payers also use the CCI as part of the claims review process. You might try having the surgeon dictate a general letter indicating the need for the total omentectomy and the work involved including the additional time and risk. The letter should clearly indicate that the procedure is not a partial omentectomy. Another coding alternative might be code 58954 but this includes a debulking and assumes there is intra-abdominal disease. Page 6 of 16 SGO Coding Frequently Asked Questions (08/02/10) Category Question Answer 24 General How do you code for a radical hysterectomy when there was not a node dissection performed because the patient had pre-op radiation? There is not a specific CPT code for a radical hysterectomy without lymphadenectomy. The best choice would be to report code 58210 with the reduced service modifier 52. This assumes that the parametria were excised and the ureters were dissected as is done typically with a radical hysterectomy. If this as not done, then it should be coded as 58150-22. 25 General Is it appropriate to report code 38562 when a complete lymphadenectomy is done in conjunction with 58150? Code 38562 is described as a "limited lymphadenectomy" that is performed for staging. In addition, it is designated as a separate procedure in CPT and may therefore be bundled into other procedures reported on the same day. It is likely that code 58210 is most appropriate if the parametria were excised and the ureters were dissected as is done typically with a radical hysterectomy. In general, codes 38570-38572 are most commonly reported when it is appropriate to report nodes separately from other procedures. 26 General How do you code for a laparoscopic (robotic assisted) trachelectomy, BSO, and lymphadenectomy? I was considering reporting codes 58661, 57530, and 38571 but a colleague suggested code 58552 with 38571. It would not be appropriate to report code 58552 (Laparoscopy surgical; with vaginal hysterectomy, for uterus 250 grams or less; with removal of tube(s) and/or ovary(s)) since a hysterectomy was not performed. As you suggested, the BSO would be reported using code 58661 (Laparoscopy, surgical; with removal of adnexal structures (partial or total oophorectomy and/or salpingectomy) and the bilateral pelvic lymphadenectomy with code 38571 (Laparoscopy surgical; with bilateral total pelvic lymphadenectomy). Since there is not a code for a laparoscopic trachelectomy, a code using a different approach would have to be used. Code 57530 is intended to be used when the uterus is still in place and the surgeon simply removes the cervix and leaves the uterus in place. In this case, the uterus was previously removed. A “Cervical stump” occurs when the uterus was removed from the cervix and the cervix was left in place. Therefore, you would choose either 57550 (Excision of cervical stump, vaginal approach;) or 57540 (Excision of cervical stump, abdominal approach) depending on which best represents the work performed by the surgeon. In either case, you might want to submit a special report indicating that portion was done via a laparoscopic approach. There are not codes specific to the use of the robotic arm. 27 General How do you code for a robotic trachelectomy when the uterus has been previously removed? Since there is not a code for a laparoscopic approach, the unlisted code 58578 (unlisted laparoscopy procedure). The unlisted code will require a special report and payment may be delayed. Page 7 of 16 SGO Coding Frequently Asked Questions (08/02/10) Category Question Answer 28 General What is the difference between codes 58552 (Laparoscopy surgical, with vaginal hysterectomy, for uterus 250 grams or less; with removal of tube(s) and/or ovary(s)) and 58571 (Laparoscopy, surgical, with total hysterectomy, for uterus 250 g or less; with removal of tube(s) and/or ovary(s))? Codes 58550-58554 describe laparoscopically assisted vaginal hysterectomy which includes a laparoscopic detachment of ovarian vessels and skeletonization of the uterine attachments. The uterus is removed vaginally. Codes 58570-58573 describe services in which the uterine fundus and cervix are all performed laparoscopically and the vaginal cuff is sewn laparoscopically. Often, the specimen is removed via the vagina. Codes 58570-58573 are typically performed using the robot. 29 General What is the most appropriate code for thickened endometrial stripe? The code is 793.5 (abnormal findings on radiograph, genitourinary). 30 General Is it appropriate to use code 209.29 for Vipoma? A true VIPoma is a tumor of the endocrine pancreas cells. Code 209.29 would not be appropriate. Code 209.29 is for carcinoids (malignant carcinoid tumor of other sites). A Vipoma may show signs of carcinoid syndrome, but is not a carcinoid, per se. Codes C25.4 (malignant neoplasm, endocrine pancreas) or E16.8 (other disorders of pancreatic intestinal secretion) would be more appropriate. 31 General What is the difference between codes 58950-58952 and codes 58953 and 58954? Codes 58953-58954 include a hysterectomy as a required component and radical debulking of the tumor(s). Codes 58950 and 58952 do not include a hysterectomy. While code 58951 does describe a hysterectomy and lymphadenectomy, it does not represent a radical debulking as described by codes 58953-58954. Code 58951 is more appropriate when you fully stage an otherwise clinical stage 1 ovarian cancer. It is recommended that you discuss these distinctions with the surgeons and request that the surgical procedure be described using the language found in CPT. This will help you to better assist in the proper selection of the surgical codes. 32 General Can you report a cystoscopy at the time of a pelvic procedure to make sure there is no injury to the ureters? A cystoscopy performed routinely at the time of a surgical procedure is not separately reportable. When procedures are done to "check" one's work, it is considered inherent in the procedure. Additionally, there is not an ICD code that can be appended to support a clinical need for the service. If there has been an injury to the ureters at the time of the surgery, then it would be appropriate to report the cystoscopy with the appropriate ICD code, such as hematuria. 33 General Is code 58720 bundled into code 49203? CPT lists a number of procedure codes that should not be reported in conjunction with code 49203 (Excision or destruction, open, intra-abdominal tumors, cysts or endometriomas, 1 or more peritoneal, mesenteric, or retroperitoneal primary or secondary tumors; largest tumor 5 cm diameter or less). Code 58720 (Salpingooophorectomy, complete or partial, unilateral or bilateral (separate procedure)) is not among them however codes 58900-58960 are listed. These codes describe ovarian work including 58940 (Oophorectomy, partial or total, unilateral or bilateral). Therefore, it would be reasonable to assume that code 58720 should not be reported in conjunction with code 49203. In addition, Medicare's Correct Coding Initiative (CCI) bundles 58720 into the payment for 49203 and does not allow it to be reported with a modifier. Page 8 of 16 SGO Coding Frequently Asked Questions (08/02/10) Category Question Answer 34 General What is meant by “bundle/unbundle? I reported codes 58952, 44950, and 44120 and received a note from a managed care payer stating that 44120 is a “Medicare Unbundle Code”. In answer to your underlying question regarding "Medicare Bundled Code", Medicare determines lesser services to be included in the payment (bundled) for more comprehensive services. The codes that are considered "bundled" into a specific procedure are noted in Medicare's bundling guidelines, known as the National Correct Coding Initiative (CCI). In some instances, both the comprehensive procedure and the lesser procedures can be reported if a modifier is appended. Modifier 59 is the most common modifier used for this purpose. In the code combination you noted, Medicare's CCI actually bundles 44950 into the payment for 58953. This is because an "incidental" appendectomy is not separately payable when another surgery is performed. If the appendectomy was done for an indicated purpose (inflamed, diseased, etc.), then the proper CPT code is 44955 (Appendectomy; when done for indicated purpose at time of other major procedure (not as separate procedure) (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure). A modifier is not required since this is an add-on code. Based on your question, it seems that 44950 was reimbursed even though it may not be the most accurate code for the surgery. Under CCI guidelines, Code 44120 can be reported in addition to 58953 using the 51 modifier. The denial of this code may have to do with code 44950 as it is bundled into many of the GI codes. I suggest that you review the operative note for clarification. The full CCI, along with background information, is available on the CMS website and noted as the National Correct Coding Initiative. 35 General Is there a difference in coding for a pelvic lymphadenectomy vs. a pelvic lymph node sampling? These services represent different procedures and different work. This is most obvious when you look at the laparoscopic lymphadenectomy codes (38570-38572). If this service is provided with a TAH/BSO for endometrial cancer, code 58200 is used for sampling, whereas code 58210 is used for lympahdenectomy. The lymph node sampling is considered a biopsy as the CPT language suggests and lymphadenectomy is the dissection out of the lymph nodes. 36 General What code would you report for the removal of 2 large pelvic nodes at the time of a TAH/BSO on a patient with post-menopausal bleeding? The nodes were benign. The best option would be code 38500 (Biopsy or excision of lymph node(s); open, superficial). You should append modifier 51 (multiple procedures) to code 38500 and associate with the appropriate ICD code, such as 785.6 (enlargement of lymph nodes). 37 General Can one report a radical debulking code (58952-58954) when there is no tumor outside the ovary? The radical ovarian tumor debulking codes are designed for when there is tumor outside of the ovary/fallopian tube/endometrium. If there is only staging performed, then the more appropriate codes are 58943 or 58950-59951. Page 9 of 16 SGO Coding Frequently Asked Questions (08/02/10) Category Question Answer 38 General What code is reported when a TAH/BSO/Omentectomy/Staging is performed for LMP or borderline tumor? This is a common concern because none of the existing codes fit this exactly. Code 58956 includes a TAH/BSO with total omentectomy. If this is the only staging performed, then this would be appropriate. A more likely choice would be code 58951, which includes a TAH/BSO, omentectomy, and P&P nodes, but does not include peritoneal biopsies. Code 58943 also describes the procedure, but does not include the TAH, and therefore is problematic. If lymph node dissection was not done, then one could code 58952-52 (reduced services). 39 General Can ureterolyisis (50715) be reported in addition to code 58150 (TAH/BSO? Code 50715 is a code used to manage ureteral obstruction secondary to retroperitoneal fibrosis. Absent this indication, the code should not be reported. If the need to dissect the ureters added significant work to the hysterectomy you may append a 22 modifier to code 58150 to indicate the increased difficulty of the procedure. 40 General Can management of total parenteral nutrition be reported for a postop patient? This is considered part of the global package reported by the surgeon. For pre- op patients or patients not having surgery, you can bill use the 99221-99233 series. It may be more cost-effective to consult another physician for management of parenteral nutrition, and allow that person to manage and bill for those services. 41 Exenteration How do you code for placement of a matrix (graft) during pelvic exenteration and reconstruction? Placement of material in the pelvis to prevent bowel obstruction would be considered an inherent part of the procedure, and should not be billed separately. Therefore, you should report only code 58240 for the pelvic exenteration. An exception would be placement of an omental pedicle flap in the pelvis (+49905). 42 Exent Would it be appropriate to code construction of the vagina (57292) with pelvic exenteration (58240) or is the construction of the vagina bundled into the exenteration code? Vaginal reconstruction is not included in the pelvic exenteration code, and can therefore be coded separately for construction of an artificial vagina with a skin graft (57292). If anything other than a skin graft is performed (e.g. myocutaneous flaps) this should be coded separately (i.e. 15734). The 51 modifier needs to be used for each additional procedure. 43 GI How do you code for a Hartmann procedure done in conjunction with a radical hysterectomy? The Hartmann procedure is reported with code 44143. The 51 modifier (multiple procedure) should be appended to code 44143 as it has fewer RVUs than the radical hysterectomy (58210). 44 GI How do you code for a mesh closure done at the time of a loop ileostomy and mucofistula? There is no separate code for mesh closure of an abdominal wound. The surgery is best coded by reporting code 44310 with a 22 modifier for the mucous fistula and complex abdominal wall closure. If a 22 modifier is reported the documentation must reflect significant additional work and the reason for the additional work. It may be helpful to send a cover letter highlighting the work associated with the complex wound closure and the mucous fistula. Page 10 of 16 SGO Coding Frequently Asked Questions (08/02/10) Category Question Answer 45 GI How do you code for an ileo jejunal bypass anastamosis and drainage of small bowel fistula with malecot drain on a patient with a history of cervical cancer with secondary small bowel obstruction secondary to severe radiation enteritis? Based on your scenario, it is assumed that a resection was performed. In that situation, code 44120 (Enterectomy, resection of small intestine; single resection and anastomosis) would be the most appropriate code. The fistula drainage and placement of the associated drain are not separately reported but rather are considered to be part of the primary procedure. 46 GI Can you report an appendectomy done at the time of surgery for tumor reduction when the appendix was involved with the tumor? Yes, there is a specific CPT code that should be used in these circumstances. The code is 44955 (Appendectomy, when done for indicated purpose at time of other major procedure). This is an add-on code and therefore does not require the 51 modifier and is not subject to a multiple procedure reduction. You should associate the appropriate cancer diagnosis with the appendectomy to support the fact that it is not an incidental appendectomy. 47 GI Can you code for an appendectomy if the reason it is being taken is to avoid possible appendiceal mucinous lesions? In the situation that you describe, it sounds as if you are coding for an incidental appendectomy. In the CPT book it clearly states: " an incidental appendectomy during intra-abdominal surgery does not usually warrant a separate identification.” When an appendectomy is performed for an indicated procedure, i.e. tumor metastatic to the appendix or involvement with endometriosis, at the time of another major procedure, then you would use code 44955. This is an "add-on" code and therefore does not require a 51 modifier. 48 GI How should you code for an ileotransverse entero-colostomy without a bowel resection? You would report code 44130 (Enteroenterostomy, anastomosis of intestine, with or without cutaneous enterostomy (separate procedure)) 49 Modifier Is the 22 modifier appropriate if you convert from a laparoscopic to an open procedure with diagnosis code V64.41 (Laparoscopic surgical procedure converted to open procedure)? Does the operative report need to indicate additional time or just state that the procedure was converted? The 22 modifier is appended when the work to perform the procedure was substantially greater than that typically required. The conversion from laparoscopic to an open procedure might be an instance in which the 22 modifier is appended, but the documentation will need to reflect “substantial” additional work as specified in CPT. CPT also states that the reason for the additional work such be documented. It lists increased intensity, time, technical difficulty, severity of patient's condition, and physical and mental effort as reasons for additional work. (See modifier 22 descriptor in Appendix A). The note does not specifically need to indicate additional time if any of the above reasons for the additional work is documented. 50 Other What is the code for scalpel excision and cauterization of a 2 cm condyloma growing out of the distal urethra? You should report code 11422 (Excision, benign lesion including margins, except skin tag (unless listed elsewhere), scalp, neck, hands, feet, genitalia; excised diameter 1.1 to 2.0 cm). Code selection is determined by measuring the greatest clinical diameter of the apparent lesion plus that margin required for complete excision (lesion diameter plus the most narrow margins required equals the excised diameter). Therefore, you should consider this when selecting your code. In the event that the "excised diameter" is greater than 2 cm, you would report the appropriate code in this family of codes. That would most likely be code 11423 (excised diameter 2.1 to 3.0 cm). Page 11 of 16 SGO Coding Frequently Asked Questions (08/02/10) Category Question Answer 51 Laparoscopy Is there a corresponding laparoscopic code for codes 58952 (Resection (initial) of ovarian, tubal or primary peritoneal malignancy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and omentectomy; with radical dissection for debulking (ie, radical excision or destruction, intraabdominal or retroperitoneal tumors) and 44955 (Appendectomy; when done for indicated purpose at time of other major procedure (not as separate procedure) (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure)? You should report the unlisted code 58679 (unlisted procedure, ovary) if there is not a laparoscopic code available to describe the procedure performed. If an unlisted procedure code is reported, the claim should be filed manually (paper claim) with a copy of the operative note and a brief explanation of the procedure and reason for the unlisted code. You should base your fee on a comparable open procedure code. For a laparoscopic appendectomy at the time of another procedure, the coding choice is code 44970 (laparoscopic surgical appendectomy). You will need to append modifier 59 to this code to indicate it is separate and distinct from the other surgery. The operative report documentation should clearly describe the procedure and the reason for performing it. You should also append a distinct ICD code if available. 52 Laparoscopy Is there a laparoscopic code for the open procedure code 58825 (Transposition, ovary(s))? There is not a corresponding code for a laparoscopic 58825. You can report code 58679 (Unlisted Laparoscopy procedure, oviduct, ovary). If an unlisted procedure code is reported, the claim should be filed manually (paper claim) with a copy of the operative note and a brief explanation of the procedure and reason for the unlisted code. Alternatively, you might report code 58660 (Laparoscopy, surgical; with lysis of adhesions (salpingolysis, ovariolysis) (separate procedure) to justify any manipulation of the ovary. The lysis of adhesions must be well documented. As a point of information, the RVUs for codes 58825 and 58860 are very similar. 53 Laparoscopy How do I code for a laparoscopic omentectomy done at the time of a laparoscopic BSO and pelvic and para-aortic lymph node dissection for a borderline tumor? There is not a code for laparoscopic omentectomy. You can elect to report code 49329 (unlisted laparoscopy procedure, abdomen, omentum, peritoneum) for the omentectomy in addition to the codes for the other procedures. You will need to send a copy of the operative report and a special report. Alternatively, you might report code 49321-22 (Laparoscopy, surgical; with biopsy (single or multiple). The payer may not provide additional reimbursement for the omentectomy. Medicare’s CCI bundles an omentectomy in the payment for all open hysterectomy codes. If the payer follows this CCI logic, then payment will not likely be made for the omentectomy. 54 Laparoscopy How do you code for a laparoscopic ureterolysis? You should report an unlisted code for procedures that do not have specific laparoscopic CPT codes. It is not appropriate to report the open code in these instances. A laparoscopic ureterolysis should be reported using the unlisted code 50949 (Unlisted laparoscopy procedure, ureter). The open version of this code falls under the “may be paid” category under Medicare's CCI and is intended for the diagnosis of retroperitoneal fibrosis. In general, the same should apply to laparoscopic ureterolysis. Therefore, depending on the circumstances you may not be reimbursed for the ureterolysis. bYou should make certain that the appropriate ICD code is reported for the procedure. Page 12 of 16 SGO Coding Frequently Asked Questions (08/02/10) Category Question Answer 55 Laparoscopy Is it permissible to report an open procedure code when there is not a corresponding laparoscopic code? CPT guidelines indicate that an unlisted code be reported when there is not a specific CPT code for the service provided. More specifically, the guidelines indicate that it is not appropriate to report an open procedure code for a procedure performed laparoscopically. In these instances, the coder is instructed to report the appropriate unlisted code. You will need to send in a special report or cover letter as well as the operative report to describe the need for the unlisted code. 56 Laparoscopy What code do you use for laparoscopic staging of ovarian cancer? There are no specific CPT codes that describe laparoscopic staging/surgery for ovarian cancer or debulking. The final code depends on whether the uterus, tubes/ovaries were removed as part of the procedure or not. If so, then you can use the laparoscopic hysterectomy codes (either LAVH-58550-58554 series or TLH58570-58573 series), or laparoscopic BSO (58661), PLUS laparoscopic P&P nodes (38572), and 49329 (unlisted laparoscopy procedure, abdomen, peritoneum, omentum) for the omentectomy and peritoneal biopsies. 57 Laparoscopy What codes do you recommend for surgeons to use for robotic assisted surgery? There are no specific codes or modifiers to use for robotic surgery. You should select the appropriate laparoscopic code for the surgery you performed. If the work required to perform the procedure was substantially greater than typically required, you can append the 22 modifier and describe the increased work and the reason for the additional work. The modifier should not be used solely because the procedure was done using a robotic approach. 58 Laparoscopy Could you comment on the use of the S2900 code as an additional code for robotic surgery? The "S" codes are created for use for payers other than Medicare. The recognition and utilization of these codes vary according to the payer. You would report code S2900 as a secondary CPT code when you perform a surgery using robotics. It is not necessary to append a modifier. You should apply some incremental charge to the code for the work associated with the robotic approach that is different from the basic surgery you report. Reimbursement will vary by payer. CPT has made the decision not to have a modifier or specific codes for robotic surgery thereby restricting any additional payment for this technique. 59 Laparoscopy How do you code for a laparoscopic hysterectomy, BSO, bilateral total pelvic lymphadenectomy and paraortic lymph node sampling using a robotic arm? You should report either CPT codes 58571 (Laparoscopy, surgical, with total hysterectomy, for uterus 250 g or less; with removal of tube(s) and/or ovary(s)) or 58573 (Laparoscopy, surgical, with total hysterectomy, for uterus greater than 250 g; with removal of tube(s) and/or ovary(s)) depending on the size of the uterus. Code 38571 (Laparoscopy, surgical; with bilateral total pelvic lymphadenectomy) should be reported as the second procedure with modifier 51. Code 38572 (Laparoscopy, surgical; with bilateral total pelvic lymphadenectomy and peri-aortic lymph node sampling (biopsy), single or multiple) would be reported if para-aortic node sampling was also done. There is no code or modifier for use of the robotic arm. These services are reported using the applicable laparoscopic codes. Page 13 of 16 SGO Coding Frequently Asked Questions (08/02/10) Category Question Answer 60 Laparoscopy Can robotic surgery be performed as an outpatient procedure? Our hospital billers insist that it is an inpatient procedure and should be documented to that effect. The status of the patient with the hospital (inpatient or outpatient) is what determines how the claim should be billed and how the operative report and medical records are documented. As there are not specific codes for robotic surgery, the appropriate laparascopic code should be reported for the surgery performed. Some laparoscopic procedures are commonly performed as outpatient surgery. The codes for total laparoscopic hysterectomy (58570-58573) were valued to include a brief inpatient hospital stay. You should explore with the hospital’s billing department the background and issues associated with the request. It may be that the hospital has designated the patient as an inpatient for these procedures, thus creating a mismatch between the hospital and physician billing. It is also possible that a payer may not reimburse the hospital unless the surgery if performed on an inpatient basis. 61 Cervix How do you code for a radical parametrectomy? Report a code from the series 57107-57111 (vaginectomy with removal of paravaginal tissue) 62 Cervix How should you code for EUA/cystoscopy/proctoscopy for staging of cervical cancer? EUA-57410. Cystoscopy (52000) and proctoscopy (45300) have separate procedure codes and are frequently not reimbursed when used with 57410 for a diagnosis of cervical cancer. However, if there is a separate diagnosis specific for cystoscopy or proctoscopy, (hematuria, melena, dysuria, constipation) you may use code(s) 52000 and/or 45300 linked with code 57410 using the 59 modifier. 63 Cervix What code do you use to charge for a trucut needle biopsy of the pelvic soft tissue performed along with an exam under anesthesia? Report code 20206 (Deep biopsy using percutaneous needle). 64 Ovarian How do you report a radical hysterectomy/bso without nodes; rectosigmoid resection; infragastric omentectomy; and optimal debulking on a patient with ovarian cancer? The best approach is to report code 58953 (Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy with omentectomy, total abdominal hysterectomy and radical dissection for debulking) plus the appropriate colectomy code (e.g.44145) or other more appropriate code. If there was also a takedown of the splenic flexure, then you would also report code 44139 (Mobilization (take-down) of splenic flexure performed in conjunction with partial colectomy (List separately in addition to primary procedure). Code 44139 is not subject to multiple procedure reduction since it is an add-on code. The omentectomy is considered part of code 58953 and thus is not reported separately. If the hysterectomy was particularly difficult, then modifier 22 can be appended to the primary code. According to CPT, the documentation must support the substantial additional work and the need for the additional work. 65 Ovary How do you code for a resection of a left ovarian CA; radical dissection and tumor reduction of pelvic tumor involving the rectosigmoid, mesentery and left pelvic retroperitoneal spaces; omentectomy; and pelvic and paraaortic lymphadenectomy on a patient with Stage III malignant germ cell tumor? The uterus and right ovary and tube were preserved. ACOG, in conjunction with SGO, suggests in its coding manual that code 58954-52 (Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy with omentectomy, total abdominal hysterectomy and radical dissection for debulking; with pelvic lymphadenectomy and limited paraaortic lymphadenectomy) be reported in this instance. The 52 modifier indicates a "reduced service" since the hysterectomy component was not performed. Not all payers recognize modifier 52 so that the full allowable amount may be reimbursed for the procedure. You can choose to decrease your fee as you deem appropriate. Page 14 of 16 SGO Coding Frequently Asked Questions (08/02/10) Category Question Answer 66 Ovary How do you code for ovarian cancer staging for early disease? We perform a TAH/BSO, pelvic and para-aortic dissection, omentectomy, and biopsies. The codes for ovarian cancer procedures are in the 58943-58960 for open procedures. The options for the above would be code 58951 (Resection (initial) of ovarian, tubal or primary peritoneal malignancy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and omentectomy; with total abdominal hysterectomy, pelvic and limited para-aortic lymphadenectomy). If radical dissection for debulking is done, then you would report code 58954 (Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy with omentectomy, total abdominal hysterectomy and radical dissection for debulking; with pelvic lymphadenectomy and limited para-aortic lymphadenectomy). Codes 58953-58956 can be used for cancer at all sites including the uterus. Although the selection of codes for treatment of gyn malignancy is fairly robust, there may be those occasions when the procedure actually performed is varied slightly from the available codes. In these instances, you can consider appending either a 52 (reduced services) or 22 (increased services) modifier to the basic procedure. 67 Ovary How do you code for a radical abdominal hysterectomy and an ovarian suspension? You should report code 58210 (Radical abdominal hysterectomy, with bilateral total pelvic lymphadenectomy and para-aortic lymph node sampling (biopsy), with or without removal of tube(s), with or without removal of ovary(s)) and 58825 (Transposition, ovary(s)). The CPT instructions beneath code 58210 state "For radical hysterectomy with ovarian transposition, use also 58825". The term "ovarian suspension" is another way to state "ovarian transposition". You may need to append modifier 51 (multiple procedure) to 58825. 68 Ovary Can you use a BRCA-1 mutation as a diagnosis? No. There is no specific code for BRCA-1 mutations. Other possibilities include: V84.01-genetic susceptibility to breast cancer, V84.02-genetic susceptibility to ovarian cancer, or 758.9-conditions due to anomaly of unspecified chromosome. 69 Vulva How do you code for a partial urethrectomy done en bloc with a radical vulvectomy for vulvar cancer? It would be reasonable to report code 53210 (Urethrectomy, total, including cystostomy; female) for the partial urethrectomy with the reduced services modifier 52. Code 53210 is not bundled into the vulvectomy codes. 70 Vulva How do you code for bilateral inguinal sentinel lymph node removal performed at the time of radical vulvectomy? The procedure should be reported using the appropriate vulvectomy code plus code 38500 (Biopsy or excision of lymph node(s); open, superficial) with the 50 modifier (bilateral procedure). The identification of the sentinel nodes is reported using code 38792 (Injection procedure for identification of sentinel node) with the 50 modifier. Page 15 of 16 SGO Coding Frequently Asked Questions (08/02/10) Category 71 Vulva Question Answer How do you code for a skinning vulvectomy? Is it better to report code 56620 or a code from the integumentary section of CPT? In general, it is better to be more specific for coding purposes. Codes 56620 and 56625 are specifically meant for vulvar procedures and should be used instead of integumentary codes. The 80% rule applies. If you remove >80% of the total vulva, it is considered “Vulvectomy, simple; complete” (56625). If <80% is removed, it is considered “Vulvectomy, simple; (56620). If a graft is required, you cannot code for suturing a skin graft into place, as that is considered part of the repair portion of the vulvectomy codes. If you harvest the skin graft as well, you should use code 15120 (split thickness autograft, genitalia). Page 16 of 16