Vitamins
advertisement

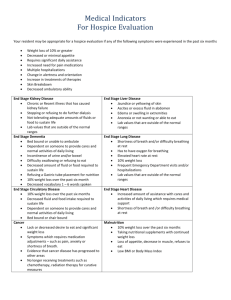
H “H” VITAMINS Fat Soluble Vitamins A, D, E, K -excess intake is stored in body -best absorbed in presence of fats or oils; absorption decreased if intake is with mineral oil -increased requirement in pregnancy, lactation VITAMIN A -destroyed by acids, freezing, UV lights, and exposure to air -liver carrots, dark green leafy vegetables, cod liver oil, fish, butter, margarine, egg yolk, cheese (except cottage cheese), apricots, yellow melons and squash, peaches, nectarines, broccoli, tomato, sweet potato -deficiency may result in… retarded growth, skin, tooth, and eye disease, blindness, reproduction problems, decreased ability to fight infection, allergies, poisons (insecticides, PCB, alpha-toxins) and cancer, loss of sense of smell and taste (xerophthalmia – thick, dry, wrinkled skin) VITAMIN D (cholecalciferol) -destroyed by exposure to light -liver, oils, egg yolk, margarine, herring, salmon, tuna, sardines, shrimp, butter, fortifies or irradiated milk, cheese, sunflower seeds, SUNSHINE -deficiency may result in… rickets, bone abnormalities and demineralization (osteoporosis), slow growth, easy fractures, osteomalcia, possible skin aging, decreased ability to fight lead poisoning -synthesized by body with sunlight -need to absorb calcium and phosphorus VITAMIN E -destroyed by overheating of oils, freezing, alkali, exposure to light and air, refining of cereals and grains -vegetable oils and margarine especially unhydrogenated, peanuts, soybeans, whole wheat (in germ), chocolate, cabbage, spinach, asparagus, almonds -deficiency may result in… anemia, poor muscle development, possibly fetal death, possible rapid aging, skin spots, poor fat absorption, gall bladder disease, breakdown of vascular and nervous systems -increased requirement with diet high in vegetable oils, stress, pregnancy, lactation, exposure to toxins and ionizing radiation; vitamin E protects vitamin A, vitamin C, and unsaturated fatty acids from being destroyed in foods and in the body (by oxidation and peroxidation) VITAMIN K -destroyed by alkali, exposure to light, irradiation -cabbage, cauliflower, soybeans, spinach, and other dark green leafy vegetables, pork, liver tomatoes, potatoes, strawberries, whole wheat:::: in humans produced in the intestines by normal bacteria -deficiency may result in increased bleeding/hemorrhage, easy bruising -need for blood clotting Water Soluble Vitamins -dissolve into cooking water -increased requirement in pregnancy and lactation -not stored – needed daily 3% loss – 20 – 30 % performance loss 5% loss – heat exhaustion 7% loss – hallucinations 10% loss – heat stroke B1 – Thiamin -releases ATP -transmits nerve impulses -breakdown alcohol -destroyed by heat (above 325), alkali (adding baking soda to cooking water – okay in baked products), exposure to UV light and oxygen, excess tea, raw fish, refining of cereals -brewer’s yeast (cooked), lean pork, soybeans, wheat germ, whole grains, raisins, sunflower seeds, nuts, dried beans, fortified flours, noodles and cereals, most vegetables and meats -deficiency may result in beriberi, mental and sensory disturbances, muscle weakness, constipation, circulatory and heart disease, retarded growth, appetite and weight loss -absorption increased in presence of onion and/or garlic, decreased by antacids -increased requirements in pregnancy, lactation, older age, alcohol use, contraceptive pill B2 – Riboflavin -cell respiration -growth and skin formation -destroyed by alkali, exposure to UV and visible light (ie: milk in glass bottles) -liver, organ meats, mushrooms, yeast, avocado, currants, green vegetables, nuts, milk, cheese, eggs, meat, fortified cereals -deficiency may result in… sores and irritation of tongue, lips, mouth, eyes, skin, dandruff, decreased resistance to disease, mental depression, visual disturbances, deficient growth and development, deformed babies -chelosis: lesions in the mouth -glossitis: inflamed tongue B6 – Pyridoxin -form antibodies -form red blood cells -functions in nervous system -destroyed by exposure to air and light, cooking (50% lost), freezing (25% lost), irradiation, refining of grains (up to 90% lost) -liver, herring, salmon, peanuts, walnuts, brewer’s yeast, brown rice, wheat germ, whole wheat, egg yolk, soybeans, banana, grape, pear, carrot, corn, potato, tomato, brussel sprout, spinach, meat, fish -deficiency causes… anemia, skin and nervous disorders, convulsions, decreased white blood cell count, antibodies and hormone levels -involved in dental caries, stress, mineral balance, energy production -increased requirement with contraceptive pills, estrogens, tobacco B12 – Cobalamin -forms RNA and DNA -metabolism -destroyed by heat, acid, alkali, exposure to light and air -animal resources only: liver, kidney, egg yolk, shellfish, fish, meat, cheese, milk, eggs -deficiency causes… pernicious anemia (too large red blood cells), inflamed tongue, retarded growth, spinal cord degeneration, nervous disease, decreased white blood cell count -increased requirement with contraceptive pills, tobacco C – Ascorbic Acid -forms collagen -absorbs iron -aids in wound healing -growth and reproduction -destroyed by heat, alkali (soda), exposure to light and air, and copper -broccoli, brussel sprouts, green pepper, dark green leafy vegetables, cabbage, cauliflower, citrus fruits and juices, strawberries, tomatoes, potatoes, summer squash, and melon -deficiency may result in… scurvy, skin, bone, tooth, and gum defects, poor wound healing, swelling, weakness, aching joints, decreased ability to fight infection, allergies, stress, poisons, ionizing, radiation, anemia, poor iron and calcium absorption, decreased hormone levels, easy bleeding due to weakened capillaries -increased requirement with contraceptive pills, in pregnancy, stress, infection, exposure to poisons, radiation, tobacco use, aspirin use Folic Acid -red blood cell formation -protein metabolism -formation of antibodies -destroyed by heat, acid, exposure to UV light, air, refining of grains -liver, asparagus, spinach, whole wheat, dry beans, lettuce, fruit, mushrooms, legumes, yeast, orange juice, bananas -deficiency may result in… anemia, inflamed tongue and intestines, diarrhea, easy bleeding, decreased antibody and white blood cell formation (decreased resistance to infection and cancer) -increased requirement with contraceptive pills, alcoholism, many drugs, hyperthyroidism, pregnancy, aspirin Niacin -cell reproduction -protein synthesis -not easily destroyed -nuts and peanut butter, rabbit, poultry, tuna, halibut, yeast, liver, brown rice, organ meats, whole grains, beef, mushrooms, cheese, seafood, legumes -deficiency may result in pellagra, retarded growth, weakness, diarrhea, indigestion, skin, tongue, and intestinal disturbances, mental disturbances, decreased hormone levels, pigmentation, headaches, insomnia, and 3D’s: dermatitis, diarrhea, dementea Pantothenic Acid -cell respiration -nervous system -mucous section in intestine -immune system -destroyed by dry heat, acid, alkali, canning: 50 – 75 % loss; refining 50 % loss -liver, organ meats, eggs, soybeans, broccoli, peanuts, mushrooms, meat, fish, whole grains, yeast, royal jello -deficiency may result in… reduced resistance to infection, cancer, and stress, heart nerve, muscle, and digestive disturbances, weakness, depression, muscle cramps, poor coordination, “burning” feet