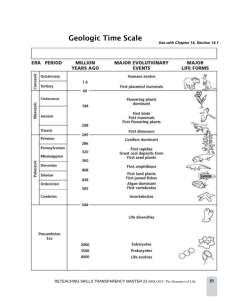
Chapter 8 and Chapter 9 8. State the principle of uniformitariansim
advertisement
Chapter 8 and Chapter 9 Uniformitarianism Relative age Law of superposition Unconformity Law of crosscutting relationships Absolute age Varve Radiometric dating Half-life Fossil Paleontology Trace fossil Index fossil Geologic column Era Period Epoch Evolution Precambrian time Paleozoic era Mass extinction Mesozoic era Cenozoic era 8. State the principle of uniformitariansim. Explain how the law of superposition can be used to determine the relative age of rocks. Compare three types of unconformities. Apply the law of crosscutting relationships to determine the relative age of rocks (show and explain examples.) Summarize the limitations of using the rates of erosion and deposition to determine the absolute age of rock formations. Explain how the process of radioactive decay can be used to determine the absolute age of rocks. Describe four ways in which entire organisms can be preserved as fossils. List five examples of fossilized traces of organisms. Describe how index fossils can be used to determine the age of rocks. 9. Summarize how scientists worked together to develop the geologic column. List the major divisions of geologic time. Describe the major changes to life on Earth in each period. Summarize how evolution is related to geologic change. Identify two characteristics of Precambrian rock. Identify one major geologic and two major biological developments during the Paleozoic era. List the periods of the Mesozoic and “Cenozoic Eras. Identify two major geologic and biological developments during the Mesozoic Era. . Identify two major geologic and biological developments during the Cenozoic Era.