Acids and Bases Worksheet: Neutralization & pH
advertisement

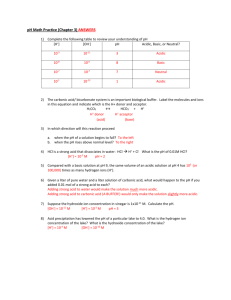
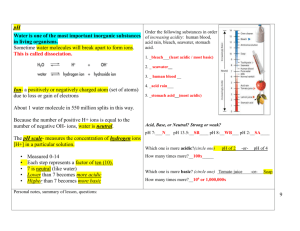
Acids and Bases Name ______________________________ Date ________________ Period _______ Neutralization: Acids and Bases Together True or False: For each false statement, change the underlined word(s) to the correct word(s). 1. ________________ If you dip some blue litmus paper into a neutral solution, the litmus paper turns pink. 2. ________________ If sodium hydroxide is mixed with hydrochloric acid, table salt is formed. 3. ________________ HOH is another way of writing a formula for a base. 4. ________________ Bases always contain a metal ion and a nonmetal ion. 5. ________________ To form a salt, an acid is mixed with a neutral solution. 6. ________________ If a base is added to an acid, one drop at a time, the phenolphthalein indicator in the solution will change from colorless to pink. 7. ________________ A neutral solution contains less hydrogen ions than an acidic solution. 8. ________________ A basic solution contains less hydroxide ions than a neutral solution. 9. ________________ NaF is an example of a base. 10. ________________ An acid is the chemical opposite of a salt. Completion: Write in the word(s) which best complete(s) each statement. 11. A ___________________ solution is neither acidic or basic. 12. If you mix an acid and a base, you produce a ________________ plus ___________________. 13. The above reaction is called ______________________. 14. When an acid and a base are mixed, the water is formed from the _________________ ion of the acid and the _________________ ion of the base. 15. Potassium nitrate is made by mixing _________________ acid and __________________ hydroxide. 16. Whenever an acid is mixed with a base, the compound which is always produced is ______________. 17. Aluminum hydroxide is an example of a(n) ________________. 18. Aluminum chloride is an example of a(n) _________________. 19. HF is the formula for _________________________________. 20. If you mix hydrochloric acid and calcium hydroxide, you produce water and a salt called ______________________________. Acids and Bases pH: Acid or Base True or False: For each false statement, change the underlined word(s) to the correct word(s). 21. _________________ A strong acid gives off many hydroxide ions in water. 22. _________________ The pH of a solution is found to be 5.5. This means the solution is basic. 23. _________________ A pH of 10 is more basic than a pH of 8. 24. _________________ Club soda is shown to have a pH of about 4, so club soda is an acidic solution. 25. _________________ The pH of a dilute solution of calcium hydroxide would be greater than 7. 26. _________________ The pH of a vinegar solution would be greater than 7. 27. _________________ A low pH tells you that few hydrogen ions are present. 28. _________________ As a solution becomes more basic, its pH decreases. 29. _________________ Air pollution from industry often causes rainwater to become acidic. 30. _________________ Unpolluted rainwater is slightly acidic. Completion: Write in the word(s) which best complete(s) each statement. 31. You can think of pH as the _________________ of hydrogen ions. 32. A solution with a pH of 6 is a (slightly, strongly) __________________ acidic. 33. Methyl violet, which changes the color at different pH’s is known as a(n) __________________. 34. The pH of pure water should be __________. 35. An electrical device which can measure the pH is called a ____________________. 36. A strong _______________ gives off many hydroxide ions in water. 37. If you mix equal amounts of equal molarities of sodium hydroxide with hydrochloric acid, the pH will be __________. 38. If vinegar is added to a potassium hydroxide solution, the pH __________________. 39. The pH of your blood should be between 7.2 and 7.4, this means blood is slightly ________________. 40. The pH of a sample of polluted rainwater is found to be 2. This means the rain is ________________. Thought Questions: 41. Tell the difference between a strong acid and a weak acid. 42. Tell the difference between a strong base and weak base. Naming Acids Name the following acids: 43. HNO3 _____________________________________ 44. HCl _____________________________________ 45. H2SO4 _____________________________________ 46. H2SO3 _____________________________________ 47. HC2H3O2 _____________________________________ 48. HBr _____________________________________ 49. HNO2 _____________________________________ 50. H3PO4 _____________________________________ 51. H2S _____________________________________ 52. H2CO3 _____________________________________ Write the formulas for the following acids: 53. sulfuric acid ________________ 54. nitric acid ________________ 55. hydrochloric acid ________________ 56. acetic acid ________________ 57. hydrofluoric acid ________________ 58. phosphorous acid ________________ 59. carbonic acid ________________ 60. nitrous acid ________________ 61. phosphoric acid ________________ 62. hydrosulfuric acid ________________ Oxo or Binary 63 Chemical Formula H3BO3 64 65 CH3COOH 66 H2SO4 67 H2SO3 68 69 70 C17H35COOH 71 H2CO3 72 73 HClO4 74 75 H2S Common Use or Name Boracic acid; eye wash Muriatic acid; digestion Vinegar Oil of vitriol; most used chemical With H2SO4 is acid rain In many cleaners Name of Acid Hydrochloric acid Oxalic acid Fertilizer production In fats; to produce soap Carbonated beverages Fertilizer production The strongest acid Phosphoric acid Bleach Hypochlorous acid Stearic acid Nitric acid In sour gas wells 78 Etches glass Hydrofluoric acid 79 Forms a yellow solution Chromic acid Some common and uncommon laboratory acids Nitrous acid 80 HCN 81 82 C6H5COOH 83 H2SiO3 84 Benzoic acid Thiosulfuric acid 85. pH [H+] pOH (14 – pH) [OH-] 1 1 x 10-1 13 1 x 10-13 2 1 x 10-2 12 1 x 10-12 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 The pH of a solution indicates how acidic or basic that solution is. pH range of 0 – 7 acidic 7 neutral 7 – 14 basic Since [H+] [OH−] = 1.0 x 10−14 at 25°C, if [H+] is known, the [OH−] can be calculated and vice versa. pH = − log [H+] So if [H+] = 1.0 x 10−6, pH = 6 pOH = − log [OH−] So if [OH−] = 1.0 x 10−8, pOH = 8 Together, pH + pOH = 14 Complete the following chart. 86. [H+] pH [OH−] pOH Acidic or Basic 1.0 x 10−5 M 5 1.0 x 10−9 M 9 Acidic 87. 7 1.0 x 10−4 M 88. 89. 1.0 x 10−2 M 90. 11 91. 12 1.0 x 10−5 M 92. 93. 1.0 x 10−11 M 94. 95. 13 6 Self-ionization of Water & pH Name________________________________ 15.2 Review Period________Date____________________ Matching: On the line at left, write the letter of the best-matching definition. _____ 96. self-ionization _____ 97. pure water a. has H3O+ concentration greater than 1 x 10−7 M b. has H3O+ and OH− concentrations of 1 x 10−7 M _____ 98. Kw - ion product constant c. has a pH greater than 7 _____ 99. pH scale d. describes the reaction: H2O + H2O ↔ H3O+ + OH− _____ 100. acidic solution e. has a pH=7;may contain ions other than H3O+& OH− _____ 101. basic solution f. is equal to 1 x 10−14 at 25ºC _____ 102. neutral solution g. describes the acidity or basicity of a solution Short Answer: Answer the following questions in the space provided. True or False: If the statement is true write “true.” If it is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. Write your answer on the line provided. ___________________________ 103. An acidic solution contains only H3O+ ions. ___________________________ 104. A solution with a pH of 4 is acidic. ___________________________ 105. When the pH of a solution decreases from 9 to 7, the [H3O+] increases by a factor of 2. Problems: Solve each of the problems as directed. Show all your work. 106. Based on the given information, classify the following as neutral, acidic, or basic. a. [H+] = 1 x 10−5 M _______________________________________ b. [OH−] = 1 x 10−5 M _______________________________________ c. [H+] = 1 x 10−7 M _______________________________________ 107. Given that a solution has a pH of 3, calculate the [H3O+] and [OH−]. 108. Calculate the [OH−] for an aqueous solution in which [H3O+] is 1 x 10−10 M. Is the solution acidic, basic, or neutral? 109. Determine the [H3O+] for aqueous solutions that have the following pH values. a. 3 b. 6 c. 10 110. The concentration of H3O+ ions in a solution is 3.8 x 10-9 M. What is the pH of the solution? Is the solution acidic, basic or neutral? What is the concentration of OH- ions? pH Problems 111. What is the concentration of OH- ions in saturated limewater if [H3O+] = 3.98 x 10-13 M? What is the pH of the limewater and is limewater acidic, basic or neutral? 112. What is the concentration of OH- ions in a potato and water solution if [H3O+] = 1.6 x 10-6 M? What is the pH of potatoes and water and is it acidic, basic or neutral? 113. What is the concentration of H3O+ ions in 0.1 M ammonia if [OH-] = 1.26 x 10-3 M? What is the pH of ammonia and is it acidic, basic or neutral? 114. What is the concentration of OH- ions in butter if [H3O+] = 6.0 x 10-7 M? What is the pH of butter and is it acidic, basic or neutral? 115. What is the concentration of H3O+ ions in peaches if [OH-] = 3.16 x 10-11 M? What is the pH of peaches and are they acidic, basic or neutral? 116. What is the concentration of OH- ions in 0.1 M borax if [H3O+] = 6.31 x 10-10 M? What is the pH of borax and is it acidic, basic or neutral? 117. What is the concentration of H3O+ ions in eggs if [OH-] = 6.0 x 10-7 M? What is the pH of eggs and are they acidic, basic or neutral? 118. What is the concentration of OH- ions in 0.1 M bicarbonate of soda if [H3O+] = 3.98 x 10-9 M? What is the pH of bicarbonate of soda and is it acidic, basic or neutral? 119. During the course of the day, human salvia varies between being acidic and basic. What is the concentration of H3O+ ions in salvia if [OH-] = 3.16 x 10-8 M? What is the pH of salvia and is this sample acidic, basic or neutral? 120. Analysis of a sample of maple syrup reveals that the concentration of OH− is 5.0 x 10−8 M. What is the pH of this syrup? Is it acidic, neutral, or basic? 121. In a sample of bananas and water, it is found that [H3O+] = 2.51 x 10−5 M. What is the corresponding pH value, and are the bananas and water acidic, basic, or neutral? 122. [OH−] = 7.94 x 10−12 M in a sample of vinegar. What is the pH of the vinegar, and is it acidic, neutral, or basic? 123. A sample of human blood plasma is found to have a concentration of H3O+ ions of 3.72 x 10−8 M. What is the pH of this sample? Is it an acid, a base, or neutral? 124. In a sample of saturated magnesia, it is found that [OH−] = 3.22 x 10−4 M. What is the pH of this sample, and is it acidic, neutral, or basic? 125. Tomatoes are found to have a hydronium ion (H3O+) concentration of 6.12 x 10−5 M. What is the pH of these tomatoes, and are they acidic, neutral, or basic? 126. A saturated solution of calcium carbonate has a hydroxide ion concentration of 2.44 x 10−4 M. What is the pH of this solution, and is it acidic, neutral, or basic? 127. The hydronium ion concentration in a urine specimen is measured to be 6.3 x 10−6 M. What is the pH of this sample, and is it acidic, neutral, or basic? 128. What is the pH of sour pickles if [OH-] = 1.6 x 10-10 M? What is the pH of the pickles? Are the pickles acidic, basic or neutral? 129. The hydroxide content of a popular soft drink is measured and found to be 4.11 x 10-9 M. What is the pH of the soft drink, and is it acidic, basic or neutral? Acid-Base Titration Complete the following statements by filling in the appropriate word or phrase from the list below. Not all choices will be used. acid-base titration equivalence point phenolphthalein water and a salt end point standard solution equal indicator NaCl and water titration curve not equal H2SO4 and water 130. The point at which exactly enough standard solution is added to neutralize the unknown solution is the __________________________. 131. A(n) __________________________________ is used to represent pH data. 132. A(n) __________________________________ is a carefully controlled neutralization reaction. 133. A(n) __________________________________ changes color at certain pH values. 134. A(n) __________________________________ contains an acid or base in known concentration. 135. A common indicator used in titrations is ___________________________________. 136. The point at which the indicator changes color is the ____________________________ of the reaction. 137. The reaction in a titration produces ______________________________________. 138. At the end point of a titration, the number of H+ ions donated by the acid is ______________ to the number of H+ ions accepted by the base. 139. The titration between NaOH and HCl results in a solution of ______________________________. 140. A 30. mL volume of HCl is titrated with 23 of mL of 0.20 M NaOH. What is the molarity HCl in this solution? 141. A 26 mL volume of NH3 is titrated with 23 mL of 0.20 M HCl. What is the molarity of the NH3 in this solution? 142. A 40. mL volume of H2SO4 is titrated with 38 mL of 0.25 M NaOH. What is the molarity of the H2SO4 solution? 143. A volume of 30. mL of 0.25 M HCl neutralizes a 50. mL sample of KOH solution. What is the concentration of the KOH? 144. A volume of 9.0 mL of 0.70 M NH3 neutralizes a 35 mL sample of HClO4 solution. What is the concentration of the HClO4? 145. A volume of 90. mL of 0.2 M HBr neutralizes a 60. mL sample of NaOH solution. What is the concentration of the NaOH? 146. A volume of 37 mL of 0.36 M KCN neutralizes a 75 mL sample of HClO solution.What is the concentration of the HClO? 147. A volume of 46 mL of 0.40 M NaOH neutralizes a 80. mL sample of HCN solution.What is the concentration of the HCN? 148. A volume of 50. mL of 0.30 M HCl neutralizes a 60. mL sample of Ca(OH)2 solution. What is the concentration of the Ca(OH)2? 149. A volume of 20. mL of 0.25 M Al(OH)3 neutralizes a 75 mL sample of H2SO4 solution. What is the concentration of the H2SO4? 150. A volume of 135 mL of 0.40 M HCl neutralizes a 90. mL sample of Ca(OH)2 solution. What is the concentration of the Ca(OH)2? 151. A volume of 60. mL of 0.60 M HBr neutralizes a 80. mL sample of Ca(OH)2 solution. What is the concentration of the Ca(OH)2? 152. A volume of 10. mL of 0.75 M NaOH neutralizes a 30. mL sample of HClO solution. What is the concentration of the HClO? 153. A standard solution of NaOH was prepared in order to determine the molarity of an unknown HCl solution. 5.25 g of NaOH were dissolved in enough distilled water to prepare 100. mL of solution. If 18.5 mL of the HCl solution is used to neutralize 14.5 mL of the NaOH solution what is the molarity of the HCl solution? Titration Problems Solve the following problems. Complete, balanced equations must be written for each! 154) A sodium hydroxide solution is titrated with a 3.0 M hydrochloric acid solution to determine its molarity. If 15.8 mL of the hydrochloric acid is required to neutralize 28.9 mL of the sodium hydroxide solution, determine the molarity of the sodium hydroxide. 155) 139.8 mL of 1.50 M potassium hydroxide is required to neutralize 50.0 mL of nitric acid. What is the molarity of the nitric acid? 156) 24.9 mL of 2.88 M calcium hydroxide completely neutralizes 38.9 mL of a hydrobromic acid solution. What is the molarity of the hyrdobromic acid? 157) 56.0 mL of lithium hydroxide is titrated with 27.4 mL of 0.500 M hydrofluoric acid. Determine the molarity of the base solution. 158) 15.0 mL of phosphoric acid is titrated with 48.3 mL 0.612 M potassium hydroxide. What is the molarity of the phosphoric acid solution? 159) Determine the molarity of hydrochloric acid given the following data: HCl + NaOH Initial buret reading (mL) Final buret reading (mL) 160) + H2O Hydrochloric acid 1.5 37.6 1.75 M sodium hydroxide 0 22.3 strontium hydroxide 11.0 49.2 0.202 M perchloric acid 5.0 38.6 Determine the molarity of phosphoric acid given the following data: Initial buret reading (mL) Final buret reading (mL) 162) NaCl Determine the molarity of strontium hydroxide given the following data: Initial buret reading (mL) Final buret reading (mL) 161) phosphoric acid 0.0 42.5 0.25 M sodium carbonate 0.80 25.0 Determine the molarity of strontium hydroxide given the following data: Initial buret reading (mL) Final buret reading (mL) 2.00 M hydrochloric acid 1.5 37.6 strontium hydroxide 0 22.3 Acid - Base Review I. Vocabulary: 163) __________________________: An ionic compound formed when an acid reacts with a base. 164) __________________________: The reaction between an acid and a base. 165) __________________________: A substance that conducts an electric current when in solution. 166) __________________________: A proton donor. 167) __________________________: A substance that has different characteristic colors in acids and bases. 168) __________________________: A substance that supplies hydroxide ions in solution. 169) __________________________: Can react as either an acid or a base. 170) __________________________: The ion formed when a proton is added to a water molecule. II. Write A for acid, B for base or an X if the indicated property can apply to either. _____171. feels slippery _____189. sour taste _____172. stings in open wounds _____190. reacts with most metals _____173. phenolphthalein is colorless _____191. litmus paper turns red _____174. does not react with metals _____192. [H3O+] = 1.0 x 10-11 _____175. is an electrolyte _____193. has a bitter taste _____176. can produce a salt in some reactions _____194. has a pH > 7 Acids, Bases and Salts 177. Write an E if the indicated substance is an electrolyte or an N if it is a non-electrolyte. _____ HBr 178. _____ CaS _____N2O5 _____KOH Write an A for acids, B for bases and S for salts. ______ CO2 ______ Fe(NO3)2 179. _____ Zn(OH)2 _____ NH4Br _____ LiOH _____ HClO4 Write the name for the following acids: a. HNO3 b. HBr c. H2CO3 d. H2S e. HNO2 f. HC2H3O2 180. Write the formula for the following acids: a. chloric acid b. hydrofluoric acid c. sulfurous acid d. sulfuric acid e. hydroiodic acid f. phosphoric acid 181. Write complete balanced equations for the following neutralization reactions a. barium hydroxide + nitric acid → b. hydrobromic acid + aluminum hydroxide → c. sulfuric acid + rubidium hydroxide → pH Problems 182. Determine the following quantities for a .00045 M HCl solution: a. [H3O+] b. [OH-] c. pH 183. Determine the following quantities for a 0.0034 M NaOH solution: a. [H3O+] b. [OH-] c. pH 184. Calculate the pH for the following solutions and indicate whether each solution is acidic, basic or neutral? a. [H3O+] = 2.9 x 10-9 M b. [OH-] = 1.07 x 10-8 M Titration Problems 185) A sodium hydroxide solution is titrated with a 3.0 M HCl solution to determine its molarity. If 15.8 mL of the HCl is required to neutralize 28.9 mL of the NaOH solution, determine the molarity of the sodium hydroxide. 186) 139.8 mL of 1.50 M KOH is required to neutralize 50.0 mL of H2SO4. What is the molarity of the H2SO4? 187) 56.0 mL of LiOH is titrated with 27.4 mL of 0.500 M HF. Determine the molarity of the base solution. 188) 15.0 mL of HI is titrated with 48.3 mL 0.612 M KOH. What is the molarity of HI?