CE4002-Hydraulic Engineering and water r (1)
advertisement

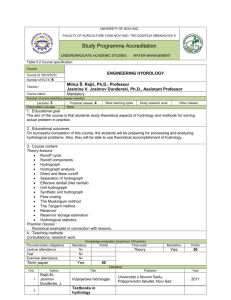
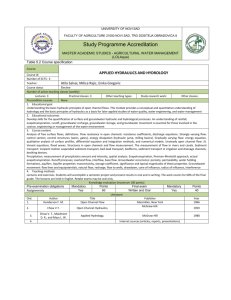
CE 4002 Hydraulic Engineering and Water Resources Subject Code CE4002 Credits 4.0 GPA/NGPA GPA Subject Title Total Hours Hydraulic Engineering and Water Resources Lectures 55 hrs Lab/Assignt` 10 hr Prerequisites CE3004 or equivalent Aims To provide students with an understanding of the principles of Hydraulic Engineering and Water Resources as applied to problem solving and applications in engineering practice. Learning outcomes At the successful completion of this subject course, the learner will be able to: Identify characteristics of non-uniform flowin open channels, recognize different flow profiles and analyse sub-critical, critical and super-critical flows and hydraulic jump Recognize various types of hydraulic structures, their uses and needs;estimate discharges, produce layouts and design key components such as inlet controls, transfer sections, and transitions, etc. Apply concepts of sediment transportation, estimate sediment loads; design conveyance channels considering soil engineering properties and flow requirements/restraints. Recognize important components of hydrologic cycle, related analyses and measurements; apply theories and concepts of surface water hydrology, estimate catchment peak discharges for design storm events; construct/derive hydrographs based on given data and determine hydrograph characteristics and carry out hydrograph analyses. Apply concepts of reservoir operation, reservoir and flood routing in engineering applications Differentiate between types of aquifers, determine aquifer characteristics, develop groundwater flow equations, and analyze groundwater pumping test data. Syllabus Hydraulic Engineering Non-Uniform Flow in Open Channels: Specific Energy (Variation of specific energy with depth at constant discharge and with discharge at constant head ), Critical Depth, Super critical and Sub-critical depths, Alternate depths, Determination of Surface Profiles by Numerical, Graphical and Analytical methods, Hydraulic jump on horizontal bed, Initial depth, sequent depth, Loss of energy in a hydraulic jump, Length of jump, Practical applications of hydraulic jump, Flow from a reservoir to a channel, Flow between two reservoirs, Branching channels, Flow at a clear overfall. Hydraulic Structures: Introductory description and calculation of discharge for flumes, Sluices (with free flow and submerged flow), Weirs (sharp crested, ogee type and Broad crested), Spillways (Weir type, Morning glory and Siphon types), Energy dissipaters. Sediment Transportation: Modes of sediment movement, Suspended load, Bed load, Stable channels Design of Channels: Design of channels in erodible and non-erodible material, Criteria for Design, Economic section, Maximum and minimum permissible velocities, Maximum permissible unit tractive force, Cohesive and Granular materials. Water Resources Hydrology and Water Resource Management: Hydrologic cycle (Precipitation, Infiltration, Evaporation and Runoff), Water balance concept, Water resource development and management, Regional/Global water related issues. Surface Water Hydrology: Components of hydrologic cycle, Precipitation (Measurement of precipitation, Estimation of missing data, Tests for consistency, Hyetograph, Pluviograph, Computation of Mean Precipitation over a given area from gauge measurements using Simple Average, Theissen Polygon and Isohyetal Method, Intensity/Frequency/Duration Curves), Runoff (Measurement of Runoff Flow, Rating Curve, Correction of Flow Rating Curve, Extension of Flow Rating Curve, Statistical Analysis of floods, Probability and Return Period, Flood Frequency Analysis, Gumbel and Normal Distributions, Rational Formula, Run-off Coefficient, Time of Concentration). Hydrograph Analysis: Separation of Base Flow, Infiltration Index, ϕ Index, Estimation of Net Rainfall and Surface Run-off, Unit Hydrograph Theory, Derivation of Unit Hydrograph from Natural Hydrograph, Conversion of Unit Hydrograph from one duration to another, S Curve, Instantaneous Unit Hydrograph, Derivation of IUH from Unit Hydrograph and vice-versa, Synthetic Unit Hydrograph, Snyder's Method. Design and Operation of Reservoirs: Use of the Mass Curve in Reservoir Capacity, Spill Volume and Sustainable Yield Studies. Flood and Reservoir Routing: Simple techniques of Routing a Flood Hydrograph through a reservoir and through a section of Channel, Muskingum Method. Groundwater Hydrology: Introduction to Groundwater as a component of the Hydrological Cycle, Types of Aquifers, Igneous/Metamorphic/Sedimentary formations, Non-indurated Sediments, Equations of Groundwater Flow in Cartesian and Radial Coordinates for Steady and Unsteady Flow including recharge and abstraction, Boundary and Initial Conditions, Steady State flow in Confined and Unconfined Aquifers with Cartesian coordinates (one dimensional only) and Radial coordinates, Pumping Tests, Analysis of Pumping Test data using Theis Equation, Jacob's Method, Theis Method, Analysis of Recovery Data, Introduction to Groundwater Models, Finite Difference Digital Models, Electrical Resistance Capacitance Models. Assessment Seven laboratory assignments, each 2 hour duration: 30% i). Determination of Surface Profiles in Non Uniform Flow in a Channel. ii). Determination of Initial and Sequent Depth. Length of Jump, Energy Loss and Location of Hydraulic Jump. iii). Field Measurement of Infiltration Capacity. iv). Measurement of Stream Flow in the field. v). Use of Computer Models for simulation of Run-off from Rainfall data. vi). Pumping test of a borehole. vii). Electrical Resistance Analogue Model for Aquifer Simulation. End of stage examination of 3 hour duration: 70% Recommended Texts: 1). 2). 3). 4). 5). 6). 7). Open Channel Hydraulics, Ven Te Chow, McGraw-Hill. Open Channel Flow, Henderson, F.M., MacMillan. Flow through Open Channels, Ranga Raju K.G., Tata McGraw-Hill. Engineering Hydrology, Subramanya K., Tata McGraw-Hill. Groundwater Hydrology, Todd D. K., John Willey. Engineering Hydrology, Wilson, E. M., ELB. Water Resources Engineering, Larry W. Mays, John Wiley & Sons.