Unit 10 Review Name Hour ______ LG 10.1: DNA Structure and
advertisement

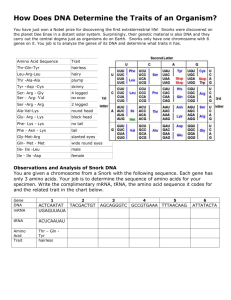
Unit 10 Review Name ______________________________ Hour ________ LG 10.1: DNA Structure and Replication Review the “I Can” statements on your Learning Goal Sheets or Board and answer the following questions. 1. The shape of DNA is known as a ____double helix__________ 2. The two scientist given credit for the discovery of this shape are ___Watson____ and ____Crick___ 3. DNA contains the instructions for making which macromolecule? ___Proteins______ 4. The segment of DNA that contains a particular sequence of nucleotides that code for a specific molecule is called a ______Gene________. 5. The building blocks (monomers) of DNA are called ______nucleotides______ 6. What three things are the subunits from question #5 made of? phosphate groups, _deoxyribose sugar_ and _a nitrogen base___ 7. A always bonds with __T (thymine)____ and G always bonds with ___C (Cytosine)___. 8. The process of replication is when _____DNA makes a copy of itself during interphase____________. 9. During replication the complementary sequence bases for GCTAGAA is ____CGATCTT__ 10. Where does replication occur? ______Nucleus_______ 11. During what phase of the cell cycle does replication occur? _____Interphase_______ 12. Below is a diagram of DNA. a) What is represented in the box labeled #1? ____Nitrogen Bases_______ b) What is represented in the box labeled #4? ____Nucleotide______ c) Structures 2 and 3 make up the _____Backbone_________ of DNA d) G,C,T, and A are called ___Nitrogen Bases________ e) What holds both sides (strands) of the DNA molecule together? _____Hydrogen bonds___ LG 10.2: Protein Synthesis Review the “I Can” statements on your Learning Goal Sheets or Board and answer the following questions. 13. Compare and contrast DNA with RNA by creating a Venn diagram DNA RNA Double stranded Deoxyribose Sugar Uses the base Thymine made of nucleotides single stranded Both nucleic Acids Ribose sugar Uses 4 nitrogen bases Uses the base Uracil A, G, C 14. Summarize the process of transcription. Include its location within the cell and any structures involved. Transcription is step 1 of protein synthesis. It is when enzymes make a copy of a gene (on DNA) onto mRNA. DNA unravels because of the enzyme and bases pairs are added to make a copy of the gene sequence for a particular protein. mRNA then leaves the nucleus through a pore and travels into the cytoplasm towards the ribosome. Transcription takes place in the nucleus of the cell. Transcribe the following sequences: DNA Sequence ACTTAGTAT DNA Sequence ATTCGATGC mRNA ____UGAAUCAUA________ mRNA ______UAAGCUACG_______ What are the three-nitrogen base units on mRNA that code for amino acids called? ____codons____ 15. Summarize the process of translation. Include its location within the cell and any structures involved. Translation is step 2 of protein synthesis. It occurs after the mRNA brings the code to the ribosomes (code is in the three bases units called codons) and when tRNA brings amino acids (monomers) from the cytoplasm to ribosome. Together mRNA and tRNA match up (codon to anticodon) and assemble a protein from many amino acids. Translation occurs at the ribosome. Translate the following sequences mRNA: UCC UCG UCU mRNA: AGA CAU GAG tRNA _AGG___ __AGC___ __AGA___ tRNA _UCU__ __GUA__ __CUC___ Amino Acids __Ser___ ___Ser___ ___Ser____ Amino Acids __Arg__ __Hist__ _Glutamic Acid_ What do you notice about the first sequence? ___All code for the same amino acid________ How does the cell know when to end translation? ___stop codon________ Give an example __UGA__ What are the three-nitrogen base units called on tRNA that match up with mRNA called? anticodons 16. Coding Practice: Which two mRNA codons correspond to Histidine? ___CAU____ and ___CAC____ How many different mRNA codons correspond to threonine? 4 What are they? ACG, ACA, ACU, ACC mRNA Code Amino Acid AUA Isoleucine GCG Alanine GAU Aspartic Acid CAA Glutamine CAC Histidine UUU Phenylalanine 17. Create an analogy for DNA, mRNA, and tRNA (Let’s go with a Shoe Factory) DNA – In a shoe factory, the shoe designer has all of the information and specs on building new shoes. He never leaves his office, but relays his plans to the shoe factory manager. mRNA – the manager helps build the shoes by carrying messages/instructions from the shoe designer to the factory workers. He travels from the office to the assembly areas regularly relaying the shoe building designs. tRNA – The different workers who bring the supplies to build the shoes. These include the leather crafters who bring the right leather, the shoe solers who bring the materials to make the soles, and the lacers who bring the right fabric and color laces that is necessary to build the correct shoes according to the info from the manager. 18. What kingdoms of life use Protein Synthesis? All life goes through protein synthesis, however in bacteria transcription cannot take place in the nucleus. Also, in bacteria DNA is single stranded so enzymes are different for transcription as well. Eukaryotes (Animalia, plantae, Protista, and fungi) go through protein synthesis as discussed in class. LG 10.3: Mutations Review the “I Can” statements on your Learning Goal Sheets or Board and answer the following questions. 19. What is a mutation? What can happen if a sex cell has a mutation? A mutation is any change in DNA. It can result in a change in genetics, cause a disorder, or result in death. In a sex cell, any change will be passed to the offspring and it can die if severe enough. 20. What things can cause a mutation? List several. Mutagens like UV sunlight, radioactive materials, high temps, and other carcinogens. deletion Point mutation Inversion Frameshift deletion Duplication Frameshift insertion DNA or Gene Mutations 21. Demonstrate your knowledge of a point mutation by creating one. Normal DNA ACT GGC Point Mutation DNA ____ACTCGC___(One G got turned into C)___ 22. Demonstrate your knowledge of a frame shift mutation by creating one. Normal DNA ACCTTTGGC Frame shift deletion __ACTTTGGG__(Missing C)____ Frame shift insertion __ACCTTTGGGC_(another G got added)_____ Chromosomal Mutations 23. Draw a chromosome with the genes A, B, C, D, E, and F on it. Then draw one of each of the 4 types of mutations that could happen to that chromosome. Original Chromosome: Mutant 1 (Inversion): Mutant 2 (Deletion): Mutant 3 (Translocation): Mutant 4 (Duplication):